Ch 37 – Introduction to Body Structure
... In early development the skeleton is mostly cartilage, a type of connective tissue that serves as a template for bone formation. ...
... In early development the skeleton is mostly cartilage, a type of connective tissue that serves as a template for bone formation. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells
... blood and body cells – O2 from the blood into the body cells – CO2 from the body cells into the blood ...
... blood and body cells – O2 from the blood into the body cells – CO2 from the body cells into the blood ...
Cells and Tissues
... cells are shorter than others – Often looks like a double cell layer – Sometimes ciliated, such as in the respiratory tract – May function in absorption or secretion ...
... cells are shorter than others – Often looks like a double cell layer – Sometimes ciliated, such as in the respiratory tract – May function in absorption or secretion ...
Pathogen
... Active immunity results from the body producing antibodies and memory cells. Passive immunity results from the individual receiving antibodies. ...
... Active immunity results from the body producing antibodies and memory cells. Passive immunity results from the individual receiving antibodies. ...
glossary - Skinners` School Physics
... taking substances (e.g. food, drink) into the body through the mouth the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation substances that do not derive from living things hormone that helps reduce a high blood glucose level muscles between the ribs coloured part of the eye that chan ...
... taking substances (e.g. food, drink) into the body through the mouth the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation substances that do not derive from living things hormone that helps reduce a high blood glucose level muscles between the ribs coloured part of the eye that chan ...
Module 1 themes of life review
... d. Blood type O is a universal donor; type AB is the universal acceptor. e. A vaccine is an injection of a dead or weakened pathogen. This causes the body to make antibodies against that pathogen. ...
... d. Blood type O is a universal donor; type AB is the universal acceptor. e. A vaccine is an injection of a dead or weakened pathogen. This causes the body to make antibodies against that pathogen. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Practice Test
... a. to mediate communication among different parts of the body and interactions with the with the environment b. to provide exchange of nutrients and wastes c. convert macromolecules into smaller molecules 2. Label the parts of a neuron: ...
... a. to mediate communication among different parts of the body and interactions with the with the environment b. to provide exchange of nutrients and wastes c. convert macromolecules into smaller molecules 2. Label the parts of a neuron: ...
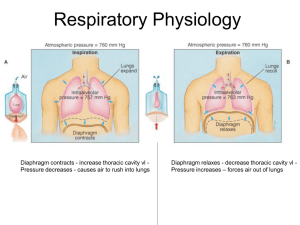
Respiratory Physiology
... Chronic exposure to irritants causes the number of layers to increase. The ciliated and mucus-secreting cells disappear and are replaced by a disorganized mass of cells with abnormal nuclei. If the process continues, the growing mass penetrates the underlying basement membrane. Malignant cells can b ...
... Chronic exposure to irritants causes the number of layers to increase. The ciliated and mucus-secreting cells disappear and are replaced by a disorganized mass of cells with abnormal nuclei. If the process continues, the growing mass penetrates the underlying basement membrane. Malignant cells can b ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Organ
... To support healthy organs and body systems, we all have the same basic needs. •Clean air and water •A nutritious and well-balanced diet •Exercise •Restful sleep ...
... To support healthy organs and body systems, we all have the same basic needs. •Clean air and water •A nutritious and well-balanced diet •Exercise •Restful sleep ...
Worms - edl.io
... Have tissues and internal organ systems Known as “acoelomates” – means without coelom Coelom – fluid filled body cavity Contain “flukes” which are parasitic and tapeworms ...
... Have tissues and internal organ systems Known as “acoelomates” – means without coelom Coelom – fluid filled body cavity Contain “flukes” which are parasitic and tapeworms ...
ch 40: an introduction to animal structure and function
... adjust to environmental temperature changes. They also have low metabolic rates so the heat they generate would be too like to regulate their body temperature 2. Endotherms use metabolic heat generated by chemical reactions within their bodies to regulate their body temperatures. This is a very ener ...
... adjust to environmental temperature changes. They also have low metabolic rates so the heat they generate would be too like to regulate their body temperature 2. Endotherms use metabolic heat generated by chemical reactions within their bodies to regulate their body temperatures. This is a very ener ...
Human Body Systems
... direction. The flaps create a “lub-dup” sound. • A heart attack is caused by a blood vessel blocked by a clot. • The average person has about 5 liters of blood. • The body can replace blood within a few weeks after loss. • Platelets in the blood help it to clot, or stick together, to make scabs. • T ...
... direction. The flaps create a “lub-dup” sound. • A heart attack is caused by a blood vessel blocked by a clot. • The average person has about 5 liters of blood. • The body can replace blood within a few weeks after loss. • Platelets in the blood help it to clot, or stick together, to make scabs. • T ...
Human Body Systems
... direction. The flaps create a “lub-dup” sound. • A heart attack is caused by a blood vessel blocked by a clot. • The average person has about 5 liters of blood. • The body can replace blood within a few weeks after loss. • Platelets in the blood help it to clot, or stick together, to make scabs. • T ...
... direction. The flaps create a “lub-dup” sound. • A heart attack is caused by a blood vessel blocked by a clot. • The average person has about 5 liters of blood. • The body can replace blood within a few weeks after loss. • Platelets in the blood help it to clot, or stick together, to make scabs. • T ...
The Respiratory System
... oxygen in the lungs and carrying the oxygen to all the body cells that need it. The red blood cells drop off the oxygen to the body ...
... oxygen in the lungs and carrying the oxygen to all the body cells that need it. The red blood cells drop off the oxygen to the body ...
Chapter 45
... 1. Muscle 2. Nervous 3. Epithelial 4. Connective Muscle Tissue *Can contract and relax. a) Skeletal muscle- voluntary, usually moves bones b) Smooth muscle- involuntary, breathing, digestion …. c) Cardiac muscle – involuntary, in the heart Nervous Tissue *Cells that receive and send messages by elec ...
... 1. Muscle 2. Nervous 3. Epithelial 4. Connective Muscle Tissue *Can contract and relax. a) Skeletal muscle- voluntary, usually moves bones b) Smooth muscle- involuntary, breathing, digestion …. c) Cardiac muscle – involuntary, in the heart Nervous Tissue *Cells that receive and send messages by elec ...
Human Body Systems - Hamilton Township High School
... This section describes human organ systems and explains how the body maintains homeostasis. ...
... This section describes human organ systems and explains how the body maintains homeostasis. ...
Human Body Systems
... This section describes human organ systems and explains how the body maintains homeostasis. ...
... This section describes human organ systems and explains how the body maintains homeostasis. ...
Digestive and Respiratory System
... Organ System - group of organs working together Organ - Tissue form organs Tissue - cells with similar structure and function form tissue Cells – Basic unit of life ...
... Organ System - group of organs working together Organ - Tissue form organs Tissue - cells with similar structure and function form tissue Cells – Basic unit of life ...
agustiniano ciudad salitre school science area circulation in living
... Like other living things, plants perform vital functions that allow them to grow, develop and reproduce. Circulation is also a vital process for plants. In the inferior plants (bryophytes), circulation takes place by ____________________ and ____________________. The superior plants (tracheophytes) ...
... Like other living things, plants perform vital functions that allow them to grow, develop and reproduce. Circulation is also a vital process for plants. In the inferior plants (bryophytes), circulation takes place by ____________________ and ____________________. The superior plants (tracheophytes) ...
Phylum/
... Internal fertilization Monotremes: egg laying mammals like the duck billed platypus and the spiny anteater Marsupials: pouched mammals like the opossum and ...
... Internal fertilization Monotremes: egg laying mammals like the duck billed platypus and the spiny anteater Marsupials: pouched mammals like the opossum and ...
File
... • Blood vessels are divided into 3 categories: o Arteries • Carry blood away from the heart o Veins • Carry blood to the heart (viens) o Capillaries • The smallest blood vessels • Have very thin walls that allow for gas exchange between blood and cells of the body ...
... • Blood vessels are divided into 3 categories: o Arteries • Carry blood away from the heart o Veins • Carry blood to the heart (viens) o Capillaries • The smallest blood vessels • Have very thin walls that allow for gas exchange between blood and cells of the body ...
Cell cycle
... Location and general function of kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra, urinary sphincter muscle. Role of the excretory system (its importance) Structure and function (simple function only) of the nephron: recognize glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, tubules(proximal convoluted tubule in particular), lo ...
... Location and general function of kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra, urinary sphincter muscle. Role of the excretory system (its importance) Structure and function (simple function only) of the nephron: recognize glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, tubules(proximal convoluted tubule in particular), lo ...