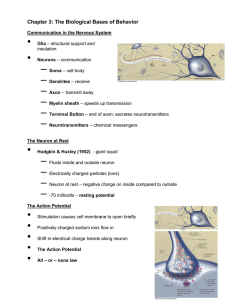
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
The Neuron
... Very thin—single long fiber that extends from the cell body Length varies 1-2 inches up to 3 feet long Carries outgoing messages Action Potential = electrical charge that travels down the axon when a message is sent Group of axons bundled together like electrical cable is called a nerve My ...
... Very thin—single long fiber that extends from the cell body Length varies 1-2 inches up to 3 feet long Carries outgoing messages Action Potential = electrical charge that travels down the axon when a message is sent Group of axons bundled together like electrical cable is called a nerve My ...
Nervous System - Gordon State College
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
neuron
... receives signals from other neurons or sensory organs, processes these signals, and sends signals to other neurons, muscles, or bodily ...
... receives signals from other neurons or sensory organs, processes these signals, and sends signals to other neurons, muscles, or bodily ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Voltage-gated Na+ channels are also effectors. Threshold depolarization causes shape changes in the channel ...
... Voltage-gated Na+ channels are also effectors. Threshold depolarization causes shape changes in the channel ...
introduction to peripheral nervous system 26. 02. 2014
... defined long before anything significant was known about the functional specialization of the cerebral cortex. Nevertheless, it turns out that these general areas are often useful in describing areas of the cortex that are involved in particular behaviors. The vast majority of cerebral cortex in hum ...
... defined long before anything significant was known about the functional specialization of the cerebral cortex. Nevertheless, it turns out that these general areas are often useful in describing areas of the cortex that are involved in particular behaviors. The vast majority of cerebral cortex in hum ...
Nervous System - healthsciencesMBIT
... Schwann Cells that wrap the axons around the CNS The fibers are called Myelinated Fibers Nodes of Ranvier are indentations between ...
... Schwann Cells that wrap the axons around the CNS The fibers are called Myelinated Fibers Nodes of Ranvier are indentations between ...
White Substance Information
... Source of energy. Source of food for yeast. Tissue growth. Tissue repair. Helps produce collagen (found in bones, cartilage, and teeth). Prevents scurvy (disease that causes joints to ache and gums to bleed) Used by the body for muscle movement, heartbeat, and nerve functioning. Used as a preservati ...
... Source of energy. Source of food for yeast. Tissue growth. Tissue repair. Helps produce collagen (found in bones, cartilage, and teeth). Prevents scurvy (disease that causes joints to ache and gums to bleed) Used by the body for muscle movement, heartbeat, and nerve functioning. Used as a preservati ...
Ch12.Nervous.Tissue
... Neuronal Regeneration in the PNS • Neural injuries may cause permanent dysfunction • If axons alone are destroyed, cell bodies often survive & axons may regenerate – PNS macrophages invade & destroy axon distal to the injury • Schwann cells form regeneration tube • Axon filaments grow peripherall ...
... Neuronal Regeneration in the PNS • Neural injuries may cause permanent dysfunction • If axons alone are destroyed, cell bodies often survive & axons may regenerate – PNS macrophages invade & destroy axon distal to the injury • Schwann cells form regeneration tube • Axon filaments grow peripherall ...
Regulation of Breathing
... By increasing ventilation the PaCO2 reduces Central chemoreceptors regulate ventilation Minute Changes CO2 retention ...
... By increasing ventilation the PaCO2 reduces Central chemoreceptors regulate ventilation Minute Changes CO2 retention ...
Science - edl.io
... What are nerves? They're the thin threads of nerve cells, called neurons that run throughout your body. Bundled together, they carry messages back and forth just the way that telephone wires do. Sensory nerves send messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord insi ...
... What are nerves? They're the thin threads of nerve cells, called neurons that run throughout your body. Bundled together, they carry messages back and forth just the way that telephone wires do. Sensory nerves send messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord insi ...
• The neuron is similar to other cells: •Cell body: lipid bilayer
... 4. Overview of the Nervous System: Golgi-Stained Pyramidal and Stellate Neurons ...
... 4. Overview of the Nervous System: Golgi-Stained Pyramidal and Stellate Neurons ...
The Central Nervous System
... of the spinal cord surround the central canal. Sensory nuclei are dorsal, motor nuclei are ventral. A thick layer of white matter consisting of ascending and descending axons covers the gray matter. These axons are organized into columns of axon bundles with specific functions. This highly organized ...
... of the spinal cord surround the central canal. Sensory nuclei are dorsal, motor nuclei are ventral. A thick layer of white matter consisting of ascending and descending axons covers the gray matter. These axons are organized into columns of axon bundles with specific functions. This highly organized ...
A&P Ch 8 PowerPoint(Nervous System)
... of the spinal cord surround the central canal. Sensory nuclei are dorsal, motor nuclei are ventral. A thick layer of white matter consisting of ascending and descending axons covers the gray matter. These axons are organized into columns of axon bundles with specific functions. This highly organized ...
... of the spinal cord surround the central canal. Sensory nuclei are dorsal, motor nuclei are ventral. A thick layer of white matter consisting of ascending and descending axons covers the gray matter. These axons are organized into columns of axon bundles with specific functions. This highly organized ...
The Nervous System
... Reflexes help to protect the body. Ex – Move hand away from hot object Duck if something is thrown at you Blink if something comes close to your eye Sneezing to clear airway ...
... Reflexes help to protect the body. Ex – Move hand away from hot object Duck if something is thrown at you Blink if something comes close to your eye Sneezing to clear airway ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies) - densely staining areas that contain large number of ribosomes (ribosomes produce proteins, many of which are neurotransmitters, the chemicals released at axons synaptic terminals). neurofibrils - filaments of cytoskeleton that extend from cell body through a ...
... chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies) - densely staining areas that contain large number of ribosomes (ribosomes produce proteins, many of which are neurotransmitters, the chemicals released at axons synaptic terminals). neurofibrils - filaments of cytoskeleton that extend from cell body through a ...
A unifying concept: the history of cell theory
... inorganic matter to the primordial cell and its evolution — the origin of life. If it everproves possible to recreate in the laboratory the prebiotic physicochemical conditions required for the spontaneous generation of life, the link between these two generalizations will be finally at hand and a u ...
... inorganic matter to the primordial cell and its evolution — the origin of life. If it everproves possible to recreate in the laboratory the prebiotic physicochemical conditions required for the spontaneous generation of life, the link between these two generalizations will be finally at hand and a u ...
RA 1 Chp 4
... cardiac muscle tissue. smooth muscle tissue. nerve tissue. all types of muscle tissue. skeletal muscle tissue. 15. All of the following are true of neurons, except that when mature, they lose the ability to divide. they are a very specialized form of connective tissue. they conduct a nervous impulse ...
... cardiac muscle tissue. smooth muscle tissue. nerve tissue. all types of muscle tissue. skeletal muscle tissue. 15. All of the following are true of neurons, except that when mature, they lose the ability to divide. they are a very specialized form of connective tissue. they conduct a nervous impulse ...
Tarsal Tunnel Release
... Epidemiology: Specific causes of the syndrome can be identified in 60-80% of patients. The most common causes including trauma, varicosities, heel varus, fibrosis, and heel valgus. Tendonitis within the tunnel can cause entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve due to the decreased space, and tetheri ...
... Epidemiology: Specific causes of the syndrome can be identified in 60-80% of patients. The most common causes including trauma, varicosities, heel varus, fibrosis, and heel valgus. Tendonitis within the tunnel can cause entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve due to the decreased space, and tetheri ...
Case Study 55
... • The tissue shows a large segment of hypercellular grey matter with predominantly small and irregularly shaped neurons admixed with increased numbers of atypical astrocytes and increased background vascularity. Within this region of cortex and adjacent white matter are multiple well-circumscribed g ...
... • The tissue shows a large segment of hypercellular grey matter with predominantly small and irregularly shaped neurons admixed with increased numbers of atypical astrocytes and increased background vascularity. Within this region of cortex and adjacent white matter are multiple well-circumscribed g ...
CHAPTER 2 RAPID REVIEW
... dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitter called a neural regulator that controls the release of other neurotransmitters. When endorphin is released in the body, they neurons transmitting information about pain are not ab ...
... dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitter called a neural regulator that controls the release of other neurotransmitters. When endorphin is released in the body, they neurons transmitting information about pain are not ab ...
Document
... gland, or the dendrites of another neuron. A synapse is the junction of an axon and the structure with which it communicates. The axon does not actually touch the muscle, gland, or dendrites. There is a space of about .00002 mm between the axon and the next structure. ...
... gland, or the dendrites of another neuron. A synapse is the junction of an axon and the structure with which it communicates. The axon does not actually touch the muscle, gland, or dendrites. There is a space of about .00002 mm between the axon and the next structure. ...
File
... neuron to the other? Which candy will receive the message? 2. If a synapse is a gap between neurons, how is the message received? 3. Neurons are affected by genetics, how do you ...
... neuron to the other? Which candy will receive the message? 2. If a synapse is a gap between neurons, how is the message received? 3. Neurons are affected by genetics, how do you ...
Neurohistology I
... B. Neurons (nerve cells)—neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system; they are specialized to conduct electrical signals. Note: The plasma membrane of the neuron contains both voltage gated ion channels (involved in generation and conduction of electrical signals) and recep ...
... B. Neurons (nerve cells)—neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system; they are specialized to conduct electrical signals. Note: The plasma membrane of the neuron contains both voltage gated ion channels (involved in generation and conduction of electrical signals) and recep ...























