* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
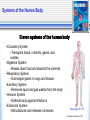
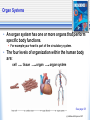
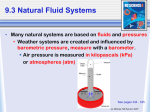
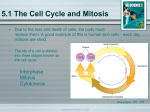
2.1 Body Systems • A system is made of parts that work together as a whole. • The Characteristics of Systems 1. A system is made of individual parts that work together as a whole. 2. A system is usually connected to one or more systems. 3. If one part of a system is missing or damaged, the system will not function well or may not function at all. A stereo system has many parts that work together. See pages 54 - 55 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Systems of the Human Body Eleven systems of the human body •Circulatory System •Transports blood, nutrients, gases, and wastes •Digestive System •Breaks down food and absorbs the nutrients •Respiratory System •Exchanges gases in lungs and tissues •Excretory System •Removes liquid and gas wastes from the body •Immune System •Defends body against infections •Endocrine System •Manufactures and releases hormones See pages 56 - 57 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Systems of the Human Body More Systems… •Reproductive System •Includes reproductive organs for producing offspring •Integumentary System •Creates a waterproof barrier around the body •Skeletal System •Supports, protects, and works with muscles to move parts of the body •Muscular System •Has muscles that work with the bones to move parts of the body •Nervous System •Detects changes in the environment and signals the body to carry out a response See pages 56 - 57 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Organ Systems • An organ system has one or more organs that perform specific body functions. For example your heart is part of the circulatory system. • The four levels of organization within the human body are: cell tissue organ organ system See page 58 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007 Tissues: The Foundation of Body Systems • Tissue is a group of cells that have the same structure and function. • Four types of body tissue: Muscle tissue Assists in body movement Nerve tissue Transfers signals to and from brain Connective tissue Holds together and supports other tissue Epithelial tissue Covers the surface of organs and body See pages 58 -59 (c) McGraw Hill Ryerson 2007