* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
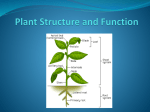
Biology Slide 1 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Slide 2 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Seed Plant Structure What are the three principal organs and tissues of seed plants? Slide 3 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure The three principal organs of seed plants are roots, stems, and leaves. These organs perform functions such as the transport of nutrients, protection, and coordination of plant activities. Slide 4 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Roots: • absorb water and dissolved nutrients. • anchor plants in the ground. • protect the plant from harmful soil bacteria and fungi. Slide 5 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Stems provide: • a support system for the plant body. • a transport system that carries nutrients. • a defense system that protects the plant against predators and disease. Slide 6 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Seed Plant Structure Leaves: • are a plant’s main photosynthetic systems. • increase the amount of sunlight plants absorb. Adjustable pores conserve water and let oxygen and carbon dioxide enter and exit the leaf. Slide 7 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Vascular Tissue Vascular tissue forms a transport system that moves water and nutrients throughout the plant. Vascular tissue is made up of xylem, a waterconducting tissue, and phloem, a food-conducting tissue. Slide 8 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue What specialized cells make up vascular tissue? Slide 9 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Vascular Tissue Vascular tissue contains several types of specialized cells. • Xylem consists of tracheids and vessel elements. • Phloem consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells. Slide 10 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Cross Section of a Stem Tracheid Companion cell Vessel element Sieve tube element Phloem Xylem Slide 11 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Xylem All seed plants have tracheids. Tracheids are long, narrow cells that are impermeable to water. They are pierced by openings that connect neighboring cells to one another. Tracheid Vessel element Slide 12 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Angiosperms also have vessel elements. Vessel elements form a continuous tube through which water can move. Tracheid Vessel element Slide 13 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Phloem Phloem contains sieve tube elements and companion cells. Sieve tube elements are phloem cells joined end-to-end to form sieve tubes. Companion cell Sieve tube element Slide 14 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue The end walls of sieve tube elements have many small holes. Companion cell Sugars and other foods can move through these holes Sieve tube element from one adjacent cell to another. Slide 15 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show 23–1 Specialized Tissues in Plants Vascular Tissue Companion cells are phloem cells that surround sieve tube elements. Companion cell Companion cells support the phloem Sieve tube element cells and aid in the movement of substances in and out of the phloem. Slide 16 of 34 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall End Show END OF SECTION