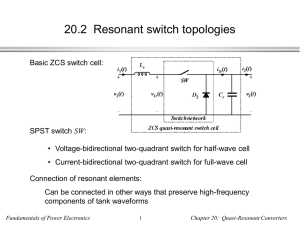
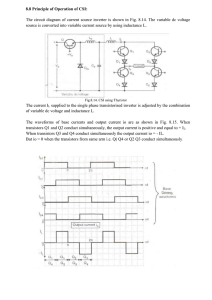
Noninverting_Amplifier_revised
... – the gain of the inverting amplifier in the linear region of the voltage transfer characteristic using a least squares determination of the slope in the linear region – the output voltage at the positive and negative saturation regions. ...
... – the gain of the inverting amplifier in the linear region of the voltage transfer characteristic using a least squares determination of the slope in the linear region – the output voltage at the positive and negative saturation regions. ...
1 A circuit consists of three identical lamps connected to a battery
... difference (V) as a function of position (clockwise from X) around the electronic circuit (below). Assume all wires and the switch have zero resistance. ...
... difference (V) as a function of position (clockwise from X) around the electronic circuit (below). Assume all wires and the switch have zero resistance. ...
M5400-PM - Panamax!
... LiFT EMI/RFI noise filtration is provided by a twostage balanced Pi filter which also provides noise isolation from all other outlet banks. ...
... LiFT EMI/RFI noise filtration is provided by a twostage balanced Pi filter which also provides noise isolation from all other outlet banks. ...
Ques1: State Ohm`s law and its limitations
... a)Any two terminals network can be replaced by a current source of current output , IN in parallel with a resistance, RN. b) Any two terminals network can be replaced by a current source of current output, IN in series with a resistance, RN. c) Any two terminals network can be replaced by a voltage ...
... a)Any two terminals network can be replaced by a current source of current output , IN in parallel with a resistance, RN. b) Any two terminals network can be replaced by a current source of current output, IN in series with a resistance, RN. c) Any two terminals network can be replaced by a voltage ...
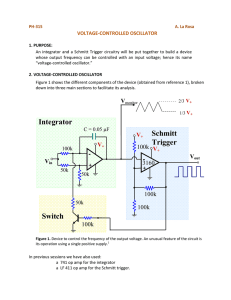
Written - Rose
... between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the input voltages of the second op amp. We want to find the output voltage of the second op amp. Firstly we need to determine the output voltage of the first op amp, which can be labeled as v1 ...
... between the inverting terminal and the output node. The output voltage of the first op amp becomes one of the input voltages of the second op amp. We want to find the output voltage of the second op amp. Firstly we need to determine the output voltage of the first op amp, which can be labeled as v1 ...
AN2063 - STMicroelectronics
... Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 ...
... Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 ...
DC Circuits PowerPoint
... in which the current divides into two or more paths before recombining to complete the circuit. They are wired in such a way so that if one part of the circuit is broken, the whole circuit is still closed! Many complex electronic devices are wired in parallel. This allows a single source to provide ...
... in which the current divides into two or more paths before recombining to complete the circuit. They are wired in such a way so that if one part of the circuit is broken, the whole circuit is still closed! Many complex electronic devices are wired in parallel. This allows a single source to provide ...
Physics I Honors Name
... 16. Which of the five combinations shown produces the least total resistance? a) I b) II c) III d) IV e) V 17. Which of the five combinations shown produces the greatest total resistance? a) I b) II c) III d) IV e) V 18. Which of the following capacitors, each of which has plates of area A, would st ...
... 16. Which of the five combinations shown produces the least total resistance? a) I b) II c) III d) IV e) V 17. Which of the five combinations shown produces the greatest total resistance? a) I b) II c) III d) IV e) V 18. Which of the following capacitors, each of which has plates of area A, would st ...
Circuit Design Issues in Multi
... logic circuits, especially for a <110> channel surface orientation [1] Discrete transistor widths are a concern for SRAM cells which are composed of single-fin devices. In SRAM the drive currents of single-fin MUGFETs can be modified only by different gate lengths. ...
... logic circuits, especially for a <110> channel surface orientation [1] Discrete transistor widths are a concern for SRAM cells which are composed of single-fin devices. In SRAM the drive currents of single-fin MUGFETs can be modified only by different gate lengths. ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.