Lecture_1
... Ideal Sources Ideal Voltage sources supply a fixed voltage V independent of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sou ...
... Ideal Sources Ideal Voltage sources supply a fixed voltage V independent of the resistance of the load. (i.e., they have zero internal resistance.) However, real voltage sources have an internal non-zero resistance and the voltage delivered depends upon the resistance of the load. Ideal Current sou ...
Circuit description for phase control power supply
... MOSFET Q4 (2N7000) is connected between the input of optocoupler IC2 (MOC3021) and Ground. When its Gate voltage is close to zero (0.12V), Q4 is OPEN circuit. If a voltage greater than its threshold (about 2V) is applied to its Gate, Q4 turns ON and shorts the control pulses to Ground. Resistors R29 ...
... MOSFET Q4 (2N7000) is connected between the input of optocoupler IC2 (MOC3021) and Ground. When its Gate voltage is close to zero (0.12V), Q4 is OPEN circuit. If a voltage greater than its threshold (about 2V) is applied to its Gate, Q4 turns ON and shorts the control pulses to Ground. Resistors R29 ...
THAT Corporation Design Note 100
... only 100nF. The exact tuning of the NLC is best done by ear, but there is an in-depth explanation of this circuit, which includes some rough guidelines for tuning, at the end of THAT Corporation's Design Note 03 (formerly Application Note 103). We suggest reviewing that document before beginning to ...
... only 100nF. The exact tuning of the NLC is best done by ear, but there is an in-depth explanation of this circuit, which includes some rough guidelines for tuning, at the end of THAT Corporation's Design Note 03 (formerly Application Note 103). We suggest reviewing that document before beginning to ...
1 - University of California, Berkeley
... (b) Now calculate the voltage drop on Vo if both A and B change to VDD (under the above conditions) (c) If we do not want Vo to drop more than 10% VDD, how big should we make CL (d) What is the maximum number of transistors that can be connected in series to M1 and M2 (including M1 and M2, excluding ...
... (b) Now calculate the voltage drop on Vo if both A and B change to VDD (under the above conditions) (c) If we do not want Vo to drop more than 10% VDD, how big should we make CL (d) What is the maximum number of transistors that can be connected in series to M1 and M2 (including M1 and M2, excluding ...
Internal Resistance
... We call this drop in the voltage of the cell the LOST VOLTS. Remember that it only occurs when a current starts to flow. V 1.5 V E ...
... We call this drop in the voltage of the cell the LOST VOLTS. Remember that it only occurs when a current starts to flow. V 1.5 V E ...
Chapter 8 Special Semiconductor Devices
... which is a must in order to attain the turn-on process required to maintain conduction when the gate signal is removed. ...
... which is a must in order to attain the turn-on process required to maintain conduction when the gate signal is removed. ...
Transistor Hybrid model:-
... The partial derivatives are taken keeping the collector voltage or base current constant as indicated by the subscript attached to the derivative. ΔvB , ΔvC , Δ iC , Δ iB represent the small signal(increment) base and collector voltages and currents,they are represented by symbols vb , vc , ib and i ...
... The partial derivatives are taken keeping the collector voltage or base current constant as indicated by the subscript attached to the derivative. ΔvB , ΔvC , Δ iC , Δ iB represent the small signal(increment) base and collector voltages and currents,they are represented by symbols vb , vc , ib and i ...
The Transistor
... TRANSISTORS (STAR OF SHOW) Power amplification comes from transistorother components needed for transistor to work. ...
... TRANSISTORS (STAR OF SHOW) Power amplification comes from transistorother components needed for transistor to work. ...
Ohm`s Law and Power Equation Practice Worksheet
... 12. . If a blender is plugged into a 110 V outlet that supplies 2.7 A of current, what amount of power is used by the blender? ...
... 12. . If a blender is plugged into a 110 V outlet that supplies 2.7 A of current, what amount of power is used by the blender? ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
A Triangular Wave Oscillator
... •The circuit operates as a regular integrator when the negative input dc voltage –VIN is applied •The PUT triggers on when the output ramp (at the anode) exceeds the gate voltage by 0.7 V •The gate is set to the approximate desired sawtooth peak voltage. •When the PUT turns on, the capacitor rapidly ...
... •The circuit operates as a regular integrator when the negative input dc voltage –VIN is applied •The PUT triggers on when the output ramp (at the anode) exceeds the gate voltage by 0.7 V •The gate is set to the approximate desired sawtooth peak voltage. •When the PUT turns on, the capacitor rapidly ...
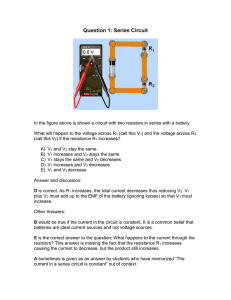
Question 1 - cloudfront.net
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
... D is correct. As R1 increases, the total current decreases thus reducing V2. V1 plus V2 must add up to the EMF of the battery (ignoring losses) so that V1 must increase. Other Answers: B would be true if the current in the circuit is constant. It is a common belief that batteries are ideal current s ...
Circuits - cottonphysics
... the charges to a higher energy level (voltage source). •As the charges move through the resistors (represented by the paddle wheels) the charges do work (J/C), and subsequently, lose energy (experience a voltage drop). •The charges do more work as they pass through the larger resistor. ...
... the charges to a higher energy level (voltage source). •As the charges move through the resistors (represented by the paddle wheels) the charges do work (J/C), and subsequently, lose energy (experience a voltage drop). •The charges do more work as they pass through the larger resistor. ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.