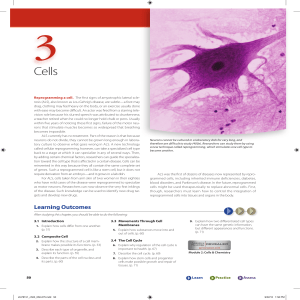
cell – structure and function
... 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be made of small compartments which he called “cells” (Latin cell = small room). In 1672, Leeuwenhoek observed bacteria, sperms and red blood corpuscles, all of which were Notes cells. Much later, in 1831, Robert Brown, an Englishman ...
... 1665 observed a piece of cork under the microscope and found it to be made of small compartments which he called “cells” (Latin cell = small room). In 1672, Leeuwenhoek observed bacteria, sperms and red blood corpuscles, all of which were Notes cells. Much later, in 1831, Robert Brown, an Englishman ...
Final RG
... 1) List the major components of blood. Briefly describe their function and differentiate between the cellular components and the liquid components. ...
... 1) List the major components of blood. Briefly describe their function and differentiate between the cellular components and the liquid components. ...
Ch. 3 - SBCC Biological Sciences Department
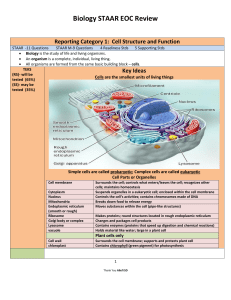
... the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope, and other organelles. The ER provides a vast tubular network that transports molecules from one cell part to another. It winds from the nucleus out toward the cell membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum participates in the synthesis of protein and lipid molecule ...
... the cell membrane, the nuclear envelope, and other organelles. The ER provides a vast tubular network that transports molecules from one cell part to another. It winds from the nucleus out toward the cell membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum participates in the synthesis of protein and lipid molecule ...
Bone and Muscle Previous Exam Review
... Training produces a number of changes within your body that help to improve your endurance and performance. Respiratory/chest muscles become stronger which helps the lungs draw in more oxygen for ATP production. Training encourages the formation of new capillaries/blood vessels to the muscles. This ...
... Training produces a number of changes within your body that help to improve your endurance and performance. Respiratory/chest muscles become stronger which helps the lungs draw in more oxygen for ATP production. Training encourages the formation of new capillaries/blood vessels to the muscles. This ...
Objectives
... A tissue is composed of groups of cells that are similar in structure, and function together to carry out one or more common or related activities. Body tissues are classified into four basic categories: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. The tissues of the body ...
... A tissue is composed of groups of cells that are similar in structure, and function together to carry out one or more common or related activities. Body tissues are classified into four basic categories: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. The tissues of the body ...
Objectives
... A tissue is composed of groups of cells that are similar in structure, and function together to carry out one or more common or related activities. Body tissues are classified into four basic categories: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. The tissues of the body ...
... A tissue is composed of groups of cells that are similar in structure, and function together to carry out one or more common or related activities. Body tissues are classified into four basic categories: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. The tissues of the body ...
Cloning and Stem Cells
... Scientists believe that stem cells may, at some point in the future, become the basis for treatment of diseases caused by irreversibly damaged and injured tissue, such as occurs in diabetes, heart disease and Parkinson’s disease. They are particularly optimistic in cases where the disease is caused ...
... Scientists believe that stem cells may, at some point in the future, become the basis for treatment of diseases caused by irreversibly damaged and injured tissue, such as occurs in diabetes, heart disease and Parkinson’s disease. They are particularly optimistic in cases where the disease is caused ...
Virus & Bacteria PPt Notes
... • They vary in size and structure. • They enter living cells & use the machinery of the infected cell to produce more viruses. • Composed of: – A core DNA or RNA (which has the instructions for making copies) – This is surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid which binds the virus to the surface ...
... • They vary in size and structure. • They enter living cells & use the machinery of the infected cell to produce more viruses. • Composed of: – A core DNA or RNA (which has the instructions for making copies) – This is surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid which binds the virus to the surface ...
K CHAPTER 2: BODY TISSUES AND MEMBRANES At the end of
... epithelium by diffusing from blood vessels with many layers of cells, the most metabolically active cells are close to the basement membrane, 6. Epithelial cells retain the ability to undergo mitosis and therefore are able to replace damaged cells with new epithelial cells. Undifferentiated cells (s ...
... epithelium by diffusing from blood vessels with many layers of cells, the most metabolically active cells are close to the basement membrane, 6. Epithelial cells retain the ability to undergo mitosis and therefore are able to replace damaged cells with new epithelial cells. Undifferentiated cells (s ...
Human Systems
... • Lymph nodes contain filtering tissue and a large number of lymph cells. When fighting certain bacterial infections, the lymph nodes swell with bacteria and the cells fighting the bacteria, to the point where you can actually feel them. Swollen lymph nodes may therefore be a good indication that yo ...
... • Lymph nodes contain filtering tissue and a large number of lymph cells. When fighting certain bacterial infections, the lymph nodes swell with bacteria and the cells fighting the bacteria, to the point where you can actually feel them. Swollen lymph nodes may therefore be a good indication that yo ...
File
... Animal PHYLA What are the two things that you can “tell” when reading a Cladogram? 1. .Evolutionary relationships ...
... Animal PHYLA What are the two things that you can “tell” when reading a Cladogram? 1. .Evolutionary relationships ...
Major Organs
... includes the lymphoid tissue through which the lymph travels. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated with the digestive system such as the tonsils. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and pr ...
... includes the lymphoid tissue through which the lymph travels. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated with the digestive system such as the tonsils. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and pr ...
Function of Blood - Catherine Huff`s Site
... They are broken down into the pigments bilinubin, biliviridin and iron. These components are then transported to the liver where the iron is recycled for use by new erythrocytes. The blood pigments for bile salts. Anisocytosis: variation in size A slight variation in size is considered normal. Aniso ...
... They are broken down into the pigments bilinubin, biliviridin and iron. These components are then transported to the liver where the iron is recycled for use by new erythrocytes. The blood pigments for bile salts. Anisocytosis: variation in size A slight variation in size is considered normal. Aniso ...
detailed lecture outline
... o Implantation begins with the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrium of the uterus and continues as the blastocyst invades maternal tissues. Important events during implantation set the stage for the formation of vital embryonic structures. o Placentation occurs as blood vessels form aroun ...
... o Implantation begins with the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrium of the uterus and continues as the blastocyst invades maternal tissues. Important events during implantation set the stage for the formation of vital embryonic structures. o Placentation occurs as blood vessels form aroun ...
standards - Henry County Schools
... Evaluate properties of H2O in a lab setting with an emphasis on living systems. Synthesizing & breaking down organic macromolecules. Modeling macromolecule functions & relating them to biological systems. Demonstrate enzyme activity in a lab setting. ...
... Evaluate properties of H2O in a lab setting with an emphasis on living systems. Synthesizing & breaking down organic macromolecules. Modeling macromolecule functions & relating them to biological systems. Demonstrate enzyme activity in a lab setting. ...
Renal Physiology - part 2
... 9). These looped blood vessels are called the ‘vasa recta’ and are necessary in order to supply blood to the renal medulla and still maintain the osmotic gradients established in the medulla by the loop of Henle. If blood was supplied to the medulla and loop of Henle by a simple straight capillary, ...
... 9). These looped blood vessels are called the ‘vasa recta’ and are necessary in order to supply blood to the renal medulla and still maintain the osmotic gradients established in the medulla by the loop of Henle. If blood was supplied to the medulla and loop of Henle by a simple straight capillary, ...
Human Body Systems Review
... correct path that water takes from your mouth to the toilet. At some point the water is carried by blood – make sure you include the organ where the water leaves and how the water gets to the next organ. ...
... correct path that water takes from your mouth to the toilet. At some point the water is carried by blood – make sure you include the organ where the water leaves and how the water gets to the next organ. ...
USABO Semifinal exam 2006 Answer Key
... (inorganic phosphates). What is the maximum amount of ethanol that can be produced in these conditions? Cell Biology – Structure/Function of Cells Metabolism (Methods). Contributor Unknown. A: 2 mM B. 20 mM C. 40 mM D. 200 mM E. 400 mM 6. The concentration of ions inside an amoeba is expressed below ...
... (inorganic phosphates). What is the maximum amount of ethanol that can be produced in these conditions? Cell Biology – Structure/Function of Cells Metabolism (Methods). Contributor Unknown. A: 2 mM B. 20 mM C. 40 mM D. 200 mM E. 400 mM 6. The concentration of ions inside an amoeba is expressed below ...
Study Material - Class- XI - Biology
... 7-Systematics: Branch of biology dealing with taxonomy along with evolutionary relationship between organisms. 8-Species :Group of Individual organisms with fundamental similarities (with capacity of interbreeding). LEARNING TIPS: 1-Concentrate on minute points of the chapter keeping very short answ ...
... 7-Systematics: Branch of biology dealing with taxonomy along with evolutionary relationship between organisms. 8-Species :Group of Individual organisms with fundamental similarities (with capacity of interbreeding). LEARNING TIPS: 1-Concentrate on minute points of the chapter keeping very short answ ...
Study Material - Class- XI- Biology
... 7-Systematics: Branch of biology dealing with taxonomy along with evolutionary relationship between organisms. 8-Species :Group of Individual organisms with fundamental similarities (with capacity of interbreeding). LEARNING TIPS: 1-Concentrate on minute points of the chapter keeping very short answ ...
... 7-Systematics: Branch of biology dealing with taxonomy along with evolutionary relationship between organisms. 8-Species :Group of Individual organisms with fundamental similarities (with capacity of interbreeding). LEARNING TIPS: 1-Concentrate on minute points of the chapter keeping very short answ ...
Chapter 3 PDF
... groundwork for all biological research that followed. However, it had to be refined over the years as additional data led to new conclusions. For example, Schwann stated in his publication that cells form spontaneously by free-cell formation. As later scientists studied the process of cell division, ...
... groundwork for all biological research that followed. However, it had to be refined over the years as additional data led to new conclusions. For example, Schwann stated in his publication that cells form spontaneously by free-cell formation. As later scientists studied the process of cell division, ...
Chapter 3 PDF
... groundwork for all biological research that followed. However, it had to be refined over the years as additional data led to new conclusions. For example, Schwann stated in his publication that cells form spontaneously by free-cell formation. As later scientists studied the process of cell division, ...
... groundwork for all biological research that followed. However, it had to be refined over the years as additional data led to new conclusions. For example, Schwann stated in his publication that cells form spontaneously by free-cell formation. As later scientists studied the process of cell division, ...
Chapter 9 Review Key
... sensory data from the external environment and transmits signals throughout the body. Endocrine system: regulates hormone levels. Circulatory system: carries hormones and other chemicals needed for homeostasis throughout the body. Immune system: protects the body from, and fights, infections. Digest ...
... sensory data from the external environment and transmits signals throughout the body. Endocrine system: regulates hormone levels. Circulatory system: carries hormones and other chemicals needed for homeostasis throughout the body. Immune system: protects the body from, and fights, infections. Digest ...
FIRST QUARTER TOPICS
... Cells have specific structures and functions that make them distinctive. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, and reproduction Why are cells considered the basic unit of structure of life? How does life at the cellular level affect life at levels further up in the hi ...
... Cells have specific structures and functions that make them distinctive. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, and reproduction Why are cells considered the basic unit of structure of life? How does life at the cellular level affect life at levels further up in the hi ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.