Introducing a New Product
... Voltage-gated Na+ channels stay open for only about 1 msec before they automatically close; action potential is an all-or-none response After action potential peaks, membrane begins to move back toward the resting membrane potential when K+ channels open, allowing outward diffusion of K+; process is ...
... Voltage-gated Na+ channels stay open for only about 1 msec before they automatically close; action potential is an all-or-none response After action potential peaks, membrane begins to move back toward the resting membrane potential when K+ channels open, allowing outward diffusion of K+; process is ...
Full Text
... including the generation of GFP-SOD1 chimaeric proteins for studies in protein localization by direct visualization using fluorescence microscopy. However, little is known about the biochemical and physical properties of these chimaeric proteins, and whether they behave similarly to their untagged S ...
... including the generation of GFP-SOD1 chimaeric proteins for studies in protein localization by direct visualization using fluorescence microscopy. However, little is known about the biochemical and physical properties of these chimaeric proteins, and whether they behave similarly to their untagged S ...
Review Article Type 3 adenylyl cyclase: a key enzyme mediating the
... have been found to be expressed in primary cilia of cerebellar granular neuron precursors (CGNPs) and regulate the hedgehog pathway [49]. However, apparently AC3 is more predominantly enriched in primary cilia than AC5/6 [49] and AC5/6 have strong distribution in other subcellular locations. AC5/6 ( ...
... have been found to be expressed in primary cilia of cerebellar granular neuron precursors (CGNPs) and regulate the hedgehog pathway [49]. However, apparently AC3 is more predominantly enriched in primary cilia than AC5/6 [49] and AC5/6 have strong distribution in other subcellular locations. AC5/6 ( ...
Technologies émergentes de mémoire résistive pour les systèmes
... following entities and people for their support, without which the current manuscript that you are reading wouldn’t have existed. First I thank CEAGrenoble, DGA-France and Univeristy of Grenoble-INPG for supporting my PhD scholarship and providing me the laboratory resources to perform this research ...
... following entities and people for their support, without which the current manuscript that you are reading wouldn’t have existed. First I thank CEAGrenoble, DGA-France and Univeristy of Grenoble-INPG for supporting my PhD scholarship and providing me the laboratory resources to perform this research ...
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Directly Activates Noradrenergic
... activation of LC neurons is unknown. Moreover, given the apparent absence of mRNA for CRH receptors in LC neurons, the exact location of action of CRH within the cerulear region is debated. Using in vitro intracellular recordings from rat brainstem, we examined whether CRH exerts a direct effect on ...
... activation of LC neurons is unknown. Moreover, given the apparent absence of mRNA for CRH receptors in LC neurons, the exact location of action of CRH within the cerulear region is debated. Using in vitro intracellular recordings from rat brainstem, we examined whether CRH exerts a direct effect on ...
Estradiol, Substance P, and the PI3K-Akt
... supposedly written around 2600 BCE, but is dated to around 300 BCE. However, as a collection of preexisting writings and oral history, it is the earliest known description of nociception and inflammatory pain. In classical Greece, pain was first mentioned in Homer’s epics (8 th century BCE), followe ...
... supposedly written around 2600 BCE, but is dated to around 300 BCE. However, as a collection of preexisting writings and oral history, it is the earliest known description of nociception and inflammatory pain. In classical Greece, pain was first mentioned in Homer’s epics (8 th century BCE), followe ...
Zebrafish Get Connected: Investigating Neurotransmission Targets
... Once released into the synaptic cleft, glutamate binds to receptors on postsynaptic neurons and adjacent glial cells. Most glutamate receptors are located on the dendritic spines of the postsynaptic neurons [38]. Glutamate receptors fall into two categories, ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic r ...
... Once released into the synaptic cleft, glutamate binds to receptors on postsynaptic neurons and adjacent glial cells. Most glutamate receptors are located on the dendritic spines of the postsynaptic neurons [38]. Glutamate receptors fall into two categories, ionotropic and metabotropic. Ionotropic r ...
Program
and
Abstracts
from
the
Fifth
Annual
Canadian
Neuroscience
Meeting
May
29
–
June
1
2011
Quebec
City
Convention
Center
... neurogenesis. Intensive investigation has revealed myriad molecular cues involved in this form of neurogenesis, however molecules signaling exclusively for adult neurogenesis are yet to be described. Tenascin R (TNR) an extracellular matrix molecule known to take part in neurogenesis is expressed ...
... neurogenesis. Intensive investigation has revealed myriad molecular cues involved in this form of neurogenesis, however molecules signaling exclusively for adult neurogenesis are yet to be described. Tenascin R (TNR) an extracellular matrix molecule known to take part in neurogenesis is expressed ...
Neuronal control of leech behavior - Emory Biology
... visible in the adult brain as neuromeres 1–4. (B) Types of preparations used to study the neuronal bases of leech behaviors. The kinematics of all behaviors have been characterized in intact animals (top panel) by measuring the distances between markers placed on the external body wall in successive ...
... visible in the adult brain as neuromeres 1–4. (B) Types of preparations used to study the neuronal bases of leech behaviors. The kinematics of all behaviors have been characterized in intact animals (top panel) by measuring the distances between markers placed on the external body wall in successive ...
Neuropathological Characteristics of Brachial Plexus Avulsion Injury
... ChAT-positive motor neurons were counted on both the intact and lesioned side of the C5, C6, and C7 spinal segments. Because ChAT immunoreactivity may be changed as a consequence of injury, serials sections stained with CV were also used to quantify the motor neurons as an independent marker. Only C ...
... ChAT-positive motor neurons were counted on both the intact and lesioned side of the C5, C6, and C7 spinal segments. Because ChAT immunoreactivity may be changed as a consequence of injury, serials sections stained with CV were also used to quantify the motor neurons as an independent marker. Only C ...
JAMA SIDS
... Context The serotonergic (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]) neurons in the medulla oblongata project extensively to autonomic and respiratory nuclei in the brainstem and spinal cord and help regulate homeostatic function. Previously, abnormalities in 5-HT receptor binding in the medullae of infants dying ...
... Context The serotonergic (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]) neurons in the medulla oblongata project extensively to autonomic and respiratory nuclei in the brainstem and spinal cord and help regulate homeostatic function. Previously, abnormalities in 5-HT receptor binding in the medullae of infants dying ...
Calcium Regulation of Dendritic Growth via CaM Kinase IV and
... Note that all four panels show the same group of cells. (L–O) Nifedipine reduces the intracellular Ca2⫹ increase induced by KCl. Raw fluorescence images of Fura fluorescence in NSS ⫹ 20 M Nifedipine before stimulation (L) and after stimulation with 50 mM KCl (N). (M) and (O) show colorimetric repre ...
... Note that all four panels show the same group of cells. (L–O) Nifedipine reduces the intracellular Ca2⫹ increase induced by KCl. Raw fluorescence images of Fura fluorescence in NSS ⫹ 20 M Nifedipine before stimulation (L) and after stimulation with 50 mM KCl (N). (M) and (O) show colorimetric repre ...
The Classical Complement Cascade Mediates
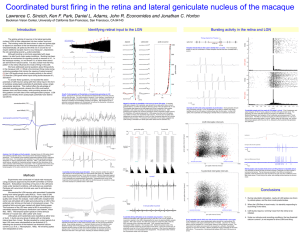
... elimination (Jaubert-Miazza et al., 2005; Hooks and Chen, 2006). Axons from retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) terminate in distinct nonoverlapping eye-specific domains in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN). The majority of eye-specific segregation occurs postnatally before the onset of vision, ...
... elimination (Jaubert-Miazza et al., 2005; Hooks and Chen, 2006). Axons from retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) terminate in distinct nonoverlapping eye-specific domains in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN). The majority of eye-specific segregation occurs postnatally before the onset of vision, ...
The Time Course and Amplitude of EPSPs Evoked at Synapses
... which were lost suddenly in the presence of steady current). The average input resistance was 20.2 f 10.8 MQ (n = 54). These values are comparable to other reports for guinea pig CA1 pyramidal cells in vitro (e.g., Turner, 1988). The CA3 pyramidal cells were generally more robust than CA1 neurons, a ...
... which were lost suddenly in the presence of steady current). The average input resistance was 20.2 f 10.8 MQ (n = 54). These values are comparable to other reports for guinea pig CA1 pyramidal cells in vitro (e.g., Turner, 1988). The CA3 pyramidal cells were generally more robust than CA1 neurons, a ...
Are there differences between the secretion characteristics of NGF
... mechanism(s) and site(s) of secretion are of primary importance. It has been demonstrated that NGF is secreted from both hippocampal slices and NGFtransfected hippocampal cultures along the constitutive and activity-dependent pathway (Blöchl and Thoenen, 1995, 1996). The activity-dependent NGF secr ...
... mechanism(s) and site(s) of secretion are of primary importance. It has been demonstrated that NGF is secreted from both hippocampal slices and NGFtransfected hippocampal cultures along the constitutive and activity-dependent pathway (Blöchl and Thoenen, 1995, 1996). The activity-dependent NGF secr ...
Laryngeal nerve “anastomoses”
... Laryngeal nerves have been observed to communicate with each other and form a variety of patterns. These communications have been studied extensively and have been of particular interest as it may provide an additional form of innervation to the intrinsic laryngeal muscles. Variations noted in incid ...
... Laryngeal nerves have been observed to communicate with each other and form a variety of patterns. These communications have been studied extensively and have been of particular interest as it may provide an additional form of innervation to the intrinsic laryngeal muscles. Variations noted in incid ...
Coordinate Roles for LIM Homeobox Genes in Directing the
... and Goodman, 1996). The specificity evident in the response of axons to the variety of cues presented in their local environment demands a precise coordination in the expression of guidance molecules within neurons and surrounding cells. In vertebrates, the coordinated development of neurons and the ...
... and Goodman, 1996). The specificity evident in the response of axons to the variety of cues presented in their local environment demands a precise coordination in the expression of guidance molecules within neurons and surrounding cells. In vertebrates, the coordinated development of neurons and the ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.