Bio1001Ch12W
... When a cell copies a DNA molecule, each strand serves as a _________ for ordering nucleotides into a new ________________ strand. ...
... When a cell copies a DNA molecule, each strand serves as a _________ for ordering nucleotides into a new ________________ strand. ...
Lab 5 minipreps
... tell what other genes were close to "his" gene, but he could not physically locate the gene on the chromosome nor manipulate it. The scientist could purify the chromosome but then he had a huge piece of DNA containing thousands of genes. The only way to break it into smaller segments was to physical ...
... tell what other genes were close to "his" gene, but he could not physically locate the gene on the chromosome nor manipulate it. The scientist could purify the chromosome but then he had a huge piece of DNA containing thousands of genes. The only way to break it into smaller segments was to physical ...
Genome Variant Calling: A sta>s>cal perspec>ve
... • for tumors copy number varies and the varia2on in the genome tends to be a func2on of the type of cancer (or lifestyle: smoking induces G-‐>T transversions) so reasonable priors are harder to ob ...
... • for tumors copy number varies and the varia2on in the genome tends to be a func2on of the type of cancer (or lifestyle: smoking induces G-‐>T transversions) so reasonable priors are harder to ob ...
DNA structure lab protocol
... almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). The information in DNA is stor ...
... almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). The information in DNA is stor ...
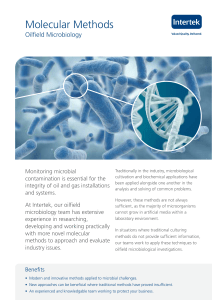
Molecular Methods
... with bands at different positions The first step is the extraction contamination in a in the gel. Each band represents of DNA (or RNA if looking at a network of pipelines. a different microbial population functional gene) from samples. and some idea of their respective Then multiple copies of the DN ...
... with bands at different positions The first step is the extraction contamination in a in the gel. Each band represents of DNA (or RNA if looking at a network of pipelines. a different microbial population functional gene) from samples. and some idea of their respective Then multiple copies of the DN ...
MBP 1022, LECTURE 3 DAN-ct30
... General structure of nucleic acids Mechanism of DNA synthesis Not responsible for nucleosomes and heterochromatin ...
... General structure of nucleic acids Mechanism of DNA synthesis Not responsible for nucleosomes and heterochromatin ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 09_p01-58
... Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. ...
... Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. ...
Bio-inspired Programmable Self
... • The goal of molecular architecture is to precisely arrange molecules or even atoms in space and to make them operate as intended • Conventional synthetic approaches for such self-assembling systems are not efficient enough ...
... • The goal of molecular architecture is to precisely arrange molecules or even atoms in space and to make them operate as intended • Conventional synthetic approaches for such self-assembling systems are not efficient enough ...
Chapter 12
... process a called transformation: - Process in which one strain of bacteria changes into another strain. ...
... process a called transformation: - Process in which one strain of bacteria changes into another strain. ...
Discovering the material for heredity: DNA
... Frederick Griffith (1928) Griffith discovers that bacteria can change from one form to another. Oswald Avery & colleagues (1944) follow up Griffith’s earlier discovery and conclude that the transforming factor is DNA. Rosalind Franklin & Maurice Wilkins (1950) provide evidence that DNA is in the for ...
... Frederick Griffith (1928) Griffith discovers that bacteria can change from one form to another. Oswald Avery & colleagues (1944) follow up Griffith’s earlier discovery and conclude that the transforming factor is DNA. Rosalind Franklin & Maurice Wilkins (1950) provide evidence that DNA is in the for ...
DNA
... • Bases are A,G,T,C • Can be damaged by exposure to ultra violet rays. • Double-stranded molecule ...
... • Bases are A,G,T,C • Can be damaged by exposure to ultra violet rays. • Double-stranded molecule ...
DNA Isolation for Low-Melting Point Agarose (using elu
... (from elu-tip column protocol) 9. Following the elu-tip protocol booklet, wash the column by pushing 5 of low salt buffer through the matrix at a rate of 0.5-1.0 ml/minute. The column may be incubated in the low salt buffer ³ 2 hours to improve recovery. ...
... (from elu-tip column protocol) 9. Following the elu-tip protocol booklet, wash the column by pushing 5 of low salt buffer through the matrix at a rate of 0.5-1.0 ml/minute. The column may be incubated in the low salt buffer ³ 2 hours to improve recovery. ...
Key
... 1. Chromosome-organized structures of DNA that stay inside the nucleus 2. DNA-Deoxyribonucleic Acid-the molecule that contains the code for traits 3. Gene-sections of chromosomes that code for specific traits 4. Environmental Trait-characteristics influenced by where and how an organism lives 5. Inh ...
... 1. Chromosome-organized structures of DNA that stay inside the nucleus 2. DNA-Deoxyribonucleic Acid-the molecule that contains the code for traits 3. Gene-sections of chromosomes that code for specific traits 4. Environmental Trait-characteristics influenced by where and how an organism lives 5. Inh ...
Nucleic acids dna the double helix worksheet answers
... proteins are key molecules of the cell nucleus. One gene makes one protein. A gene is made of DNA. Bacteria and viruses have DNA too. The DNA molecule is. DNA, DNA molecule, double helix, What is DNA, James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, DNA structure, game, Nobel, Nobelprize, educational, ...
... proteins are key molecules of the cell nucleus. One gene makes one protein. A gene is made of DNA. Bacteria and viruses have DNA too. The DNA molecule is. DNA, DNA molecule, double helix, What is DNA, James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, DNA structure, game, Nobel, Nobelprize, educational, ...
File
... 7.If a strand of DNA has the sequence T A G G T A C, write down the sequence of the parallel DNA strand. 8.If a strand of DNA has the sequence C G A T C G G T T A, write down the sequence of the parallel DNA strand. 9.In order for the DNA strands to separate, the ________________ bonds connecting th ...
... 7.If a strand of DNA has the sequence T A G G T A C, write down the sequence of the parallel DNA strand. 8.If a strand of DNA has the sequence C G A T C G G T T A, write down the sequence of the parallel DNA strand. 9.In order for the DNA strands to separate, the ________________ bonds connecting th ...
DNA sequencing

DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a strand of DNA. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern DNA sequencing technology has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA sequences, or genomes of numerous types and species of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA sequences of many animal, plant, and microbial species.The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of fluorescence-based sequencing methods with a DNA sequencer, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.