CHAPTER 2 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... the photoelectron varies linearly with frequency with a limiting frequency v = v0, below which no photoelectron is produced. ...
... the photoelectron varies linearly with frequency with a limiting frequency v = v0, below which no photoelectron is produced. ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... Spin angular momentum in quantum mechanics does not arise from a particle actually spinning like a top, rather it is an intrinsic property of a particle, like its mass. An important thing to note is that spin is quantised. It can only have discrete values. For example, protons, neutrons and electron ...
... Spin angular momentum in quantum mechanics does not arise from a particle actually spinning like a top, rather it is an intrinsic property of a particle, like its mass. An important thing to note is that spin is quantised. It can only have discrete values. For example, protons, neutrons and electron ...
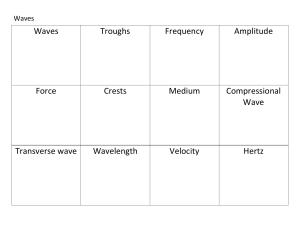
Polarization
... • Polarization in direction of applied field changes propagation speed Input linear polarization • In direction of applied field -- phase modulator • Perpendicular to applied field -- nothing • 45° to applied field -- variable waveplate ...
... • Polarization in direction of applied field changes propagation speed Input linear polarization • In direction of applied field -- phase modulator • Perpendicular to applied field -- nothing • 45° to applied field -- variable waveplate ...
Slide 1
... In the case of sound waves in air, it is air molecules that are doing the “waving”. What is “waving” in the case of light? a) Electrons. b) Protons. c) Both a and b. d) Electric and magnetic fields. e) None of the above. ...
... In the case of sound waves in air, it is air molecules that are doing the “waving”. What is “waving” in the case of light? a) Electrons. b) Protons. c) Both a and b. d) Electric and magnetic fields. e) None of the above. ...
Wavefunctions and Bound Systems
... This is not as strange as it seems – you got used to thinking of momentum as “em” times “vee” – this is just another way to think about it! ...
... This is not as strange as it seems – you got used to thinking of momentum as “em” times “vee” – this is just another way to think about it! ...
Page 1 PHYSICS 4100 Modern Physics Second Examination
... uT = (qE – mg)/b. Note that the terminal speed is linearly related to q, but not proportional to q. Thus, if q is doubled, the terminal speed (and hence the terminal velocity) will not be doubled. (5) ...
... uT = (qE – mg)/b. Note that the terminal speed is linearly related to q, but not proportional to q. Thus, if q is doubled, the terminal speed (and hence the terminal velocity) will not be doubled. (5) ...
Document
... much displacement current is encircled by the loop? The maximum induced magnetic field has a magnitude of 10 mT. At what radius (b) inside and (c) outside the capacitor gap is the magnitude of the induced magnetic field 2 mT? ...
... much displacement current is encircled by the loop? The maximum induced magnetic field has a magnitude of 10 mT. At what radius (b) inside and (c) outside the capacitor gap is the magnitude of the induced magnetic field 2 mT? ...
headingE2170: Polarization of two-spheres system inside a tube The problem:
... of one ball is −q and the charge of the other one is +q. The ball’s radius is negligible, and the electrostatic attraction between the balls is also negligible. The balls are rigid and can’t pass through each other. The balls are attached to a drop, whose surface tension causes it’s gravity constant ...
... of one ball is −q and the charge of the other one is +q. The ball’s radius is negligible, and the electrostatic attraction between the balls is also negligible. The balls are rigid and can’t pass through each other. The balls are attached to a drop, whose surface tension causes it’s gravity constant ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. Work: Work done by a force from a ...
... Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. Work: Work done by a force from a ...