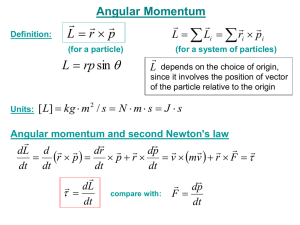
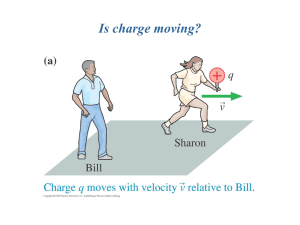
ENE 429 Antenna and Transmission Lines
... UPW is characterized by its propagation direction and frequency. ...
... UPW is characterized by its propagation direction and frequency. ...
Electricity Magnetism
... 3. An infinite cylinder capacitor consists of two concentric cylinders centered about the z-axis. The radius of the inner cylinder is r0 , and that of the outer one is r1 . The voltage between the cylinders is V . The capacitor is spinning around the z-axis at an angular velocity of ω radians/sec. ...
... 3. An infinite cylinder capacitor consists of two concentric cylinders centered about the z-axis. The radius of the inner cylinder is r0 , and that of the outer one is r1 . The voltage between the cylinders is V . The capacitor is spinning around the z-axis at an angular velocity of ω radians/sec. ...
Review PH301 -- duality, wavefunction, probability
... If you have issues with a physical quantity like wavefunction being complex all measureable quantities will be real like probability density = |Y|2. ...
... If you have issues with a physical quantity like wavefunction being complex all measureable quantities will be real like probability density = |Y|2. ...
Open Questions in Physics
... quantum jumps, then I'm sorry that I ever got involved!” E.Schrodinger • Do there exist phenomena that are truly spontaneous? Or do all phenomena, when investigated in depth, turn out to be deterministic? ...
... quantum jumps, then I'm sorry that I ever got involved!” E.Schrodinger • Do there exist phenomena that are truly spontaneous? Or do all phenomena, when investigated in depth, turn out to be deterministic? ...
Exam 4-2005 - asg.sc.edu
... 27. Particles that are engage in the strong interactions are (with one exception) are called a. Gluons b. Fermions c. ~ hadrons d. Bosons 28. Particles that do not engage in strong interactions but are Fermions are called? a. bosons b. hadrons c. ~ leptons d. mesons 29. Quarks are held together by t ...
... 27. Particles that are engage in the strong interactions are (with one exception) are called a. Gluons b. Fermions c. ~ hadrons d. Bosons 28. Particles that do not engage in strong interactions but are Fermions are called? a. bosons b. hadrons c. ~ leptons d. mesons 29. Quarks are held together by t ...
THINGSYOUNEEDTOKNOW-modern
... ELECTRONS can collide with PHOTONS. Their combined momentums and energies are conserved. If Electron losses energy, thus losses speed If photon losses energy, its frequency decreases Because photon is light and must travel at c. The sum of all mass + energy is conserved in the universe. The sum of a ...
... ELECTRONS can collide with PHOTONS. Their combined momentums and energies are conserved. If Electron losses energy, thus losses speed If photon losses energy, its frequency decreases Because photon is light and must travel at c. The sum of all mass + energy is conserved in the universe. The sum of a ...