Document
... B.) Produce cDNA from mRNA. C.) Produce a cut (usually staggered) at specific recognition sequences on DNA. D.) Reseal “sticky ends” after basepairing of complementary bases. E.) Digest DNA into single strands that can hybridize with complementary sequences. ...
... B.) Produce cDNA from mRNA. C.) Produce a cut (usually staggered) at specific recognition sequences on DNA. D.) Reseal “sticky ends” after basepairing of complementary bases. E.) Digest DNA into single strands that can hybridize with complementary sequences. ...
DNA Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • DNA from any cell of all organisms should have a 1:1 ratio of pyrimidine and purine bases. • The amount of guanine is equal to cytosine & the amount of adenine is equal to thymine. ...
... • DNA from any cell of all organisms should have a 1:1 ratio of pyrimidine and purine bases. • The amount of guanine is equal to cytosine & the amount of adenine is equal to thymine. ...
The Bioinformatics Institute
... Hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A-T or G-C) holds the two strands together ...
... Hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A-T or G-C) holds the two strands together ...
answers
... __JAMES WATSON____ & _FRANCIS CRICK_____ used _Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray images to help them figure out the structure of DNA. SUBUNIT PROTEINS ...
... __JAMES WATSON____ & _FRANCIS CRICK_____ used _Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray images to help them figure out the structure of DNA. SUBUNIT PROTEINS ...
Genetics Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of genes
... organisms. Genetics concerns the process of trait inheritance from parents to offspring, including the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior in the context of a cell or organism (e.g. dominance and epigenetics), gene distribution, and variation and change in populations (such as t ...
... organisms. Genetics concerns the process of trait inheritance from parents to offspring, including the molecular structure and function of genes, gene behavior in the context of a cell or organism (e.g. dominance and epigenetics), gene distribution, and variation and change in populations (such as t ...
chapter review answers
... 7. Transcribe and translate the following DNA molecule: AAATATGGCCCGGAT mRNA: UUUAUACCGGGCCUA Protein: Phen- Iso - Pro - Gly - Leu 8. Name two major types of mutations. What do they have in common? How are they different? Give an example of each using the sequence above. Gene and chromosomal. Both c ...
... 7. Transcribe and translate the following DNA molecule: AAATATGGCCCGGAT mRNA: UUUAUACCGGGCCUA Protein: Phen- Iso - Pro - Gly - Leu 8. Name two major types of mutations. What do they have in common? How are they different? Give an example of each using the sequence above. Gene and chromosomal. Both c ...
DNA paper 1 - DavidHein-CESRC-page
... genes are called housekeeping genes. They enable the cells to make the proteins needed for basic functions. Other genes are inactive most of the time. An example of this are genes that are active only during early embryonic development and then become inactive. A third type of gene encodes proteins ...
... genes are called housekeeping genes. They enable the cells to make the proteins needed for basic functions. Other genes are inactive most of the time. An example of this are genes that are active only during early embryonic development and then become inactive. A third type of gene encodes proteins ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... C A T • Errors sometimes occur (about 1 error/10,000 pairs) I • If a mismatch occurs, the DNA polymerase can backtrack, remove the incorrect nucleotide, and O replace it with the correct one. N ...
... C A T • Errors sometimes occur (about 1 error/10,000 pairs) I • If a mismatch occurs, the DNA polymerase can backtrack, remove the incorrect nucleotide, and O replace it with the correct one. N ...
BioSc 231 Exam 5 2005
... _____ A restriction fragment containing a specific gene of interest can be identified by gel electrophoresis followed by transferring the DNA to a membrane as a solid support matrix using a procedure called A. a Southern blot B. an allozyme C. identification of a gene D. a restriction fragment lengt ...
... _____ A restriction fragment containing a specific gene of interest can be identified by gel electrophoresis followed by transferring the DNA to a membrane as a solid support matrix using a procedure called A. a Southern blot B. an allozyme C. identification of a gene D. a restriction fragment lengt ...
Ch 12-15 Unit Overvi..
... Animal/human life cycle (plants / fungi life cycles not included–no alternation of generation or sporophyte or gametophyte) Somatic cell vs gamete, What is a karyotype? How is a karyotype prepared? Vocab: homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, centromere, sex chromosomes vs ...
... Animal/human life cycle (plants / fungi life cycles not included–no alternation of generation or sporophyte or gametophyte) Somatic cell vs gamete, What is a karyotype? How is a karyotype prepared? Vocab: homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, nonsister chromatids, centromere, sex chromosomes vs ...
What is Willy Wonka famous for?
... Who worked for him? • Oompa Loompas • They’re reaching retirement age! ...
... Who worked for him? • Oompa Loompas • They’re reaching retirement age! ...
1.PtI.SNPs and TAS2R38 Bitter Taste Receptor Gene.v3
... –! The frequency of this allele is greater than 1% of the population –! It is stable. –! The above distinguish it from a mutation. •! A SNP is a specific type of allele –! caused by a small genetic change within a DNA sequence –! result of replacement of one single nucleotide with any one of the oth ...
... –! The frequency of this allele is greater than 1% of the population –! It is stable. –! The above distinguish it from a mutation. •! A SNP is a specific type of allele –! caused by a small genetic change within a DNA sequence –! result of replacement of one single nucleotide with any one of the oth ...
Chapter 16 Review
... The DNA of somatic cells is constantly bombarded with agents from the environment that could cause mutations. Select the correct statement about mutations and somatic cells. A. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. ...
... The DNA of somatic cells is constantly bombarded with agents from the environment that could cause mutations. Select the correct statement about mutations and somatic cells. A. Somatic cells are in the various organs of organisms and are shielded from the harmful agents that might cause mutations. ...
6.G Meiosis Graphic Organizer 6.H Genetic Variation
... _____7. Bill grows two varieties of corn in his garden. One variety produces large ears of corn and one makes small ears of corn. When Bill crosses the two plants the resulting ears of corn are medium in size. Which statement best explains Bill’s result? a. The corn underwent a spontaneous mutation. ...
... _____7. Bill grows two varieties of corn in his garden. One variety produces large ears of corn and one makes small ears of corn. When Bill crosses the two plants the resulting ears of corn are medium in size. Which statement best explains Bill’s result? a. The corn underwent a spontaneous mutation. ...
DNA - morescience
... Which of the following figures correctly depicts the interactions at the lac operon when lactose is NOT being utilized? (The legend below defines the shapes of the molecules illustrated in the options.) ...
... Which of the following figures correctly depicts the interactions at the lac operon when lactose is NOT being utilized? (The legend below defines the shapes of the molecules illustrated in the options.) ...
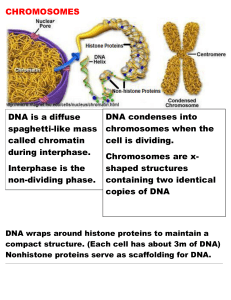
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
Guided notes 2013 Sections 1 and 2 KEY
... Vaccines made by genetic engineering techniques avoid the dangers of a traditional vaccine. ...
... Vaccines made by genetic engineering techniques avoid the dangers of a traditional vaccine. ...
Name AP EXAM REVIEW SESSION II ASSESSMENT QUIZ Use the
... d. Sample 2 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 4. e. Sample 4 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 2. 6. Once a plasmid has incorporated specific genes, such as the gene coding for ampicillin resistance, the plasmid may be cloned by a. inserting it into a virus to generat ...
... d. Sample 2 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 4. e. Sample 4 was cut at more restriction sites than was sample 2. 6. Once a plasmid has incorporated specific genes, such as the gene coding for ampicillin resistance, the plasmid may be cloned by a. inserting it into a virus to generat ...
Lab 4 Restriction Analysis
... Background. The discovery of restriction enzymes (RE's) made genetic engineering possible. RE's first made it possible to work with small, defined pieces of DNA. Before RE's were discovered, a scientist might be able to tell that a chromosome contained a gene of interest to him. He might be able to ...
... Background. The discovery of restriction enzymes (RE's) made genetic engineering possible. RE's first made it possible to work with small, defined pieces of DNA. Before RE's were discovered, a scientist might be able to tell that a chromosome contained a gene of interest to him. He might be able to ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.