Week 12: Output Stages, Frequency Response
... In low frequency side, drop in gain is caused by coupling and bypass capacitors In high frequency side, drop in gain is caused by transistor’s parasitic capacitors – More on this topic later ...
... In low frequency side, drop in gain is caused by coupling and bypass capacitors In high frequency side, drop in gain is caused by transistor’s parasitic capacitors – More on this topic later ...
Understanding the Data Sheet
... A graph of speed versus voltage is not shown however this is also linear. Actuator speed for a fixed load can be varied by varying the motor voltage. For integrated controllers or the CIB the minimum allowed voltage is ~4V. ...
... A graph of speed versus voltage is not shown however this is also linear. Actuator speed for a fixed load can be varied by varying the motor voltage. For integrated controllers or the CIB the minimum allowed voltage is ~4V. ...
Chapter 6 Electricity: Electrical Circuit
... a. Voltage is the strength of a power source. b. A power source with more voltage can produce more electric current. c. Voltage is measured in volts. i. A D cell battery has 1.5 volts. ii. Most wall outlets which gets power from a power plant have 120 volts. 3. Resistance a. Resistance is the abilit ...
... a. Voltage is the strength of a power source. b. A power source with more voltage can produce more electric current. c. Voltage is measured in volts. i. A D cell battery has 1.5 volts. ii. Most wall outlets which gets power from a power plant have 120 volts. 3. Resistance a. Resistance is the abilit ...
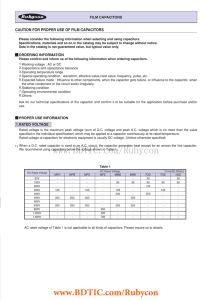
CAUTION FOR PROPER USE OF FILM CAPACITORS FILM CAPACITORS
... dielectric used. Rubycon recomend to use P2S series when use in stringent circuits such as time-constants. ...
... dielectric used. Rubycon recomend to use P2S series when use in stringent circuits such as time-constants. ...
Electronic Engineering Department, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain {aldrete, mateo,
... amplifier (OTA) structure [9]. In this case, the temperature transducers devices (TTDs) are two lateral bipolar transistors Q1 and Q2 that are inherent in the existing CMOS digital technology, since they have the same temperature behaviour with respect to standard bipolar technologies ...
... amplifier (OTA) structure [9]. In this case, the temperature transducers devices (TTDs) are two lateral bipolar transistors Q1 and Q2 that are inherent in the existing CMOS digital technology, since they have the same temperature behaviour with respect to standard bipolar technologies ...
Chapter 13
... Energy is stored by the capacitor during a portion of the voltage cycle; then the stored energy is returned to the source during another portion of the cycle. Instantaneous power is the product of v and i . True power (Ptrue) is zero, since no energy is consumed by the capacitor. The rate at which a ...
... Energy is stored by the capacitor during a portion of the voltage cycle; then the stored energy is returned to the source during another portion of the cycle. Instantaneous power is the product of v and i . True power (Ptrue) is zero, since no energy is consumed by the capacitor. The rate at which a ...
Inverter Checks
... open fuse. Open the cover and read from the output transistor side of the fuse to T1, T2, and T3. The most common mode of failure will be an output transistor short between the collector to the emitter. This will be shown by low resistance readings in either direction. When changing an IGBT, change ...
... open fuse. Open the cover and read from the output transistor side of the fuse to T1, T2, and T3. The most common mode of failure will be an output transistor short between the collector to the emitter. This will be shown by low resistance readings in either direction. When changing an IGBT, change ...
Chapter Fifteen Electric Current
... • See Fig. 15-4. The voltage difference across a resistance (resistor) is called voltage drop. • See Fig. 15-5. The electric potential at point A is the same as that at the left side of the battery (emf), and that at point D is the same as the right side of the battery. The same current must pass th ...
... • See Fig. 15-4. The voltage difference across a resistance (resistor) is called voltage drop. • See Fig. 15-5. The electric potential at point A is the same as that at the left side of the battery (emf), and that at point D is the same as the right side of the battery. The same current must pass th ...
Integrated logarithmic amplifiers for industrial
... The drawback of this circuit is that VOUT depends not only on IIN but also on m, IS(T), and VT, all of which are either current- or temperature-dependent. • The correction factor, m, takes into account the deviation between the diode characteristic and Shockley’s simplified theory of diodes. However ...
... The drawback of this circuit is that VOUT depends not only on IIN but also on m, IS(T), and VT, all of which are either current- or temperature-dependent. • The correction factor, m, takes into account the deviation between the diode characteristic and Shockley’s simplified theory of diodes. However ...
MAX748A/MAX763A 3.3V, Step-Down, Current-Mode PWM DC-DC Converters __________________General Description
... Drain of internal P-channel power MOSFET* ...
... Drain of internal P-channel power MOSFET* ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.