Nervous Tissue Homeostasis
... What type of nervous system and body symmetry do Cnidarians (jellyfish, anemones, etc) and adult Echinoderms (seastars, urchins, etc) have? 10. Bilateral symmetry allows cephalization, as well as distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is i ...
... What type of nervous system and body symmetry do Cnidarians (jellyfish, anemones, etc) and adult Echinoderms (seastars, urchins, etc) have? 10. Bilateral symmetry allows cephalization, as well as distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is i ...
meiosis_chapter_4.3_notes
... mitosis. A cell that divide by meiosis goes through two cell divisions, but the chromosomes are not copied before the second division. In mitosis, the chromosomes are always copied before division. Daughter cells produced by meiosis, which are haploid (1n), only contain half the genetic material of ...
... mitosis. A cell that divide by meiosis goes through two cell divisions, but the chromosomes are not copied before the second division. In mitosis, the chromosomes are always copied before division. Daughter cells produced by meiosis, which are haploid (1n), only contain half the genetic material of ...
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Materials
... K. Flagella are long whip like tails of microtubules bundles used for movement (usually 1-3 in number) 1. Help sperm cells swim to egg L. Nucleus (nuclei) in the middle of the cell contains DNA (hereditary material of the cell) & acts as the control center 1. Most cells have 1 nucleolus, but some ha ...
... K. Flagella are long whip like tails of microtubules bundles used for movement (usually 1-3 in number) 1. Help sperm cells swim to egg L. Nucleus (nuclei) in the middle of the cell contains DNA (hereditary material of the cell) & acts as the control center 1. Most cells have 1 nucleolus, but some ha ...
Biology Study Guide - Jackson School District
... 4. What two taxa (names) are used in binomial nomenclature to make up an organism’s scientific name? 5. List the 7 taxa (categories) in order from most diverse to the least diverse. ...
... 4. What two taxa (names) are used in binomial nomenclature to make up an organism’s scientific name? 5. List the 7 taxa (categories) in order from most diverse to the least diverse. ...
Unit 2
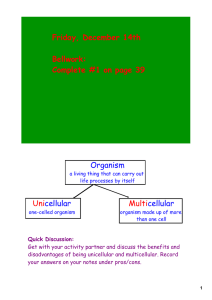
... environment, grow, etc.). Unicellular/Single-celled organisms consist of a single cell and perform all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell and have differentiated cells that perform specialized functions in the organism. ...
... environment, grow, etc.). Unicellular/Single-celled organisms consist of a single cell and perform all life processes within a single cell. Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell and have differentiated cells that perform specialized functions in the organism. ...
Cell Structure - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dominant allele and the symbol a for the recessive allele. ...
... Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dominant allele and the symbol a for the recessive allele. ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... All living things, such as those in Figure 1, are composed of one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small t ...
... All living things, such as those in Figure 1, are composed of one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small t ...
Topic 1 – Measurement and graphing
... Consumer – any organism that eats other organisms to obtain energy Herbivore – an organism that only eats plants, a primary consumer Carnivore – an animal that eats other animals, a secondary consumer Omnivore – an animal that eats both plants and animals Decomposer – bacteria and other or ...
... Consumer – any organism that eats other organisms to obtain energy Herbivore – an organism that only eats plants, a primary consumer Carnivore – an animal that eats other animals, a secondary consumer Omnivore – an animal that eats both plants and animals Decomposer – bacteria and other or ...
Pregnancy and Development
... • Next 5 weeks embryo grows rapidly 1000xs the original egg and differentiate into 3 layers of cells: • 1. ectoderm: will turn into brain, spine, and nerves and hair, skin, nails • 2. mesoderm: will turn into bones, muscles, blood vessels, heart, and kidneys • 3. endoderm: digestive system organs an ...
... • Next 5 weeks embryo grows rapidly 1000xs the original egg and differentiate into 3 layers of cells: • 1. ectoderm: will turn into brain, spine, and nerves and hair, skin, nails • 2. mesoderm: will turn into bones, muscles, blood vessels, heart, and kidneys • 3. endoderm: digestive system organs an ...
What are Stem Cells?
... Aborted fetuses are not the only source of stem cells There are stem cells in the both placenta and blood contained in the placenta. Also the primary source of stem cells is from blastocysts. These are fertilized human eggs that were not implanted into a woman. The controversy surrounding stem cell ...
... Aborted fetuses are not the only source of stem cells There are stem cells in the both placenta and blood contained in the placenta. Also the primary source of stem cells is from blastocysts. These are fertilized human eggs that were not implanted into a woman. The controversy surrounding stem cell ...
document
... Each insect species undergoes either complete metamorphosis or gradual metamorphosis: Complete metamorphosis - insect goes through four different stages: egg, larva, pupa and adult Incomplete gradual metamorphosis – has no district larval stage – eggs hatch into nymph, or miniature adults without wi ...
... Each insect species undergoes either complete metamorphosis or gradual metamorphosis: Complete metamorphosis - insect goes through four different stages: egg, larva, pupa and adult Incomplete gradual metamorphosis – has no district larval stage – eggs hatch into nymph, or miniature adults without wi ...
31.2 Immune System
... – Antibodies: Protein that causes pathogens to clump or become ineffective. – Interferon: Proteins that stop viruses from reproducing. antibody ...
... – Antibodies: Protein that causes pathogens to clump or become ineffective. – Interferon: Proteins that stop viruses from reproducing. antibody ...
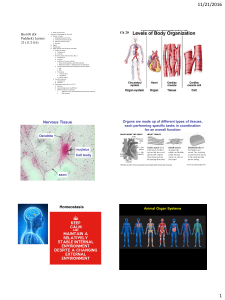
Three Major Organs: Brain Spinal Cord Nerves Organization: I) The
... I) Two cell types form nerve tissue: A) The Neuron 1) transmits electrical signals called impulses 2) live a long time---a lifetime 3) amitotic (cannot divide) 4) high metabolic rate; need more glucose and oxygen than other cells 5) live only for a few minutes without oxygen 6) At rest the brain (3. ...
... I) Two cell types form nerve tissue: A) The Neuron 1) transmits electrical signals called impulses 2) live a long time---a lifetime 3) amitotic (cannot divide) 4) high metabolic rate; need more glucose and oxygen than other cells 5) live only for a few minutes without oxygen 6) At rest the brain (3. ...
N5- Unit 1 MO4- Reproduction, variation, inheritance Sexual
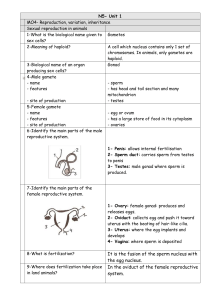
... 8-What is fertilization? 9-Where does fertilization take place in land animals? ...
... 8-What is fertilization? 9-Where does fertilization take place in land animals? ...
Living things
... reproduce, eat, and use energy. Living things include humans, animals, plants, fungi and small organisms known as bacteria. Living things are highly organized. All living things are made of cells. The cell is considered the fundamental unit of life. A primary difference between plant cells and anima ...
... reproduce, eat, and use energy. Living things include humans, animals, plants, fungi and small organisms known as bacteria. Living things are highly organized. All living things are made of cells. The cell is considered the fundamental unit of life. A primary difference between plant cells and anima ...
Chapter 1
... -They are single celled organisms that have ribosomes, a cell membrane, and DNA. -They have no nucleus and no membrane bound organelles. 2. Eukaryotic are the largest cells, but are still microscopic. They are about 10 times larger than most bacteria cells. -They have a nucleus. -They also have memb ...
... -They are single celled organisms that have ribosomes, a cell membrane, and DNA. -They have no nucleus and no membrane bound organelles. 2. Eukaryotic are the largest cells, but are still microscopic. They are about 10 times larger than most bacteria cells. -They have a nucleus. -They also have memb ...
The Wonder of Flowering Plants KEY 9 Reading
... 5. What parts make up this structure and what do they do? Stigma-collects pollen style-supports stigma ovary-holds ovules 6. What is the difference between a “perfect” and an “imperfect” flower? Perfect-female and male parts Imperfect-female or male part 7. What is pollination? When the pollen from ...
... 5. What parts make up this structure and what do they do? Stigma-collects pollen style-supports stigma ovary-holds ovules 6. What is the difference between a “perfect” and an “imperfect” flower? Perfect-female and male parts Imperfect-female or male part 7. What is pollination? When the pollen from ...
Protostome Animals
... the idea natural selection by adaptation to a new level by rapid levels of speciation ...
... the idea natural selection by adaptation to a new level by rapid levels of speciation ...
1 PRE-TEST
... Cell membrane – the outer semipermeable covering of the cell; it is very thin and flexible Cellular respiration – the process that converts the potential energy of food into other useful forms; its most important product is ATP Concentration gradient – a difference in concentration of a particle at ...
... Cell membrane – the outer semipermeable covering of the cell; it is very thin and flexible Cellular respiration – the process that converts the potential energy of food into other useful forms; its most important product is ATP Concentration gradient – a difference in concentration of a particle at ...
CHAPTER 8 • REVIEW Chapter Review
... together; The heart is an organ. 2. several organs working together; The respiratory system is an organ system. 3. long period of reduced activity; Bears enter hibernation when food is scarce. 4. openings in dermal tissues of leaves; Stomata regulate exchange with the environment. 5. transports mate ...
... together; The heart is an organ. 2. several organs working together; The respiratory system is an organ system. 3. long period of reduced activity; Bears enter hibernation when food is scarce. 4. openings in dermal tissues of leaves; Stomata regulate exchange with the environment. 5. transports mate ...
FOURTH GRADE ORGANISMS
... organism than just cells. Cells are the building blocks that are used to create larger groups of cells which perform more specific tasks. The second level of organization is the tissue. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific job. Remember that there are special ...
... organism than just cells. Cells are the building blocks that are used to create larger groups of cells which perform more specific tasks. The second level of organization is the tissue. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific job. Remember that there are special ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are