Electricity and Magnetism
... attraction between 2 charged particles depends on the amount of charge in the objects and the distance between them. ...
... attraction between 2 charged particles depends on the amount of charge in the objects and the distance between them. ...
Product Information SAMSON - S-com plus
... release time (fast or slow). The Gate switch changes the downward expander ratio from "light" to "hard" gating for control ranging from subtle to an obvious effect. A dedicated Peak/Limiter with variable control provides protection against peak and overload independently of the compressor. When used ...
... release time (fast or slow). The Gate switch changes the downward expander ratio from "light" to "hard" gating for control ranging from subtle to an obvious effect. A dedicated Peak/Limiter with variable control provides protection against peak and overload independently of the compressor. When used ...
ES1A - ES1D
... support device or system whose failure to perform can the body, or (b) support or sustain life, or (c) whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life failure to perform when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or with instructions for use prov ...
... support device or system whose failure to perform can the body, or (b) support or sustain life, or (c) whose be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life failure to perform when properly used in accordance support device or system, or to affect its safety or with instructions for use prov ...
POWER ELECTRONICS NOTES 10ES45
... trigger angle from zero to 180 degrees. Thus the half wave ac controller has the drawback of limited range RMS output voltage control. ...
... trigger angle from zero to 180 degrees. Thus the half wave ac controller has the drawback of limited range RMS output voltage control. ...
MSAE * 44L Power Electronics - V
... 1. Connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram. 2. Set R1 and R 2 to mid position and V1 and V2 to minimum. 3. Set the gate current IG = IG1 (such that forward break over voltage is between 15 to 20 V), by varying R 2 and V2 4. Slowly vary V1 in steps of 2V and note down VAK and IAK at each ...
... 1. Connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram. 2. Set R1 and R 2 to mid position and V1 and V2 to minimum. 3. Set the gate current IG = IG1 (such that forward break over voltage is between 15 to 20 V), by varying R 2 and V2 4. Slowly vary V1 in steps of 2V and note down VAK and IAK at each ...
Resistance - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... (Not enough information! We could fix either V or I?) Quiz: If we double the length of an Ohmic wire of area A and resistivity , while holding the potential difference V across the wire constant, the power dissipated in the wire will be: ...
... (Not enough information! We could fix either V or I?) Quiz: If we double the length of an Ohmic wire of area A and resistivity , while holding the potential difference V across the wire constant, the power dissipated in the wire will be: ...
Section 1-2 - Scott Buffett
... The power formula is the relationship between power (P), voltage (E), and current (I) in an electrical circuit. ...
... The power formula is the relationship between power (P), voltage (E), and current (I) in an electrical circuit. ...
Adjustable inverting negative output current mode PWM regulators
... circuit adopts a current-mode PWM control scheme to achieve good efficiency, high stability and low noise performance. The figure in the first page shown the detailed block diagram of the device. ST755 is realized in a BCD technology in order to achieve high temperature stability, the best REFERENCE ...
... circuit adopts a current-mode PWM control scheme to achieve good efficiency, high stability and low noise performance. The figure in the first page shown the detailed block diagram of the device. ST755 is realized in a BCD technology in order to achieve high temperature stability, the best REFERENCE ...
1. A 10 ohm resistor is connected across a 20 V battery. What
... 8. Two resistors are connected in parallel to a 10 V battery. The total current through the circuit is 100 mA. If the current through the first resistor is 40 mA, what is the current ...
... 8. Two resistors are connected in parallel to a 10 V battery. The total current through the circuit is 100 mA. If the current through the first resistor is 40 mA, what is the current ...
Circuits - University of Colorado Boulder
... This is also called Conservation of Current. In steady-state, the charge is not building up anywhere, it is just flowing along at a steady rate. So the current into any portion of the circuit must equal the current coming out of that portion, otherwise charge would be building up in that part of the ...
... This is also called Conservation of Current. In steady-state, the charge is not building up anywhere, it is just flowing along at a steady rate. So the current into any portion of the circuit must equal the current coming out of that portion, otherwise charge would be building up in that part of the ...
Linear Systems Offers Direct Alternative for Analog Devices MAT01
... LS312 available as bare die Please contact Micross for full package and die dimensions: Email: [email protected] Web: www.micross.com/distribution.aspx Information furnished by Linear Integrated Systems and Micross Components is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibili ...
... LS312 available as bare die Please contact Micross for full package and die dimensions: Email: [email protected] Web: www.micross.com/distribution.aspx Information furnished by Linear Integrated Systems and Micross Components is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibili ...
MS Word - Sonoma State University
... (f) We neglected any to include a parasitic series resistance in the diode (actually, all physically real fabricated diodes have some parasitic series resistance). How would you expect the inclusion of this series resistance to change the ID-VD curve on the plot above? (Note: If you want you can sho ...
... (f) We neglected any to include a parasitic series resistance in the diode (actually, all physically real fabricated diodes have some parasitic series resistance). How would you expect the inclusion of this series resistance to change the ID-VD curve on the plot above? (Note: If you want you can sho ...
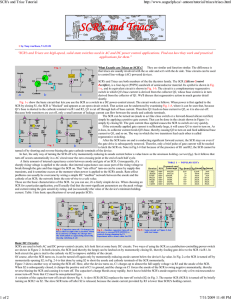
SCR`s and Triac Tutorial
... Q1's base is shorted to the cathode terminal via R1 and R2, Q1 is cut off through lack of base current. Therefore Q1 feeds no base current to Q2, so it is also cut off. Because both transistors are cut off, only a small amount of leakage current can flow between the anode and cathode terminals. The ...
... Q1's base is shorted to the cathode terminal via R1 and R2, Q1 is cut off through lack of base current. Therefore Q1 feeds no base current to Q2, so it is also cut off. Because both transistors are cut off, only a small amount of leakage current can flow between the anode and cathode terminals. The ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.