Honors Genetics: FINAL Exam Review REVIEW ALL OLD QUIZZES
... Describe/understand fetal sex development in humans. (Chap 5 Quest) Can you predict inheritance patterns of X-linked conditions in offspring? (Chap 6/Q 14) Practice Punnett Squares and recognize sex-linked pedigrees! Describe the genotype and phenotype – Be able to ID the karyotype - of the followin ...
... Describe/understand fetal sex development in humans. (Chap 5 Quest) Can you predict inheritance patterns of X-linked conditions in offspring? (Chap 6/Q 14) Practice Punnett Squares and recognize sex-linked pedigrees! Describe the genotype and phenotype – Be able to ID the karyotype - of the followin ...
Gene Technology Study Guide KEY
... machine (DNA strands, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, primers, and free nucleotides) DNA is heated in order to separate the strands. Sample is cooled down and primers are added to segments in order for DNA polymerase to attach to strands. DNA polymerase attaches to primers and adds free nucleotides ...
... machine (DNA strands, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, primers, and free nucleotides) DNA is heated in order to separate the strands. Sample is cooled down and primers are added to segments in order for DNA polymerase to attach to strands. DNA polymerase attaches to primers and adds free nucleotides ...
Modern Genetics - Trinity Regional School
... :will pass the affected X to their daughters. Women: can be carriers of the disorder if they have Inherited only one affected X or affected if they have Inherited both X chromosomes. :will pass the affected X to their sons. ...
... :will pass the affected X to their daughters. Women: can be carriers of the disorder if they have Inherited only one affected X or affected if they have Inherited both X chromosomes. :will pass the affected X to their sons. ...
Model question Paper- Gene Technology MLAB 475
... Protein is responsible for preserving, copying and transmitting information within cells and from generation to generation. ...
... Protein is responsible for preserving, copying and transmitting information within cells and from generation to generation. ...
LG and SC 2017 10 genetics
... SC5 I can explain the following terms: gametes, sex cells, sperm, ova, fertilisation, zygote, embryo, mitosis SC6 I can describe how genetic information is passed on to offspring from both parents by meiosis SC7 I can Investigate the extraction of DNA (from cheek cells and fruit) LG2 I can use model ...
... SC5 I can explain the following terms: gametes, sex cells, sperm, ova, fertilisation, zygote, embryo, mitosis SC6 I can describe how genetic information is passed on to offspring from both parents by meiosis SC7 I can Investigate the extraction of DNA (from cheek cells and fruit) LG2 I can use model ...
Slide 1
... the procedural steps. Units of service are determined by the number of times each step is performed. Different procedures may exist for the same analyte, which makes the CPT coding different. Lack of standardized coding guidelines add to the complexities of how to assign ...
... the procedural steps. Units of service are determined by the number of times each step is performed. Different procedures may exist for the same analyte, which makes the CPT coding different. Lack of standardized coding guidelines add to the complexities of how to assign ...
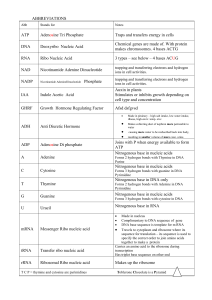
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
Slide 1
... -e.g. one gene codes for opsin green, which helps you see red and green. Some alleles of this gene give you normal vision, some others make you color deficient ...
... -e.g. one gene codes for opsin green, which helps you see red and green. Some alleles of this gene give you normal vision, some others make you color deficient ...
Station #3: DNA structure, replication, protein synthesis, mutation
... a. Genes are the proteins encoded by chromosomes b. Genes are the proteins around which DNA chromosomes are packaged c. A chromosome is a DNA molecule with many genes d. Chromosomes are proteins that carry genes made of DNA 6. Which of the following correctly describes how proteins are made? DNA is ...
... a. Genes are the proteins encoded by chromosomes b. Genes are the proteins around which DNA chromosomes are packaged c. A chromosome is a DNA molecule with many genes d. Chromosomes are proteins that carry genes made of DNA 6. Which of the following correctly describes how proteins are made? DNA is ...
DNA and RNA
... Long, single strand of nucleotides. Nitrogen bases: A,U,G,C no Thymine! Sugar: Ribose Found in cytoplasm and nucleus Types: messenger, transfer, ribosomal Function: Involved in the synthesis of protein molecules. ...
... Long, single strand of nucleotides. Nitrogen bases: A,U,G,C no Thymine! Sugar: Ribose Found in cytoplasm and nucleus Types: messenger, transfer, ribosomal Function: Involved in the synthesis of protein molecules. ...
Chromosomes
... Cryptic plasmids (plasmids that have no known function) Based on their ability to transfer to other bacteria: Conjugative plasmids Non-conjugative plasmids (incapable of initiating conjugation) Based on their ability to coexist in a single cell Compatible Incompatible ...
... Cryptic plasmids (plasmids that have no known function) Based on their ability to transfer to other bacteria: Conjugative plasmids Non-conjugative plasmids (incapable of initiating conjugation) Based on their ability to coexist in a single cell Compatible Incompatible ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology and Genomics
... 20.3 A genomic library contains copies of DNA segments from the entire genome. Thus, all genes should be represented, along with the regulatory sequences and introns. A cDNA library allows you to sequence only the exons of a gene, and also indicates which genes are expressed either in different cell ...
... 20.3 A genomic library contains copies of DNA segments from the entire genome. Thus, all genes should be represented, along with the regulatory sequences and introns. A cDNA library allows you to sequence only the exons of a gene, and also indicates which genes are expressed either in different cell ...
Genetic engineering
... DNA: Is the genetic material of living organisms is composed of a substance called deoxyribonucleic acid, abbreviated DNA. It is stores the information needed for the synthesis of all cellular proteins. In other words, the main function of the genetic blueprint is to code for the production of cell ...
... DNA: Is the genetic material of living organisms is composed of a substance called deoxyribonucleic acid, abbreviated DNA. It is stores the information needed for the synthesis of all cellular proteins. In other words, the main function of the genetic blueprint is to code for the production of cell ...
Genetic terms, punnett squares
... – Cutting and splicing pieces of DNA into other strands of DNA » Plasmids - circular DNA molecules found in bacteria, separate from other bacterial DNA » Sticky ends - matching or complimentary segments of DNA that are produced by restriction enzymes » Human genes can be inserted into bacterial plas ...
... – Cutting and splicing pieces of DNA into other strands of DNA » Plasmids - circular DNA molecules found in bacteria, separate from other bacterial DNA » Sticky ends - matching or complimentary segments of DNA that are produced by restriction enzymes » Human genes can be inserted into bacterial plas ...
Ch 15-16 DNA and RNA
... New complementary nucleotides link to the exposed bases on the separated strands. A new complementary strand is built along each ‘old’ strand. ...
... New complementary nucleotides link to the exposed bases on the separated strands. A new complementary strand is built along each ‘old’ strand. ...
Genetics and Heredity
... such traits from parents to offspring? The Blending Hypothesis of Inheritance In the early 1800’s the blending hypothesis was proposed. Genetic material contributed by the two parents mixes in a manner analogous to the way blue and yellow paints blend to ...
... such traits from parents to offspring? The Blending Hypothesis of Inheritance In the early 1800’s the blending hypothesis was proposed. Genetic material contributed by the two parents mixes in a manner analogous to the way blue and yellow paints blend to ...
Recombinant DNA technology article
... Edible vaccines to prevent widespread diseases in developing countries ...
... Edible vaccines to prevent widespread diseases in developing countries ...
El Diamante Biology
... 13. Study the food chain on page 408 (figure 13.9) and answer the following questions: a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on p ...
... 13. Study the food chain on page 408 (figure 13.9) and answer the following questions: a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on p ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
... Trisomy 21, or Down syndrome, occurs when there is a normal diploid chromosomal complement of 46 chromosomes plus one (extra) chromosome #21. Such individuals therefore have 47 chromosomes. While there is impaired fertility of both sexes, females are more likely to be fertile than males. Assume that ...
NOTES: 12-1 DNA (History, Identifying the Substance of Genes)
... To truly understand genetics, biologists first had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. How do genes control what you look like? Vocabulary: ● Transformation ...
... To truly understand genetics, biologists first had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. How do genes control what you look like? Vocabulary: ● Transformation ...
doc Review of Lecture 27
... In the second generation, three strands have replicated correctly, one strand has a mismatch ...
... In the second generation, three strands have replicated correctly, one strand has a mismatch ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.