problem set
... its complementary region of the plasmid. This prevents the two complementary strands of the plasmid DNA from reannealing at the region where the primer binds. DNA polymerases used in sequencing bind to the 3’-OH group of the primer and extend it in the sequencing reactions. DNA sequencing is covered ...
... its complementary region of the plasmid. This prevents the two complementary strands of the plasmid DNA from reannealing at the region where the primer binds. DNA polymerases used in sequencing bind to the 3’-OH group of the primer and extend it in the sequencing reactions. DNA sequencing is covered ...
11.3 and 11.4 Notes - West Branch Schools
... Contains a nitrogenous base called URACIL (U) instead of thymine of DNA RNA typically forms a single, sometimes twisted strand, not a double helix like DNA ...
... Contains a nitrogenous base called URACIL (U) instead of thymine of DNA RNA typically forms a single, sometimes twisted strand, not a double helix like DNA ...
DNA - NylandBiology2012-2013
... 9. In DNA, thymine is complementary to ________________ ; cytosine is complementary to _____________ 10. In a strand of DNA, the percentage of thymine is 30 %. What is the percentage of cytosine in the same DNA strand? _________________ 11. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1 ...
... 9. In DNA, thymine is complementary to ________________ ; cytosine is complementary to _____________ 10. In a strand of DNA, the percentage of thymine is 30 %. What is the percentage of cytosine in the same DNA strand? _________________ 11. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1 ...
DNA Collection Veterinary Form10 December
... the result on their breed database. I understand and agree that the TGCA may use this DNA data in their activities associated with the future development of the breed. ...
... the result on their breed database. I understand and agree that the TGCA may use this DNA data in their activities associated with the future development of the breed. ...
DNA Prot Syn Engineer
... Describe the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure. How did it fit the data provided by Chargaff and the X-ray diffraction pattern? Explain how DNA replicates semiconservatively. How does the antiparallel structure of the double helix affect replication? In your answer, be sure to include discussi ...
... Describe the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure. How did it fit the data provided by Chargaff and the X-ray diffraction pattern? Explain how DNA replicates semiconservatively. How does the antiparallel structure of the double helix affect replication? In your answer, be sure to include discussi ...
Study Guide Chap 6: DNA
... constructed models of the structure of DNA and used Franklin’s data to correctly identify the structure of DNA as a double helix.___________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. _DNA_____ has a ...
... constructed models of the structure of DNA and used Franklin’s data to correctly identify the structure of DNA as a double helix.___________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. _DNA_____ has a ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... Q1. Round shape denotes phosphate group and the other one is sugar unit. Q2. (a) Opposite direction, Composition of nitrogen bases (b) Complementary base pairs (c) By using diagrams of different shapes Q3. (a) adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine (b) Hydrogen bonding is a speci ...
... Q1. Round shape denotes phosphate group and the other one is sugar unit. Q2. (a) Opposite direction, Composition of nitrogen bases (b) Complementary base pairs (c) By using diagrams of different shapes Q3. (a) adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine (b) Hydrogen bonding is a speci ...
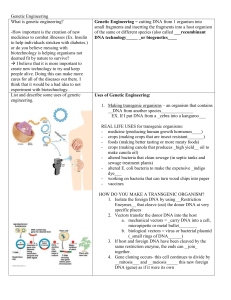
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... 35,000 -40,000 genes on the _46__ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis______ for diseases (ex. Test the cells from the fluid around fetus to see if baby has a genetic disorder) - better drugs - gene therapy = __insertion of normal genes into people who have d ...
... 35,000 -40,000 genes on the _46__ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis______ for diseases (ex. Test the cells from the fluid around fetus to see if baby has a genetic disorder) - better drugs - gene therapy = __insertion of normal genes into people who have d ...
What organelle is responsible for storing DNA in eukaryotic cells
... order: the human species has 23 pairs, designated 1 to 22 in order of decreasing size and X and Y for the female and male sex chromosomes respectively. • Our definition: The place where all the genes of an organisms are held. • Other forms: chromosomes, chromosomal ...
... order: the human species has 23 pairs, designated 1 to 22 in order of decreasing size and X and Y for the female and male sex chromosomes respectively. • Our definition: The place where all the genes of an organisms are held. • Other forms: chromosomes, chromosomal ...
Biology 105
... itself) part of the telomere does not replicate and is lost. DNA can replicate many times. However, eventually important and essential coding DNA may be lost ...
... itself) part of the telomere does not replicate and is lost. DNA can replicate many times. However, eventually important and essential coding DNA may be lost ...
Lecture 14
... ii. DNA is long but extremely thin g. How is DNA packed? i. Similar to degree to structure of proteins ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, cont ...
... ii. DNA is long but extremely thin g. How is DNA packed? i. Similar to degree to structure of proteins ii. Second degree: wrapped around protein assembly, called histones iii. Nucleosome, not base pair specific iv. Then packed into coils continuous contracting of molecule v. Most of the time, cont ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... restriction enzyme. (this leaves the human DNA and the plasmid DNA with the same “sticky ends”) ...
... restriction enzyme. (this leaves the human DNA and the plasmid DNA with the same “sticky ends”) ...
Name Date Class ______ DNA Replication Worksheet Use the
... 11. What enzyme matches the bases of free nucleotides to the bases on the parent strand? ______________________________________________ 12. If the DNA double helix were a twisted ladder, what would the sides of the ladder be made of? ______________________________________________________________ 13. ...
... 11. What enzyme matches the bases of free nucleotides to the bases on the parent strand? ______________________________________________ 12. If the DNA double helix were a twisted ladder, what would the sides of the ladder be made of? ______________________________________________________________ 13. ...
Eastern Intermediate High School
... 8. In DNA, guanine always forms hydrogen bonds with __________________. 9. The process of __________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is passed on to a new cell. 10. The double coiled, “staircase” shape of DNA is called a __________________. Directions: Answer ...
... 8. In DNA, guanine always forms hydrogen bonds with __________________. 9. The process of __________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is passed on to a new cell. 10. The double coiled, “staircase” shape of DNA is called a __________________. Directions: Answer ...
Use the diagram to answer the questions to the right
... 11. What enzyme matches the bases of free nucleotides to the bases on the parent strand? ______________________________________________ 12. If the DNA double helix were a twisted ladder, what would the sides of the ladder be made of? ______________________________________________________________ 13. ...
... 11. What enzyme matches the bases of free nucleotides to the bases on the parent strand? ______________________________________________ 12. If the DNA double helix were a twisted ladder, what would the sides of the ladder be made of? ______________________________________________________________ 13. ...
Exercise Follow up and Conclusion for: DNA Fingerprinting and Big
... Using the data for fragment HINDIII, plot your line of ‘Best fit’ on the semi-log paper blank provided for you with the handout in II. Make the Best Fit line RED. Determine the BP lengths for the other fragments using your graph and fill in the rest of your chart. ...
... Using the data for fragment HINDIII, plot your line of ‘Best fit’ on the semi-log paper blank provided for you with the handout in II. Make the Best Fit line RED. Determine the BP lengths for the other fragments using your graph and fill in the rest of your chart. ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... DNA - The Double Helix Recallthat the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. lt is often called the "control center" because it controls allthe activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes ...
... DNA - The Double Helix Recallthat the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. lt is often called the "control center" because it controls allthe activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes ...
Reading Questions Ch.13 DNA Reading
... 26. The codon is code word for a specific amino acid used to make a certain protein. How many amino acids are used to make proteins? 27. Can you break the code? What amino acids should be used for the following codons (code ...
... 26. The codon is code word for a specific amino acid used to make a certain protein. How many amino acids are used to make proteins? 27. Can you break the code? What amino acids should be used for the following codons (code ...
Genes and DNA
... Franklin’s work. They came to the conclusion that “DNA must look like a long, twisted ladder. This lead to the explanation on how DNA is copied and how it functions in the cell. ...
... Franklin’s work. They came to the conclusion that “DNA must look like a long, twisted ladder. This lead to the explanation on how DNA is copied and how it functions in the cell. ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.