BIOLOGY REVISION Levels of Organisation: LEVEL 1 – Cells Are
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
Human Development
... One of the best ways to understand the structure of the adult human body is to understand how it developed. ...
... One of the best ways to understand the structure of the adult human body is to understand how it developed. ...
Section 8 - DigitalWebb.com
... 5. Oxygenated blood back to heart into left atrium, left ventricle (repeat #1). Arteries away from heart Veins back to heart Blood pressure: hydrostatic force that blood exerts against a vessel wall Capillary exchange: exchange of materials between blood through capillary walls and interstitial flui ...
... 5. Oxygenated blood back to heart into left atrium, left ventricle (repeat #1). Arteries away from heart Veins back to heart Blood pressure: hydrostatic force that blood exerts against a vessel wall Capillary exchange: exchange of materials between blood through capillary walls and interstitial flui ...
Introduction to the Bodies Cavities
... Pseudostratified= looks like a few layers, but actually only one. ...
... Pseudostratified= looks like a few layers, but actually only one. ...
23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants
... phloem cells that surround sieve tube elements. Companion cell Companion cells support the phloem Sieve tube element cells and aid in the movement of substances in and out of the phloem. Slide 16 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... phloem cells that surround sieve tube elements. Companion cell Companion cells support the phloem Sieve tube element cells and aid in the movement of substances in and out of the phloem. Slide 16 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
1-Functional Organization of the Human Body
... Organs: are made up of one or more types of tissues (usually more). e.g. the heart, skin (is also an example of an organ. It is the largest organ, and has several tissue layers). ...
... Organs: are made up of one or more types of tissues (usually more). e.g. the heart, skin (is also an example of an organ. It is the largest organ, and has several tissue layers). ...
Chapter 2: From a Cell to an Organism
... Telophase The final phase of mitosis is telophase. During telophase, a new membrane forms around each set of chromosomes. The chromosomes also become less tightly coiled. These two events are nearly the reverse of what happens in prophase. At the end of telophase, there are two new nuclei that are i ...
... Telophase The final phase of mitosis is telophase. During telophase, a new membrane forms around each set of chromosomes. The chromosomes also become less tightly coiled. These two events are nearly the reverse of what happens in prophase. At the end of telophase, there are two new nuclei that are i ...
CSEC Biology Revision Guide Answers.indd
... membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria found in other cells. Instead of a true nucleus, their DNA would be seen in a region called the nucleoid which would lack a nuclear membrane, and also in smaller regions called plasmids throughout their cytoplasm. ...
... membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria found in other cells. Instead of a true nucleus, their DNA would be seen in a region called the nucleoid which would lack a nuclear membrane, and also in smaller regions called plasmids throughout their cytoplasm. ...
Internal transport
... as fossils. • All animals probably evolved from Protists. • The classification of animals is based on the level of organization or number of germ layers, symmetry, type of coelom, body plan, and presence or absence of segmentation. • The following evolutionary tree is based on these features and sho ...
... as fossils. • All animals probably evolved from Protists. • The classification of animals is based on the level of organization or number of germ layers, symmetry, type of coelom, body plan, and presence or absence of segmentation. • The following evolutionary tree is based on these features and sho ...
B3_Revision_notes
... The study of microorganisms is called microbiology. Scientists such as Spallanzani (1768), Schwann (1837) and Pasteur (1878) made important developments in the field of biogenesis: Spallanzani found that boiling microbes killed them Schwann observed yeast and the fermentation process Pasteur invente ...
... The study of microorganisms is called microbiology. Scientists such as Spallanzani (1768), Schwann (1837) and Pasteur (1878) made important developments in the field of biogenesis: Spallanzani found that boiling microbes killed them Schwann observed yeast and the fermentation process Pasteur invente ...
Chapter 3 Notes - the NBTSC Community Site!
... -the fluid inside cells (intracellular fluid) provides a medium in which all cell reactions take place. Its pressure also helps the cells hold their shape. Intracellular fluid is drawn from the extracellular fluid. -blood circulates to the lungs where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide w ...
... -the fluid inside cells (intracellular fluid) provides a medium in which all cell reactions take place. Its pressure also helps the cells hold their shape. Intracellular fluid is drawn from the extracellular fluid. -blood circulates to the lungs where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide w ...
membrane potential
... Average number of neurons in the human brain= 100 billion Average number of neurons in an octopus brain= 300 billion Velocity of a signal transmitted through a neuron= 1.2 to 250 mi./hr. After age 30, the brain begins to lose about 50,000 neurons per day shrinking the brain ¼ % each year. The brain ...
... Average number of neurons in the human brain= 100 billion Average number of neurons in an octopus brain= 300 billion Velocity of a signal transmitted through a neuron= 1.2 to 250 mi./hr. After age 30, the brain begins to lose about 50,000 neurons per day shrinking the brain ¼ % each year. The brain ...
Chapter 5: Tissues
... 2. Elastic connective tissue is located in the attachments between vertebrae of the spinal column, in the layers within the walls of certain hollow internal organs, including the larger arteries, some portions of the heart and larger airways. J. Cartilage 1. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue. ...
... 2. Elastic connective tissue is located in the attachments between vertebrae of the spinal column, in the layers within the walls of certain hollow internal organs, including the larger arteries, some portions of the heart and larger airways. J. Cartilage 1. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue. ...
Biology YLP 1415 - Revere Public Schools
... Reinforce graphing skills including interpreting graphs ...
... Reinforce graphing skills including interpreting graphs ...
Biodiversity
... 4. Conjugation: process in which some paramecia and some prokaryotes exchange genetic information. 5. Flagellum: structure used by protists for movement; produces movement in a wavelike motion. 6. Food vacuole: small cavity in the cytoplasm of a protist that temporarily stores food. 7. Gullet: inde ...
... 4. Conjugation: process in which some paramecia and some prokaryotes exchange genetic information. 5. Flagellum: structure used by protists for movement; produces movement in a wavelike motion. 6. Food vacuole: small cavity in the cytoplasm of a protist that temporarily stores food. 7. Gullet: inde ...
Cause. - Cleveland Clinic
... Fortunately, our immune systems are often able to correct their mistakes---though it is apparently harder to self-correct some mistakes than others, and children appear to have better capacity for self-correction than do adults. For example, the immune systems of children usually are eventually able ...
... Fortunately, our immune systems are often able to correct their mistakes---though it is apparently harder to self-correct some mistakes than others, and children appear to have better capacity for self-correction than do adults. For example, the immune systems of children usually are eventually able ...
File - Science with Mr. Davis
... 1. Put a microscope slide on a paper towel. 2. Put 1 drop of iodine-water solution on your slide. 3. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek two or three times with a toothpick. It will look like nothing is on the toothpick, but there will probably be plenty of cells to see with the microscope. 4. St ...
... 1. Put a microscope slide on a paper towel. 2. Put 1 drop of iodine-water solution on your slide. 3. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek two or three times with a toothpick. It will look like nothing is on the toothpick, but there will probably be plenty of cells to see with the microscope. 4. St ...
ECF
... that are responsible for the origin, development, and progression of life. In human physiology, we attempt to explain the specific characteristics and mechanisms of the human body that make it a living being. The basic living unit of the body is the cell. Each organ is an aggregate of many different ...
... that are responsible for the origin, development, and progression of life. In human physiology, we attempt to explain the specific characteristics and mechanisms of the human body that make it a living being. The basic living unit of the body is the cell. Each organ is an aggregate of many different ...
CHapter 1 SpED
... • Broken into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity…..the Diaphragm (domed shaped muscle) separates the two • Thoracic: separated into a Left and Right pleural cavity (has one of each lung) and a Medial cavity called the Pericardial (has the heart, trachea, esophagus) • Abdominopelvic: s ...
... • Broken into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity…..the Diaphragm (domed shaped muscle) separates the two • Thoracic: separated into a Left and Right pleural cavity (has one of each lung) and a Medial cavity called the Pericardial (has the heart, trachea, esophagus) • Abdominopelvic: s ...
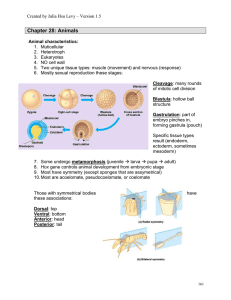
Introduction to Animals
... • Animals with a one-way digestive system have a mouth and an anus • Food enters the mouth, continues in one direction through the digestive tract, and wastes leave through the anus • Includes annelids, arthropods, & ...
... • Animals with a one-way digestive system have a mouth and an anus • Food enters the mouth, continues in one direction through the digestive tract, and wastes leave through the anus • Includes annelids, arthropods, & ...
content.njctl.org
... 28. The alimentary canal is a tube through which food moves to be ingested, digested, absorbed, and eliminated. 29. A circulatory system provides an efficient transport system to deliver nutrients and oxygen to all tissues and remove waste products. Diffusion alone will not allow materials to enter ...
... 28. The alimentary canal is a tube through which food moves to be ingested, digested, absorbed, and eliminated. 29. A circulatory system provides an efficient transport system to deliver nutrients and oxygen to all tissues and remove waste products. Diffusion alone will not allow materials to enter ...
Integumentary System ppt
... • No, it’s the bacteria • How much bacteria is on your body? • 1,000 different species AND 1,000,000,000,000 individual bacteria ...
... • No, it’s the bacteria • How much bacteria is on your body? • 1,000 different species AND 1,000,000,000,000 individual bacteria ...
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine glands: respond to signals from the environment, other cells • Signals vary… • Environmental (gases, gravity, nutrients, sunlight, temp) • Cellular (hormones) originate inside the body ...
... • Endocrine glands: respond to signals from the environment, other cells • Signals vary… • Environmental (gases, gravity, nutrients, sunlight, temp) • Cellular (hormones) originate inside the body ...
UNIT 1 – FORCE AND MOTION (SEPUP Force
... Performance Indicator 1. Compare and contrast the parts of plants, animals, and one-celled organisms. Major Understandings: LE 1.1a Living things are composed of cells. Cells provide structure and carry on major functions to sustain life. Cells are usually microscopic in size. LE 1.1b The way in whi ...
... Performance Indicator 1. Compare and contrast the parts of plants, animals, and one-celled organisms. Major Understandings: LE 1.1a Living things are composed of cells. Cells provide structure and carry on major functions to sustain life. Cells are usually microscopic in size. LE 1.1b The way in whi ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.