detection of phaeomoniella chlamydospora in soil using species
... 30 min and centrifuged for 5 min at 1000 x g. The resulting supernatant was transferred to a clean tube and extracted four times with 2 ml phenol and 2 ml chloroform, followed by a single extraction with 4 ml chloroform. DNA was precipitated by addition of 60% volume of ice-cold isopropanol and the ...
... 30 min and centrifuged for 5 min at 1000 x g. The resulting supernatant was transferred to a clean tube and extracted four times with 2 ml phenol and 2 ml chloroform, followed by a single extraction with 4 ml chloroform. DNA was precipitated by addition of 60% volume of ice-cold isopropanol and the ...
The many twists and turns of DNA: template, telomere, tool, and target
... the minor groove. Instead, only the central portion of pentamidine resides inside the groove, leaving the positively charged ends detached from the DNA and free to interact with phosphate groups from adjacent duplexes in the crystal. The potential implications of this binding mode for the antiprotoz ...
... the minor groove. Instead, only the central portion of pentamidine resides inside the groove, leaving the positively charged ends detached from the DNA and free to interact with phosphate groups from adjacent duplexes in the crystal. The potential implications of this binding mode for the antiprotoz ...
How to Use This Presentation
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
MB_10_win
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
... Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is sometimes described as a zipper. Answer: DNA is often described as a zipper because the two strands of DNA look like each lengthwise half of a zipper and the bases and hydrogen bonds between the strands look like the “teeth” of a zipper. Chapter menu ...
Mutation, Mutagens, and DNA Repair
... - 1010 nucleotides incorporated. DNA polymerases, however, are not nearly so accurate. They make mistakes once every 104 - 105 nucleotides incorporated. The proofreading activity of a polymerase will improve the overall error rate by 102 - 103 but this still leaves a difference of 102 - 103 in the e ...
... - 1010 nucleotides incorporated. DNA polymerases, however, are not nearly so accurate. They make mistakes once every 104 - 105 nucleotides incorporated. The proofreading activity of a polymerase will improve the overall error rate by 102 - 103 but this still leaves a difference of 102 - 103 in the e ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... Genetic information is encoded by molecules named nucleic acids because they were originally isolated from the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. There are two related types of nucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The master copy of each cell’s genome is stored on long mol ...
... Genetic information is encoded by molecules named nucleic acids because they were originally isolated from the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. There are two related types of nucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The master copy of each cell’s genome is stored on long mol ...
Characterization of a novel DNA polymerase activity assay enabling
... During the past 50 years, in vitro measurement of DNA polymerase activity has become an essential molecular biology tool. Traditional methods used to measure DNA polymerase activity in vitro are undesirable due to the usage of radionucleotides. Fluorescence-based DNA polymerase assays have been deve ...
... During the past 50 years, in vitro measurement of DNA polymerase activity has become an essential molecular biology tool. Traditional methods used to measure DNA polymerase activity in vitro are undesirable due to the usage of radionucleotides. Fluorescence-based DNA polymerase assays have been deve ...
NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE SPECIFICITY OF RESTRICTION
... enzyme and the methylase shared common DNA recognition sites. As a further proof that we had isolated the modification methylase, we analyzed 3’ and 5’ nearest neighbors to the 3H-methylated adenine residues produced by the enzyme. The results gave as the partial sequence for the methylase, the trin ...
... enzyme and the methylase shared common DNA recognition sites. As a further proof that we had isolated the modification methylase, we analyzed 3’ and 5’ nearest neighbors to the 3H-methylated adenine residues produced by the enzyme. The results gave as the partial sequence for the methylase, the trin ...
Methylation-sensitive RFLPs: characterisation of two oil palm
... the GDP-GTP nucleotide-exchange subunit of the translation elongation complex. The 1,096-bp CPHO63 sequence was found to contain an ORF between positions 375 and 887. Its deduced polypeptide sequence of 170 amino acids shows strong similarities to zinc-finger domain proteins, notably LIM metal-bindi ...
... the GDP-GTP nucleotide-exchange subunit of the translation elongation complex. The 1,096-bp CPHO63 sequence was found to contain an ORF between positions 375 and 887. Its deduced polypeptide sequence of 170 amino acids shows strong similarities to zinc-finger domain proteins, notably LIM metal-bindi ...
Enhancing fairness in DNA jury trials
... in DNA jury trials Jane Goodman-Delahunty and Lindsay Hewson Use of DNA evidence in Australian courts has increased exponentially since 1989 (Easteal & Easteal 1990; Walsh et al. 2004). After 20 years, DNA technology is well-tested and is no longer the subject of defence challenges (Haesler 2008). I ...
... in DNA jury trials Jane Goodman-Delahunty and Lindsay Hewson Use of DNA evidence in Australian courts has increased exponentially since 1989 (Easteal & Easteal 1990; Walsh et al. 2004). After 20 years, DNA technology is well-tested and is no longer the subject of defence challenges (Haesler 2008). I ...
Document
... 2. Describe how a molecule of DNA is replicated. Write your answer in the space below. ANS: To begin the replication process, enzymes called helicases break the hydrogen bonds that hold the two complementary strands of the DNA double helix together, allowing the helix to unwind. At a replication for ...
... 2. Describe how a molecule of DNA is replicated. Write your answer in the space below. ANS: To begin the replication process, enzymes called helicases break the hydrogen bonds that hold the two complementary strands of the DNA double helix together, allowing the helix to unwind. At a replication for ...
Replication timing and transcriptional control: beyond
... assays for replication [29]. There are only two mammalian loci for which both replication-timing switches and origin localization have been studied. At the mouse immunoglobulin IgH locus, new origins are activated in pre-B cells when the promoter region of this locus becomes transcriptionally active ...
... assays for replication [29]. There are only two mammalian loci for which both replication-timing switches and origin localization have been studied. At the mouse immunoglobulin IgH locus, new origins are activated in pre-B cells when the promoter region of this locus becomes transcriptionally active ...
dna - columbusisd.org
... • Many enzymes and proteins, such as DNA polymerases, are involved in unwinding the DNA, keeping the DNA strands apart, and assembling the new DNA strands. • Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique for replicating small quantities of DNA or broken pieces of DNA found at a crime scene, outside ...
... • Many enzymes and proteins, such as DNA polymerases, are involved in unwinding the DNA, keeping the DNA strands apart, and assembling the new DNA strands. • Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique for replicating small quantities of DNA or broken pieces of DNA found at a crime scene, outside ...
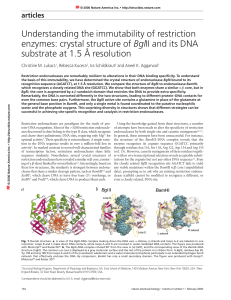
Article - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... The α/β core is similar to that of BamHI, containing a six-stranded β-sheet (β1, β3, β4, β5, β6 and β7) surrounded by five α-helices (α1, α2, α3, α4 and α5), two of which (α4 and α5) are involved in homodimerization. The loops preceding the dimerization helices (loops B and C) carry the residues tha ...
... The α/β core is similar to that of BamHI, containing a six-stranded β-sheet (β1, β3, β4, β5, β6 and β7) surrounded by five α-helices (α1, α2, α3, α4 and α5), two of which (α4 and α5) are involved in homodimerization. The loops preceding the dimerization helices (loops B and C) carry the residues tha ...
On Map Representations of DNA†
... the fact that the algorithm identifies also pairs of adjacent amino which appear only in one sequence and not in the other, and thus eliminate need for their further examination. To find more how was the exact solution in of protein alignment more recently extended to DNA alignment consult Ref. 63. ...
... the fact that the algorithm identifies also pairs of adjacent amino which appear only in one sequence and not in the other, and thus eliminate need for their further examination. To find more how was the exact solution in of protein alignment more recently extended to DNA alignment consult Ref. 63. ...
Document
... lengths from 150 to 500 base pairs from λ – phage DNA and plasmids pBR322, pUC18, pGEM7(f+) (Promega), and their modified analogs which contained different insertions into polylinkers. The results of statistical analysis have shown that: 1) The cleavage rate just after deoxycitidine is considerably ...
... lengths from 150 to 500 base pairs from λ – phage DNA and plasmids pBR322, pUC18, pGEM7(f+) (Promega), and their modified analogs which contained different insertions into polylinkers. The results of statistical analysis have shown that: 1) The cleavage rate just after deoxycitidine is considerably ...
16 System and a 10X Primer Pair Mix Stored in TE
... this change should not affect amplification results. This change is not necessary for the PowerPlex® Y System because TE-4 buffer is already used to prepare the PowerPlex® Y 10X Primer Pair Mix. We will continue to generate more real time stability data, and if the product shelf life is extended, th ...
... this change should not affect amplification results. This change is not necessary for the PowerPlex® Y System because TE-4 buffer is already used to prepare the PowerPlex® Y 10X Primer Pair Mix. We will continue to generate more real time stability data, and if the product shelf life is extended, th ...
from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... The 289 base pair Rsa I-Alu I fragment containing CEN3 DNA was isolated as described by Bloom et al. (1984). The fragment was incubated with synthetic oligonucleotide linkers encoding the Barn HI restriction recognition site in the presence of T4 DNA ligase. Enzymes were purchased from New England B ...
... The 289 base pair Rsa I-Alu I fragment containing CEN3 DNA was isolated as described by Bloom et al. (1984). The fragment was incubated with synthetic oligonucleotide linkers encoding the Barn HI restriction recognition site in the presence of T4 DNA ligase. Enzymes were purchased from New England B ...
Are Human Genes Patentable Subject Matter?
... Judge Bryson likens the creation of isolated DNA to the snapping of a leaf from a tree.64 When a person snaps a leaf from a tree, she breaks chemical bonds that had previously attached it to the branch. In doing so, she has imparted new characteristics and uses upon the leaf. It no longer can be use ...
... Judge Bryson likens the creation of isolated DNA to the snapping of a leaf from a tree.64 When a person snaps a leaf from a tree, she breaks chemical bonds that had previously attached it to the branch. In doing so, she has imparted new characteristics and uses upon the leaf. It no longer can be use ...
DNA ppt 10.8.13
... 3. The result is that there are now two doublestranded DNA molecules in the nucleus 4. So that when the cell divides, each nucleus contains identical DNA 5. This process is called replication ...
... 3. The result is that there are now two doublestranded DNA molecules in the nucleus 4. So that when the cell divides, each nucleus contains identical DNA 5. This process is called replication ...
Soliton-like base pair opening in a helicoidal DNA: An analogy with
... Electronic address: [email protected] ...
... Electronic address: [email protected] ...
Molecular Structure of the GARP Family of Plant Myb
... variant (GGAT), as shown in Figure 5A. The presumed minimum DNA binding domain of 64 amino acids (i.e., ARR10-B) was used for the gel-shift assays. The results are shown in Figure 5A. The purified ARR10-B displayed an ability to associate efficiently with AGATT and to associate slightly less efficie ...
... variant (GGAT), as shown in Figure 5A. The presumed minimum DNA binding domain of 64 amino acids (i.e., ARR10-B) was used for the gel-shift assays. The results are shown in Figure 5A. The purified ARR10-B displayed an ability to associate efficiently with AGATT and to associate slightly less efficie ...
The Pif1 family in prokaryotes: what are our helicases doing in your
... also encodes a variety of predicted helicases, with more than dozen such enzymes verified by direct biochemical assays. A universal collection of helicase types that is required for viability, however, has not been identified in bacteria or eukaryotes, likely due to functional redundancy in vivo. Th ...
... also encodes a variety of predicted helicases, with more than dozen such enzymes verified by direct biochemical assays. A universal collection of helicase types that is required for viability, however, has not been identified in bacteria or eukaryotes, likely due to functional redundancy in vivo. Th ...
Identifying the Genetic Material
... process. Scientists could determine whether it was the DNA, the protein, or both that were being transferred into the bacterial cells to reprogram the bacteria. After a few minutes, the scientists tore the 35S-labeled phages off the surfaces of the bacteria (with the help of a blender). The bacteria ...
... process. Scientists could determine whether it was the DNA, the protein, or both that were being transferred into the bacterial cells to reprogram the bacteria. After a few minutes, the scientists tore the 35S-labeled phages off the surfaces of the bacteria (with the help of a blender). The bacteria ...
Bacteria Screening PCR Kit
... In order to maintain consumer trust in the safety of food products, a high priority has been placed on assuring product quality at each step of the food supply process. PCR is recognized as one of the more useful methods for such food-related quality control applications. PCR is a technique in which ...
... In order to maintain consumer trust in the safety of food products, a high priority has been placed on assuring product quality at each step of the food supply process. PCR is recognized as one of the more useful methods for such food-related quality control applications. PCR is a technique in which ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.