Something`s Fishy
... guanine, and cytosine. This sequence of A, T, G, and C is unique to each individual. Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Each restriction enzyme recognizes a specific group of “target” base pairs and makes a cut within this area. The resulting fragments are called restriction fragment length polymorphisms ...
... guanine, and cytosine. This sequence of A, T, G, and C is unique to each individual. Restriction enzymes cut DNA. Each restriction enzyme recognizes a specific group of “target” base pairs and makes a cut within this area. The resulting fragments are called restriction fragment length polymorphisms ...
Red line lesson sketch
... You can also use GenBank to show how looking at specific gene sequences is not so informative … ...
... You can also use GenBank to show how looking at specific gene sequences is not so informative … ...
Dr . Muhammad Rafique Assist. Prof. Paediatrics College of
... F/Hx. of genetic disease, Dx. by biochemical or DNA analysis. • Parental request for sex determination because of F/Hx. of X-linked disorder. • Maternal blood sample show chromosomal abn. • As a part of work up for fetal anomalies by USG. ...
... F/Hx. of genetic disease, Dx. by biochemical or DNA analysis. • Parental request for sex determination because of F/Hx. of X-linked disorder. • Maternal blood sample show chromosomal abn. • As a part of work up for fetal anomalies by USG. ...
Name: ____________ Pd.: ______ Date: plasmid genetic
... 43. A strand of DNA formed by the splicing of DNA from two different species is called ____recombinant_____ DNA. 44. DNA ______fingerprinting__________ has been used in criminal investigations because DNA analysis is believed to allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals, ...
... 43. A strand of DNA formed by the splicing of DNA from two different species is called ____recombinant_____ DNA. 44. DNA ______fingerprinting__________ has been used in criminal investigations because DNA analysis is believed to allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals, ...
Genetics - Wantagh School
... For example: Naval oranges • Single mutation occurred in 1820 • Seedless and bigger than regular oranges ...
... For example: Naval oranges • Single mutation occurred in 1820 • Seedless and bigger than regular oranges ...
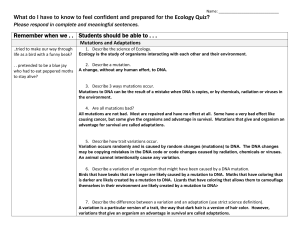
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... just plant at his monastery. Mendel’s rules of inheritance were eventually accepted, but Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection is still controversial. 13. Did our societies’ knowledge of DNA influence the conclusions drawn by either Mendel or Darwin? Mendel and Darwin’s work happened before the link ...
... just plant at his monastery. Mendel’s rules of inheritance were eventually accepted, but Darwin’s theory of Natural Selection is still controversial. 13. Did our societies’ knowledge of DNA influence the conclusions drawn by either Mendel or Darwin? Mendel and Darwin’s work happened before the link ...
BACTERIAL GENETICS
... into the host cell chromosome by recombination. 1) Homologous recombination: in which two pieces of DNA that has extensive homologous regions pair up and exchange pieces by the process of breakage and reunion 2) Non homologous recombination in which little if any homology is necessary What is Gene T ...
... into the host cell chromosome by recombination. 1) Homologous recombination: in which two pieces of DNA that has extensive homologous regions pair up and exchange pieces by the process of breakage and reunion 2) Non homologous recombination in which little if any homology is necessary What is Gene T ...
File - Dr Hayley Siddons
... • An organism’s genotype is the set of genes that it carries. • An organism’s phenotype is all of its observable characteristics—which are influenced both by its genotype and by the environment. For example, differences in the genotypes can produce different phenotypes. In these house cats, the gene ...
... • An organism’s genotype is the set of genes that it carries. • An organism’s phenotype is all of its observable characteristics—which are influenced both by its genotype and by the environment. For example, differences in the genotypes can produce different phenotypes. In these house cats, the gene ...
2nd semester exam Review packet
... 31. The left strand of a DNA molecule has the following order of bases: CGTACA. What would the right side of the same DNA molecule look like?_____________________ If the left side of the DNA molecule were used for protein synthesis, what would the mRNA ...
... 31. The left strand of a DNA molecule has the following order of bases: CGTACA. What would the right side of the same DNA molecule look like?_____________________ If the left side of the DNA molecule were used for protein synthesis, what would the mRNA ...
Bioethics Lesson Plan
... pattern of bands is formed. The gel is soaked in a chemical solution that separates the double strands in each DNA fragment. Step 3- The DNA is transferred to filter paper (blotted). A probe is added. Probes- are radioactive or florescent-labeled RNA on single-stranded DAN pieces that are complemen ...
... pattern of bands is formed. The gel is soaked in a chemical solution that separates the double strands in each DNA fragment. Step 3- The DNA is transferred to filter paper (blotted). A probe is added. Probes- are radioactive or florescent-labeled RNA on single-stranded DAN pieces that are complemen ...
AP Biology: Unit 3A Homework
... 13. Show the P, F1, and F2 generations of a cross between a homozygous gray bodied, normal winged fly and a double mutant fly. 14. Calculate the recombination frequencies. (a) A female dihybrid fly for body color and wing size is crossed with a male double mutant. They have 391 recombinant offspring ...
... 13. Show the P, F1, and F2 generations of a cross between a homozygous gray bodied, normal winged fly and a double mutant fly. 14. Calculate the recombination frequencies. (a) A female dihybrid fly for body color and wing size is crossed with a male double mutant. They have 391 recombinant offspring ...
Miniature Smooth- and Long-haired Dachshund PRA
... scientists. The main service areas of this genetic laboratory are oligonucleotide synthesis1 and DNA sequencing2. Our clients include universities and other research institutions. Inqaba has since grown in leaps and bounds and during 2009 expanded to provide animal genetic testing. Canine genetic di ...
... scientists. The main service areas of this genetic laboratory are oligonucleotide synthesis1 and DNA sequencing2. Our clients include universities and other research institutions. Inqaba has since grown in leaps and bounds and during 2009 expanded to provide animal genetic testing. Canine genetic di ...
Learning objectives
... DNA: Information and Heredity, Cellular Basis of Life Learning objectives Read pages 336-359 of “Biology” Miller & Levine (Chapter 12) and the photocopied supplements from Biology Campbell & Reece (Chapter 16) to make your Cornell notes and understand the following learning objectives. Remember thes ...
... DNA: Information and Heredity, Cellular Basis of Life Learning objectives Read pages 336-359 of “Biology” Miller & Levine (Chapter 12) and the photocopied supplements from Biology Campbell & Reece (Chapter 16) to make your Cornell notes and understand the following learning objectives. Remember thes ...
The Biological Basis of Life
... • Each alpha chain consists of 141 Amino Acids, requiring a sequence of 423 nucleotides in the DNA • Each beta chain consists of 146 Amino Acids, requiring a sequence of 438 nucleotides in the DNA ...
... • Each alpha chain consists of 141 Amino Acids, requiring a sequence of 423 nucleotides in the DNA • Each beta chain consists of 146 Amino Acids, requiring a sequence of 438 nucleotides in the DNA ...
GENETICS SOL REVIEW – 2015 PART II Name ____________________________
... Reproductive cell; eggs and sperm Specific characteristics Traits determined by genes located on the X chromosome In the first meiotic division chromosomes exchange segments of their DNA The likelihood, or chance, something will happen A change in the DNA Containing a single (half) set of chromosome ...
... Reproductive cell; eggs and sperm Specific characteristics Traits determined by genes located on the X chromosome In the first meiotic division chromosomes exchange segments of their DNA The likelihood, or chance, something will happen A change in the DNA Containing a single (half) set of chromosome ...
Genetic code molecule
... How are gene mutations different from chromosomal mutations? Gene mutations – change in a single gene Chromosomal mutations- change in chromosomes How are point mutations different from frameshift mutations? Point mutations- change in one or few bases Frameshift mutations- change the reading frame s ...
... How are gene mutations different from chromosomal mutations? Gene mutations – change in a single gene Chromosomal mutations- change in chromosomes How are point mutations different from frameshift mutations? Point mutations- change in one or few bases Frameshift mutations- change the reading frame s ...
Genetics and Heredity
... What genetic principles account for the transmission of such traits from parents to offspring? The Blending Hypothesis of Inheritance In the early 1800’s the blending hypothesis was proposed. Genetic material contributed by the two parents mixes in a manner analogous to the way blue and yellow pai ...
... What genetic principles account for the transmission of such traits from parents to offspring? The Blending Hypothesis of Inheritance In the early 1800’s the blending hypothesis was proposed. Genetic material contributed by the two parents mixes in a manner analogous to the way blue and yellow pai ...
Biologists have learned to manipulate DNA
... C. Humans use plasmids to place DNA to make useful products from bacteria 1. Plasmid is removed and the desired gene is placed in the plasmid recombinant DNA 2. Recombinant plasmid is placed back in bacteria to replicate over and over- gene cloning II. Cutting and pasting DNA A. Piece of DNA is cu ...
... C. Humans use plasmids to place DNA to make useful products from bacteria 1. Plasmid is removed and the desired gene is placed in the plasmid recombinant DNA 2. Recombinant plasmid is placed back in bacteria to replicate over and over- gene cloning II. Cutting and pasting DNA A. Piece of DNA is cu ...
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis, and Mutations
... alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one ...
... alteration can be passed on to every cell that develops from the original one ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.