Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... Genetic Transfer in Bacteria Genetic transfer-results in genetic variation ...
... Genetic Transfer in Bacteria Genetic transfer-results in genetic variation ...
Molecular Bio Questions2
... 12) Which statement below is FALSE regarding replication of the bacterial chromosome? a) Replication occurs in a bidirectional manner from the origin of replication. b) The leading strand is replicated in the 5’ to 3’ direction and the lagging strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction. c) The primase adds a ...
... 12) Which statement below is FALSE regarding replication of the bacterial chromosome? a) Replication occurs in a bidirectional manner from the origin of replication. b) The leading strand is replicated in the 5’ to 3’ direction and the lagging strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction. c) The primase adds a ...
A O R P T Y S
... • Nitrogen BASES= Instructions for Proteins • Nitrogen bases are read in units of 3 called codons • Each codon represents 1 amino acid ...
... • Nitrogen BASES= Instructions for Proteins • Nitrogen bases are read in units of 3 called codons • Each codon represents 1 amino acid ...
SG 17,18,19
... DNA and RNA. Describe the process of transcription in detail. What are the 3 most important RNAs produced, characteristics and their function. Chapter 18 Define replication, transcription, and translation. Write the Central Dogma for process of genetic info to protein. Describe what is meant by semi ...
... DNA and RNA. Describe the process of transcription in detail. What are the 3 most important RNAs produced, characteristics and their function. Chapter 18 Define replication, transcription, and translation. Write the Central Dogma for process of genetic info to protein. Describe what is meant by semi ...
Biology
... 2. diagram and label the basic structure of DNA 3. describe the basic structure of the eukaryotic chromosome 4. trace the process of DNA replication 5. summarize the role of the enzymes involved in DNA replication 6. explain how messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the tran ...
... 2. diagram and label the basic structure of DNA 3. describe the basic structure of the eukaryotic chromosome 4. trace the process of DNA replication 5. summarize the role of the enzymes involved in DNA replication 6. explain how messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA are involved in the tran ...
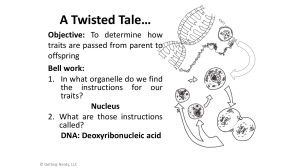
A Twisted Tale…
... Let’s start at the source… DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, resides inside the nucleus of every living cell. It was discovered in 1869 but the structure remained a mystery. In 1952, using X-ray photography, Rosalind Franklin observed DNA, but could not identify the shape. A year later, Francis Crick ...
... Let’s start at the source… DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, resides inside the nucleus of every living cell. It was discovered in 1869 but the structure remained a mystery. In 1952, using X-ray photography, Rosalind Franklin observed DNA, but could not identify the shape. A year later, Francis Crick ...
浙江万里学院《基因工程》试卷(六)
... 5. the role of cAMP is a second messenger hormone, has nothing to do with transcription. ( ...
... 5. the role of cAMP is a second messenger hormone, has nothing to do with transcription. ( ...
Teacher Notes - Solon City Schools
... Protein Synthesis Teacher Notes I. Protein Synthesis A. DNA Replication 1. Occurs in the nucleus prior to any cell division 2. Enzyme is used to “unzip” or “unwind” the DNA 3. Another enzyme is used to build a complementary strand of DNA from the template piece of original DNA a. Nitrogen bases pair ...
... Protein Synthesis Teacher Notes I. Protein Synthesis A. DNA Replication 1. Occurs in the nucleus prior to any cell division 2. Enzyme is used to “unzip” or “unwind” the DNA 3. Another enzyme is used to build a complementary strand of DNA from the template piece of original DNA a. Nitrogen bases pair ...
Directions: Use the DNA tutorials from my wiki to answer the
... • What are the four pairs of DNA bases that form in the double helix? • Which carbon in the sugar attaches to one of the four bases? • How can A distinguish T from C? • Which DNA double helix do you think would be harder to separate into two strands: DNA composed predominantly of AT base pairs, or o ...
... • What are the four pairs of DNA bases that form in the double helix? • Which carbon in the sugar attaches to one of the four bases? • How can A distinguish T from C? • Which DNA double helix do you think would be harder to separate into two strands: DNA composed predominantly of AT base pairs, or o ...
From DNA to Proteins Unit Crossword
... acids to build a protein. 3. –the making of an RNA molecule from a DNA template 5. A change of the DNA sequence within a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not found in the parental type. 6. -a type of RNA that binds to s specific amino acids and ...
... acids to build a protein. 3. –the making of an RNA molecule from a DNA template 5. A change of the DNA sequence within a gene or chromosome of an organism resulting in the creation of a new character or trait not found in the parental type. 6. -a type of RNA that binds to s specific amino acids and ...
E. coli - Madeira City Schools
... DNA polymerase III makes strand building in the 5’--3’ direction. DNA polymerase I replaces the primer For lagging strand, DNA ligase joins fragments Telomeres are present at the end of the strand so DNA doesn’t shorten DNA is proof read for mistakes ...
... DNA polymerase III makes strand building in the 5’--3’ direction. DNA polymerase I replaces the primer For lagging strand, DNA ligase joins fragments Telomeres are present at the end of the strand so DNA doesn’t shorten DNA is proof read for mistakes ...
DNA Crossword Puzzle
... 2. A molecule that along with a sugar forms the legs of the ladder of DNA. [PHOSPHATE] 4. A molecule composed of strings of nucleotides. They act as the genetic material of cells and occur as either the double helix DNA or the single helix RNA. [NUCLEICACID] 5. A simple carbohydrate molecule. Along ...
... 2. A molecule that along with a sugar forms the legs of the ladder of DNA. [PHOSPHATE] 4. A molecule composed of strings of nucleotides. They act as the genetic material of cells and occur as either the double helix DNA or the single helix RNA. [NUCLEICACID] 5. A simple carbohydrate molecule. Along ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
... 1. Why is transcription necessary? Transcription makes messenger RNA (MRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble MRNA. 3. Why ...
... 1. Why is transcription necessary? Transcription makes messenger RNA (MRNA) to carry the code for proteins out of the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 2. Describe transcription. RNA polymerase binds to DNA, separates the strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble MRNA. 3. Why ...
Biology 20 DNA Replication What do the initials DNA stand for
... Priming for DNA Replication: Before DNA polymerase can begin work on the daughter strands, a primer must be laid first. Which enzyme produces the primer? What type of molecule is the primer? Synthesis of the new DNA strands: Once the RNA primers are in place, DNA polymerase can go to work. DNA polym ...
... Priming for DNA Replication: Before DNA polymerase can begin work on the daughter strands, a primer must be laid first. Which enzyme produces the primer? What type of molecule is the primer? Synthesis of the new DNA strands: Once the RNA primers are in place, DNA polymerase can go to work. DNA polym ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... Color the phosphates blue. Color the sugars (deoxyribose) red. Label one hydrogen bond. Part II. Answer the following questions: 1. Cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine are referred to as __________________ bases. 2. Cytosine is always paired with ________________. 3. Adenine is always paired wit ...
... Color the phosphates blue. Color the sugars (deoxyribose) red. Label one hydrogen bond. Part II. Answer the following questions: 1. Cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine are referred to as __________________ bases. 2. Cytosine is always paired with ________________. 3. Adenine is always paired wit ...
Replication Transcription Translation
... complementary strand of _____________. • 1 Strand DNA 2 Strands RNA • RNA Polymerase ...
... complementary strand of _____________. • 1 Strand DNA 2 Strands RNA • RNA Polymerase ...
DNA Fingerprinting lab
... Results: Describe what the completed gel looks like. Conclusion: Compare the DNA fingerprint to the suspects. Who is the culprit? Questions: Now, click on Science in the Courtroom at the bottom of the page. What are the 4 reasons why Judge Chernoff thinks judges should be informed about DNA fingerpr ...
... Results: Describe what the completed gel looks like. Conclusion: Compare the DNA fingerprint to the suspects. Who is the culprit? Questions: Now, click on Science in the Courtroom at the bottom of the page. What are the 4 reasons why Judge Chernoff thinks judges should be informed about DNA fingerpr ...
dna vaccines - WordPress.com
... polyadenylation sequences and the production unit composed of bacterial sequences necessary for plasmid amplification and selection. The construction of bacterial plasmids with vaccine inserts is accomplished using recombinant DNA technology. Once constructed, the vaccine plasmid is transformed into ...
... polyadenylation sequences and the production unit composed of bacterial sequences necessary for plasmid amplification and selection. The construction of bacterial plasmids with vaccine inserts is accomplished using recombinant DNA technology. Once constructed, the vaccine plasmid is transformed into ...
A Model of DNA Objective: To construct a model of double
... Materials: cardboard tube from paper-towel roll, 10 toothpicks, felt-tip markers (two colors), thumbtack, metric ruler (You could use other materials…get inventive!) Procedure: Create a 3-D “live” model of DNA with Sugars and Phosphates labeled. (Here is one way) 1. The typical tube has a seam that ...
... Materials: cardboard tube from paper-towel roll, 10 toothpicks, felt-tip markers (two colors), thumbtack, metric ruler (You could use other materials…get inventive!) Procedure: Create a 3-D “live” model of DNA with Sugars and Phosphates labeled. (Here is one way) 1. The typical tube has a seam that ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.