Lecture28 - Purdue Physics
... Energy source => Potential Energy => Kinetic Energy => Heat Power = Energy/unit time P=V * I P= (I*R) *I= I2 R ...
... Energy source => Potential Energy => Kinetic Energy => Heat Power = Energy/unit time P=V * I P= (I*R) *I= I2 R ...
Series vs. Parallel Circuits
... 1. If the current through R1 is 4 amps, what is the current through a. R2? b. R3? c. The total current coming out of the battery? 2. If R1 is 3Ω, R2 is 7Ω, and R3 is 4 Ω, what is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? 3. What is the potential drop across a. R1 b. R2 c. R3 4. What is the total pot ...
... 1. If the current through R1 is 4 amps, what is the current through a. R2? b. R3? c. The total current coming out of the battery? 2. If R1 is 3Ω, R2 is 7Ω, and R3 is 4 Ω, what is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? 3. What is the potential drop across a. R1 b. R2 c. R3 4. What is the total pot ...
DN-103 Controlling a -5V Rail Using UCC2913 +3V to +8V Hot-Swap Power Manager
... Amplifier and Overcurrent comparators and therefore allows direct connection from the sense resistor to the CSP and CSN pins. The external n-channel MOSFET should be placed between the load and the input source (–5V) to provide adequate gate drive voltage when the load is switched on. ...
... Amplifier and Overcurrent comparators and therefore allows direct connection from the sense resistor to the CSP and CSN pins. The external n-channel MOSFET should be placed between the load and the input source (–5V) to provide adequate gate drive voltage when the load is switched on. ...
The Transistor as a Switch
... way that it always operates within its "active" region, that is the linear part of the output characteristics curves are used. However, both the NPN & PNP type bipolar transistors can be made to operate as "ON/OFF" type solid state switches by biasing the transistors base differently to that of a si ...
... way that it always operates within its "active" region, that is the linear part of the output characteristics curves are used. However, both the NPN & PNP type bipolar transistors can be made to operate as "ON/OFF" type solid state switches by biasing the transistors base differently to that of a si ...
LECTURER-26 GENERATION OF IMPULSE CURRENTS Lightning
... The waveshape used in testing surge diverters are 4/10 and 8/20 µ s, the figures respectively representing the nominal wave front and wave tail times the tolerances allowed on these times are ±10%only. Apart from the standard impulse current, waves, rectangular waves of long duration are also used f ...
... The waveshape used in testing surge diverters are 4/10 and 8/20 µ s, the figures respectively representing the nominal wave front and wave tail times the tolerances allowed on these times are ±10%only. Apart from the standard impulse current, waves, rectangular waves of long duration are also used f ...
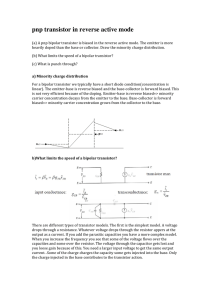
pnp transistor in reverse active mode
... linear). The emitter-‐base is reverse biased and the base-‐collector is forward biased. This is not very efficient because of the doping. Emitter-‐base is reverse biased=> minority carrier concentration decays f ...
... linear). The emitter-‐base is reverse biased and the base-‐collector is forward biased. This is not very efficient because of the doping. Emitter-‐base is reverse biased=> minority carrier concentration decays f ...
Name ______ period ____
... 25. An electrical conductor has electrons that ________________________ and an electrical insulator has electrons that are ______________________ to its atoms. 26. Explain how the following three devices that provides electrical safety work: a) circuit breaker b) fuse c) ground-fault circuit interru ...
... 25. An electrical conductor has electrons that ________________________ and an electrical insulator has electrons that are ______________________ to its atoms. 26. Explain how the following three devices that provides electrical safety work: a) circuit breaker b) fuse c) ground-fault circuit interru ...
File
... 5.6 Resistance Resistance is how difficult it is for current to flow Resistance is the opposite of conductance! A resistor is used to slow current down and convert electrical energy into heat energy (e.g. light bulb, stove element). ...
... 5.6 Resistance Resistance is how difficult it is for current to flow Resistance is the opposite of conductance! A resistor is used to slow current down and convert electrical energy into heat energy (e.g. light bulb, stove element). ...
31.63. Model: The battery and the connecting wires are ideal
... The figure shows the two circuits formed from the circuit in Figure P31.63 when the switch is open and when the switch is closed. Solve: (a) Using the rules of series and parallel resistors, we have simplified the circuit in two steps as shown in figure (a). A battery with emf E = 24 V is connected ...
... The figure shows the two circuits formed from the circuit in Figure P31.63 when the switch is open and when the switch is closed. Solve: (a) Using the rules of series and parallel resistors, we have simplified the circuit in two steps as shown in figure (a). A battery with emf E = 24 V is connected ...
New Current Sensors series fromThe Premo Group with current
... The HCT-2000LF has a wide input supply symmetrical voltage to allow power supplies from 15V to 24V then simplifying the need of DC voltage regulators and matching the most common DC supply buss standards in Power Control Electronics. Highly tolerant to noise and disturbance, it has been designed for ...
... The HCT-2000LF has a wide input supply symmetrical voltage to allow power supplies from 15V to 24V then simplifying the need of DC voltage regulators and matching the most common DC supply buss standards in Power Control Electronics. Highly tolerant to noise and disturbance, it has been designed for ...
Physics Section 17.3 Apply the properties of electric current
... Drift velocity is the average velocity of an electron in a conductor. It is only a few millimeters per second. The velocity that the electric field is established in a conductor is nearly the speed of light. (300,000,000 m/s) ...
... Drift velocity is the average velocity of an electron in a conductor. It is only a few millimeters per second. The velocity that the electric field is established in a conductor is nearly the speed of light. (300,000,000 m/s) ...
lab_report - Homework Market
... The circuit is designed to detect when the input voltage goes outside the range of +2.5V and + 3.5V.When the input voltage goes beyond these two limits an LED lights up and it stays on. The circuit should incorporate a manual reset to switch the LED off. The available components are comparator 339, ...
... The circuit is designed to detect when the input voltage goes outside the range of +2.5V and + 3.5V.When the input voltage goes beyond these two limits an LED lights up and it stays on. The circuit should incorporate a manual reset to switch the LED off. The available components are comparator 339, ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.