intermediate 1 physics - Deans Community High School
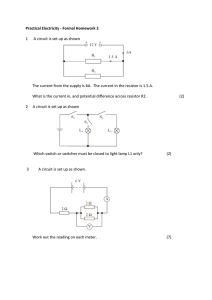
... 1. A variable resistor is used in the speed controller of a toy electric train. The variable resistor controls the current flowing to a small electric motor in the train shown in figure 1 ...
... 1. A variable resistor is used in the speed controller of a toy electric train. The variable resistor controls the current flowing to a small electric motor in the train shown in figure 1 ...
Astable multivibrator
... C1 charges up through R1 and C2 charges up through R4 As soon as B2 reaches 0.7 V T2 switches on Note that C1 charges slowly through the large resistor R1 while C2 charges more quickly through the small resistor R4. When T2 switches on O2 drops to nearly 0 V, B1 drops by 6 V to –5.3 V and T1 goes of ...
... C1 charges up through R1 and C2 charges up through R4 As soon as B2 reaches 0.7 V T2 switches on Note that C1 charges slowly through the large resistor R1 while C2 charges more quickly through the small resistor R4. When T2 switches on O2 drops to nearly 0 V, B1 drops by 6 V to –5.3 V and T1 goes of ...
Presentation_12
... An ammeter must be hooked in series with the element you want to measure the current through ...
... An ammeter must be hooked in series with the element you want to measure the current through ...
Voltage regulators 723
... General purpose voltage regulators 1.Introduction: The popular general purpose precision regulator is 723. It is monolithic IC available in different physical packages. ...
... General purpose voltage regulators 1.Introduction: The popular general purpose precision regulator is 723. It is monolithic IC available in different physical packages. ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... •Zn+ ions enter acid leaving terminal negative •Electrons leave carbon leaving it positive •Terminals connected to external circuit •‘Battery’ referred to several cells originally Ch 18 ...
... •Zn+ ions enter acid leaving terminal negative •Electrons leave carbon leaving it positive •Terminals connected to external circuit •‘Battery’ referred to several cells originally Ch 18 ...
1296 MHz AMPLIFIER Measured at 1296 MHz : NF
... Being an enhancement mode device the transistor needs a positive voltage on the gate in order to draw drain current – typ. + 0,59V on the gate to give 60 mA drain current. If the gate is put to ground potential the current will drop to a few microamperes of leakage current. This is more like biasing ...
... Being an enhancement mode device the transistor needs a positive voltage on the gate in order to draw drain current – typ. + 0,59V on the gate to give 60 mA drain current. If the gate is put to ground potential the current will drop to a few microamperes of leakage current. This is more like biasing ...
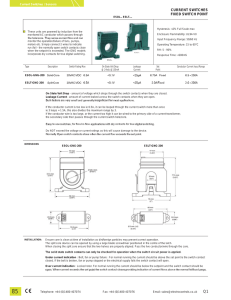
current switches fixed switch point
... Under current indication : Belt, fan or pump failure : For normal running the current should be above the set point & the switch contact closed. If the belt is broken, fan or pump stopped or the electrical supply fails the switch contact will open. Over current indication : Locked rotor. For normal ...
... Under current indication : Belt, fan or pump failure : For normal running the current should be above the set point & the switch contact closed. If the belt is broken, fan or pump stopped or the electrical supply fails the switch contact will open. Over current indication : Locked rotor. For normal ...
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR, UJT, SCR, TRIAC
... A Unijunction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device having only one p-n junction like diode but has three terminals. This device has a unique characteristics that when it is triggered, the emitter current increases regeneratively until is limited by emitter power supply. The unijunctio ...
... A Unijunction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device having only one p-n junction like diode but has three terminals. This device has a unique characteristics that when it is triggered, the emitter current increases regeneratively until is limited by emitter power supply. The unijunctio ...
6 - 10.5 CYU Suggested Answers - Tse
... (b) Since the resistors are in series, they each get 2.25 V (or one quarter of the 9 V). Using this and Ohm’s law gives 0.10 A in each resistor. (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of ...
... (b) Since the resistors are in series, they each get 2.25 V (or one quarter of the 9 V). Using this and Ohm’s law gives 0.10 A in each resistor. (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of ...
Chapter 6, Cranking, Charging and Electrical Auxiliary Systems
... Cranking, Charging and Electrical Auxiliary Systems Parts to Know-Page 1 Alternator: An electrical generator or dynamo for producing alternating current (See generator) Diode: Solid-state component which permits current to flow through in one direction. Fuse: A device designed to open the circuit wh ...
... Cranking, Charging and Electrical Auxiliary Systems Parts to Know-Page 1 Alternator: An electrical generator or dynamo for producing alternating current (See generator) Diode: Solid-state component which permits current to flow through in one direction. Fuse: A device designed to open the circuit wh ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.