Synaptic and extrasynaptic traces of long-term memory
... Experimental induction of LTP usually involves dramatic application of surprising input to the cells of interest, such as 100 or more repetitions of intense electrical stimulation. Probably the least extreme of the experiments successfully inducing LTP have been those of Remy and Spruston (2007), wi ...
... Experimental induction of LTP usually involves dramatic application of surprising input to the cells of interest, such as 100 or more repetitions of intense electrical stimulation. Probably the least extreme of the experiments successfully inducing LTP have been those of Remy and Spruston (2007), wi ...
An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
... • 15-1 Specify the components of the afferent and efferent divisions of the nervous system, and explain what is meant by the somatic nervous system. • 15-2 Explain why receptors respond to specific stimuli, and how the organization of a receptor affects its sensitivity. • 15-3 Identify the receptors ...
... • 15-1 Specify the components of the afferent and efferent divisions of the nervous system, and explain what is meant by the somatic nervous system. • 15-2 Explain why receptors respond to specific stimuli, and how the organization of a receptor affects its sensitivity. • 15-3 Identify the receptors ...
9 Propagated Signaling: The Action Potential
... electrical potential difference, across the membrane. Monitoring the additional current that is passed to clamp the membrane potential at its new value then provides a measure of the membrane current passing through the ion channels in the membrane. ...
... electrical potential difference, across the membrane. Monitoring the additional current that is passed to clamp the membrane potential at its new value then provides a measure of the membrane current passing through the ion channels in the membrane. ...
Nerve cells in the human ciliary muscle: ultrastructural and
... contact with terminal boutons that form axo-somatic synaptic contacts (arrows). The boutons contain numerous agranular vesicles (40 to 60 nm, asterisk) and some large granular vesicles (60 to 120 nm, arrowheads). Original magnification, X50000. (B, C) Ciliary muscle neurons (N) express spinelike (B, ...
... contact with terminal boutons that form axo-somatic synaptic contacts (arrows). The boutons contain numerous agranular vesicles (40 to 60 nm, asterisk) and some large granular vesicles (60 to 120 nm, arrowheads). Original magnification, X50000. (B, C) Ciliary muscle neurons (N) express spinelike (B, ...
Motor Threshold - McCausland Center | Brain Imaging
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
The Somatosensory System: Receptors and Central Pathways
... sensory coding was first studied electrophysiologically. Somatic information is provided by receptors distributed throughout the body. One of the earliest investigators of the bodily senses, Charles Sherrington, noted that the somatosensory system serves three major functions: proprioception, extero ...
... sensory coding was first studied electrophysiologically. Somatic information is provided by receptors distributed throughout the body. One of the earliest investigators of the bodily senses, Charles Sherrington, noted that the somatosensory system serves three major functions: proprioception, extero ...
mRNA at the Synapse - Journal of Neuroscience
... [Key words: mRNA localization, hippocampal mRNA, dendritic spines, synaptosomes, synapse] ...
... [Key words: mRNA localization, hippocampal mRNA, dendritic spines, synaptosomes, synapse] ...
15-5 Somatic Motor Pathways
... Carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or a deep cut Sensations reach the CNS quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes Relayed to the primary sensory cortex and receive conscious attention ...
... Carry sensations of fast pain, or prickling pain, such as that caused by an injection or a deep cut Sensations reach the CNS quickly and often trigger somatic reflexes Relayed to the primary sensory cortex and receive conscious attention ...
Peripheral Nervous System 1: The Somatic System
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
Peripheral Nervous System 1: The Somatic System
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
nerve - Ohio University
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
Peripheral Nervous System 1: The Somatic System
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
... 3. Function 1: sensory vs. motor 4. Function 2: somatic vs. visceral ...
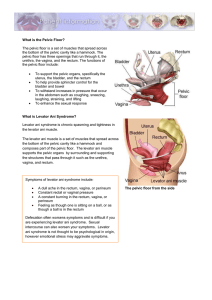
What is the Pelvic Floor? The pelvic floor is a set of muscles that
... A dull ache in the rectum, vagina, or perineum Constant rectal or vaginal pressure A constant burning in the rectum, vagina, or perineum Feeling as though one is sitting on a ball, or as though a ball is in the rectum ...
... A dull ache in the rectum, vagina, or perineum Constant rectal or vaginal pressure A constant burning in the rectum, vagina, or perineum Feeling as though one is sitting on a ball, or as though a ball is in the rectum ...
3 state neurons for contextual processing
... of neuronal dynamics is an artifact of the anesthetized state. However, these fluctuations have been observed in several different kinds of anesthesia, including local anesthesia [16]. Furthermore, it has been shown that the duration of the up-states correlate with orientation selectivity in visual ...
... of neuronal dynamics is an artifact of the anesthetized state. However, these fluctuations have been observed in several different kinds of anesthesia, including local anesthesia [16]. Furthermore, it has been shown that the duration of the up-states correlate with orientation selectivity in visual ...
The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and GABAergic
... frontal lobe epilepsy (ADNFLE). ADNFLE is a rare idiopathic epilepsy, which has been diagnosed in over a hundred families worldwide. This form of familial partial epilepsy had not been described until 1994, and is characterized by brief motor seizures during sleep. The exclusive occurrence of attack ...
... frontal lobe epilepsy (ADNFLE). ADNFLE is a rare idiopathic epilepsy, which has been diagnosed in over a hundred families worldwide. This form of familial partial epilepsy had not been described until 1994, and is characterized by brief motor seizures during sleep. The exclusive occurrence of attack ...
Document
... Visceral- provide information about conditions within internal organs. Special senses- smell, taste, vision, hearing and equilibrium or balance. ...
... Visceral- provide information about conditions within internal organs. Special senses- smell, taste, vision, hearing and equilibrium or balance. ...
Peripheral Nerve Diseases
... Special Investigation Electromyography (EMG) A fine needle is inserted into the muscle and the recorded activity displayed on an oscilloscope. Primarily of value in muscle disease but can also give indirect evidence of a neropathic process. If chronic denervation has occured, reinnervation may be p ...
... Special Investigation Electromyography (EMG) A fine needle is inserted into the muscle and the recorded activity displayed on an oscilloscope. Primarily of value in muscle disease but can also give indirect evidence of a neropathic process. If chronic denervation has occured, reinnervation may be p ...
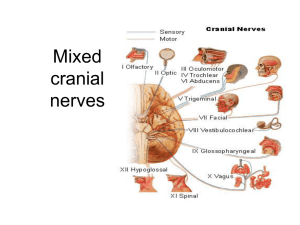
26. Mixed cranial nervest
... • Cranial nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. • Carry sensory or motor information or a combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance) ...
... • Cranial nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. • Carry sensory or motor information or a combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance) ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.