Review. Glial cells in neuronal network function
... have a strong impact on the neuronal network by influencing the extracellular diffusion of neurotransmitters (Syková & Nicholson 2008; Theodosis et al. 2008). The hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus has been a paradigmatic brain area where activity-dependent structural changes in the astrocytic coverag ...
... have a strong impact on the neuronal network by influencing the extracellular diffusion of neurotransmitters (Syková & Nicholson 2008; Theodosis et al. 2008). The hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus has been a paradigmatic brain area where activity-dependent structural changes in the astrocytic coverag ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... subpopulations, dynamically re-wiring networks over timescales of tens of milliseconds. A number of phenomenological models (Tsodyks and Markram, 1997; Abbott et al., 1997; Tsodyks et al., 1998) have been developed that can be used to classify the dynamics of synapses as being: either depressing, re ...
... subpopulations, dynamically re-wiring networks over timescales of tens of milliseconds. A number of phenomenological models (Tsodyks and Markram, 1997; Abbott et al., 1997; Tsodyks et al., 1998) have been developed that can be used to classify the dynamics of synapses as being: either depressing, re ...
REFLEXES I - michaeldmann.net
... At this point, it is appropriate to bring up the reason for interneurons in pathways such as that in Figure 15-2. Dale's principle (formulated by Sir Henry Dale) states that a single neuron synthesizes only one transmitter substance. Therefore according to the principle, if a neuron secretes acetylc ...
... At this point, it is appropriate to bring up the reason for interneurons in pathways such as that in Figure 15-2. Dale's principle (formulated by Sir Henry Dale) states that a single neuron synthesizes only one transmitter substance. Therefore according to the principle, if a neuron secretes acetylc ...
Picture 2.12. Some of the more often used neuron`s
... Firstly, they are characterised by having many inputs and one output. The input signals xi (i = 1,2,…,n) and the output signal y may take on only numerical values, generally of the range from 0 to 1 ( sometimes also from –1 to + 1), whereas the fact that within the tasks being solved by networks t ...
... Firstly, they are characterised by having many inputs and one output. The input signals xi (i = 1,2,…,n) and the output signal y may take on only numerical values, generally of the range from 0 to 1 ( sometimes also from –1 to + 1), whereas the fact that within the tasks being solved by networks t ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... Another important structure is the thalamus. Although much research has been conducted on the thalamus, most of its functions remain unknown. However, many theories about thalamic function have been proposed. The thalamus is a small, footballshaped structure that functions asthe “customs agent” of a ...
... Another important structure is the thalamus. Although much research has been conducted on the thalamus, most of its functions remain unknown. However, many theories about thalamic function have been proposed. The thalamus is a small, footballshaped structure that functions asthe “customs agent” of a ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... Another important structure is the thalamus. Although much research has been conducted on the thalamus, most of its functions remain unknown. However, many theories about thalamic function have been proposed. The thalamus is a small, footballshaped structure that functions asthe “customs agent” of a ...
... Another important structure is the thalamus. Although much research has been conducted on the thalamus, most of its functions remain unknown. However, many theories about thalamic function have been proposed. The thalamus is a small, footballshaped structure that functions asthe “customs agent” of a ...
Chapter_013
... Epinephrine can activate all alpha and beta receptors, but not dopamine receptors. Norepinephrine can activate alpha1, apha2, and beta1 receptors, but not beta2 or dopamine receptors. Dopamine can activate alpha1, beta1, and dopamine receptors. Note: Dopamine is the only neurotransmitter capable of ...
... Epinephrine can activate all alpha and beta receptors, but not dopamine receptors. Norepinephrine can activate alpha1, apha2, and beta1 receptors, but not beta2 or dopamine receptors. Dopamine can activate alpha1, beta1, and dopamine receptors. Note: Dopamine is the only neurotransmitter capable of ...
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous
... 15-3 Classifying Sensory Receptors • General Sensory Receptors • Scattered throughout the body and are simple in structure. • The simplest classification divides them into • 1. exteroreceptors provide information about the external environment • 2. proprioreceptors report positions of skeletal musc ...
... 15-3 Classifying Sensory Receptors • General Sensory Receptors • Scattered throughout the body and are simple in structure. • The simplest classification divides them into • 1. exteroreceptors provide information about the external environment • 2. proprioreceptors report positions of skeletal musc ...
EMG/ Nerve Conduction Studies
... • Study of 43 patients with EMG before and after Muscle biopsy • 50% had fibrillations 6-7 days after biopsy • At 16 days 100% had fibrillations • Fibrillations persisted up to 11 months post biopsy ...
... • Study of 43 patients with EMG before and after Muscle biopsy • 50% had fibrillations 6-7 days after biopsy • At 16 days 100% had fibrillations • Fibrillations persisted up to 11 months post biopsy ...
Neuronal cytoskeleton in synaptic plasticity and regeneration
... knockdown in dendritic spines (Jaworski et al. 2009). However, the molecular mechanism linking dynamic microtubules to F-actin stability remains unknown. Microtubules and actin do not bind directly to each other, rather they interact through proteins that mediate interactions between the cytoskeleta ...
... knockdown in dendritic spines (Jaworski et al. 2009). However, the molecular mechanism linking dynamic microtubules to F-actin stability remains unknown. Microtubules and actin do not bind directly to each other, rather they interact through proteins that mediate interactions between the cytoskeleta ...
Neural control of the circulation - Advances in Physiology Education
... synapse, called a synapse en passant, allows a single neuron to innervate many effector cells. This is unlike the highly differentiated neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle, where a single motor axon innervates a single muscle fiber and neurotransmitter release only occurs at the nerve terminal ...
... synapse, called a synapse en passant, allows a single neuron to innervate many effector cells. This is unlike the highly differentiated neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle, where a single motor axon innervates a single muscle fiber and neurotransmitter release only occurs at the nerve terminal ...
Investigating Anatomical and Molecular Aspects of
... thus contribute to proprioception through monitoring force of muscle contraction. When a muscle is stretched, or lengthened, a degree of passive tension develops in the muscle. During contraction, however, the resulting tension is deemed to be active. The current understanding is that GTOs are not e ...
... thus contribute to proprioception through monitoring force of muscle contraction. When a muscle is stretched, or lengthened, a degree of passive tension develops in the muscle. During contraction, however, the resulting tension is deemed to be active. The current understanding is that GTOs are not e ...
RNA Trafficking and Local Protein Synthesis in Dendrites: An
... long-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses and in long-term memory. Furthermore, the postsynaptic density (PSD) in the mutant mice showed a selective loss of CaMKII␣ (and enrichment of CaMKII␣), which occurred although CaMKII␣ protein was present throughout the neuron, including in the dendrite. T ...
... long-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses and in long-term memory. Furthermore, the postsynaptic density (PSD) in the mutant mice showed a selective loss of CaMKII␣ (and enrichment of CaMKII␣), which occurred although CaMKII␣ protein was present throughout the neuron, including in the dendrite. T ...
Glycine Binding Sites of Presynaptic NMDA Receptors May
... Whole cell mEPSCs recordings were performed on 58 pyramidal neurons in layer II/III of the visual cortical slices. Spontaneous mEPSCs in the presence of TTX (0.5 M), strychnine (1 M), and picrotoxin (100 M) were abolished by application of D-APV (50 M) and CNQX (10 M) in the Mg-free ACSF (data ...
... Whole cell mEPSCs recordings were performed on 58 pyramidal neurons in layer II/III of the visual cortical slices. Spontaneous mEPSCs in the presence of TTX (0.5 M), strychnine (1 M), and picrotoxin (100 M) were abolished by application of D-APV (50 M) and CNQX (10 M) in the Mg-free ACSF (data ...
How humans distinguish between smells
... The particular axons that are activated depend upon which receptor protein is targeted. Each cell produces only one type of receptor protein. In humans, there are approximately 350 different types of receptor proteins produced (Axel, 2006). In other mammals, such as mice, the number of different re ...
... The particular axons that are activated depend upon which receptor protein is targeted. Each cell produces only one type of receptor protein. In humans, there are approximately 350 different types of receptor proteins produced (Axel, 2006). In other mammals, such as mice, the number of different re ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 10 of 12
... There are three types of muscle tissue; therefore, these are Smooth Muscle Tissue, Skeletal Muscle Tissue, and Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Smooth Muscle Tissue: These muscles are elongated thin cell fibres; therefore, the fibres at the end are pointed with their nucleus being a huge oval shape. The cells ...
... There are three types of muscle tissue; therefore, these are Smooth Muscle Tissue, Skeletal Muscle Tissue, and Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Smooth Muscle Tissue: These muscles are elongated thin cell fibres; therefore, the fibres at the end are pointed with their nucleus being a huge oval shape. The cells ...
Degeneration and Regeneration in Crustacean
... axons in crustacean limbs appear to degenerate much more rapidly than those of motor axons (Fig. 3). Action potentials from sensory fibers can be identified by recording from medial branches of the meropodite thick bundle that contain at most one or two motor axons whose large spikes are clearly sep ...
... axons in crustacean limbs appear to degenerate much more rapidly than those of motor axons (Fig. 3). Action potentials from sensory fibers can be identified by recording from medial branches of the meropodite thick bundle that contain at most one or two motor axons whose large spikes are clearly sep ...
Ch. 2 - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... system code differences in sensory stimulus amplitudes? What property (or properties) of ion channels makes them selective to only one ion such as K+, and not another such as Na+? Is it the size of the channel, other factors, or a combination? Synaptic currents produce electrotonic potentials that a ...
... system code differences in sensory stimulus amplitudes? What property (or properties) of ion channels makes them selective to only one ion such as K+, and not another such as Na+? Is it the size of the channel, other factors, or a combination? Synaptic currents produce electrotonic potentials that a ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Function—function of a neurotransmitter is determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters; can also be classified according to whether receptor directly opens a channel or instead uses a second messenger ...
... Function—function of a neurotransmitter is determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters; can also be classified according to whether receptor directly opens a channel or instead uses a second messenger ...
Membrane potential synchrony of simultaneously recorded striatal
... medium-sized spiny neurons in the striatum seems to depend on convergent input within these information channels2. To determine the degree of correlated input, both below and at threshold for the generation of action potentials, we recorded intracellularly from pairs of spiny neurons in vivo. Here w ...
... medium-sized spiny neurons in the striatum seems to depend on convergent input within these information channels2. To determine the degree of correlated input, both below and at threshold for the generation of action potentials, we recorded intracellularly from pairs of spiny neurons in vivo. Here w ...
Biology Nervous System - Educational Research Center
... − the white matter includes all the nerves. The student realizes that: − dendrites receive the messages and transmit them to the cell body. − axons transmit the message away from the cell body. − axons from the nerve fibers are found in the white matter. − an axon is linked to consecutive neurons or ...
... − the white matter includes all the nerves. The student realizes that: − dendrites receive the messages and transmit them to the cell body. − axons transmit the message away from the cell body. − axons from the nerve fibers are found in the white matter. − an axon is linked to consecutive neurons or ...
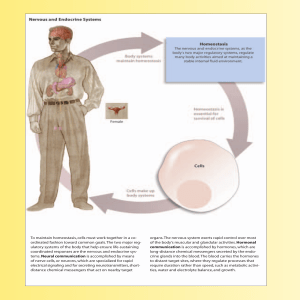
To maintain homeostasis, cells must work together in a co
... change of potential caused by inherent imbalances in the leak– pump cycle. (You will learn more about the nature of these various triggering events as our discussion of electrical signals continues.) Because the water-soluble ions responsible for carrying charge cannot penetrate the plasma membrane’ ...
... change of potential caused by inherent imbalances in the leak– pump cycle. (You will learn more about the nature of these various triggering events as our discussion of electrical signals continues.) Because the water-soluble ions responsible for carrying charge cannot penetrate the plasma membrane’ ...
Facial nerve
... • Idiopathic facial paralysis is more common in diabetic patients and in pregnancy (third trimester). ...
... • Idiopathic facial paralysis is more common in diabetic patients and in pregnancy (third trimester). ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.