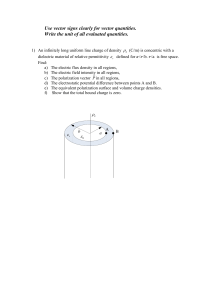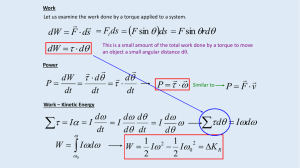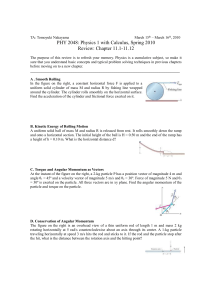
Workshop 10
... Yo! It's time for the Electromagnetic Plane Wave Boogie! Grab a partner and stand facing one another two arm lengths apart. One of you extend your right arm and point toward your partner with your index finger while the other does the same with the left arm. Your extended index fingers should be alm ...
... Yo! It's time for the Electromagnetic Plane Wave Boogie! Grab a partner and stand facing one another two arm lengths apart. One of you extend your right arm and point toward your partner with your index finger while the other does the same with the left arm. Your extended index fingers should be alm ...
Review for Chapter 7
... 7. An electromagnetic wave has an electric field component and a magnetic field component, which have the same wavelength and frequency but travel in perpendicular planes. 8. Electromagnetic waves occur over a broad spectrum of wavelengths (10 -3 to 1013 nm) and frequencies (1020 to 104 Hz). This sp ...
... 7. An electromagnetic wave has an electric field component and a magnetic field component, which have the same wavelength and frequency but travel in perpendicular planes. 8. Electromagnetic waves occur over a broad spectrum of wavelengths (10 -3 to 1013 nm) and frequencies (1020 to 104 Hz). This sp ...
Newton`s Cradle - Mercer Physics
... system of particles, the total linear momentum P of the system remains constant. Second, if the total kinetic energy of the system of two colliding bodies is unchanged by the collision then the kinetic energy of the system is conserved. In elastic collisions of several objects, kinetic energy is con ...
... system of particles, the total linear momentum P of the system remains constant. Second, if the total kinetic energy of the system of two colliding bodies is unchanged by the collision then the kinetic energy of the system is conserved. In elastic collisions of several objects, kinetic energy is con ...
Unit 9 Outline (AP Physics) 2013
... Calculate the torque of a specified force about an arbitrary origin Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid body in simple cases where this vector lies parallel to the angular velocity vector Understand angular mome ...
... Calculate the torque of a specified force about an arbitrary origin Calculate the angular momentum vector for a moving particle Calculate the angular momentum vector for a rotating rigid body in simple cases where this vector lies parallel to the angular velocity vector Understand angular mome ...
Document
... The rolling motion associated with this wheel can be modeled as if all parts of the wheel rotate about the point of contact. Using this model, what can we say about the velocities of point P, the center and point p’? For this instant in time the point of contact would have zero velocity, the center ...
... The rolling motion associated with this wheel can be modeled as if all parts of the wheel rotate about the point of contact. Using this model, what can we say about the velocities of point P, the center and point p’? For this instant in time the point of contact would have zero velocity, the center ...
Assignment for the Course `Ferroelectric materials and Applications`
... - Define in your own word the Saturation polarization Ps, the remnant polarization Pr, and the coercive field Ec. - What is the difference between Ps and Pr? Could they be the same? If yes, in which case? ...
... - Define in your own word the Saturation polarization Ps, the remnant polarization Pr, and the coercive field Ec. - What is the difference between Ps and Pr? Could they be the same? If yes, in which case? ...
Chapter 1 Quick Review
... 2. A thin-walled hollow tube rolls without sliding along the floor. The ratio of its translational kinetic energy to its rotational kinetic energy (about an axis through its center of mass) is: (Kinetic Energy of Rolling Motion.) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.1/2 e. 1/3 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the ...
... 2. A thin-walled hollow tube rolls without sliding along the floor. The ratio of its translational kinetic energy to its rotational kinetic energy (about an axis through its center of mass) is: (Kinetic Energy of Rolling Motion.) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.1/2 e. 1/3 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the ...