
What is Blood?
... How does this help the release of oxygen? The size of a red blood cell forces it to slow down as it passes through a capillary. The surface of the red blood cell is exposed to the surface of the capillary and so gas exchange will definitely happen. 19 of 40 ...
... How does this help the release of oxygen? The size of a red blood cell forces it to slow down as it passes through a capillary. The surface of the red blood cell is exposed to the surface of the capillary and so gas exchange will definitely happen. 19 of 40 ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... water, the frequency of the contractions of the vacuoles could increase or decrease (refer to lesson 3 application). The Paramecium has two contractile vacuoles, one at each end. What about solid particles that remain after the digestive enzymes have completed their work? In many unicellular organis ...
... water, the frequency of the contractions of the vacuoles could increase or decrease (refer to lesson 3 application). The Paramecium has two contractile vacuoles, one at each end. What about solid particles that remain after the digestive enzymes have completed their work? In many unicellular organis ...
contd.
... • Carnivores typically have short digestive tubes that produce enzymes to break down meat. Animals don’t produce enzymes that can break down the tough cellulose in plant tissue. • Some herbivores, such as cattle, have a four-part stomach, each with a special function. The largest stomach part is a p ...
... • Carnivores typically have short digestive tubes that produce enzymes to break down meat. Animals don’t produce enzymes that can break down the tough cellulose in plant tissue. • Some herbivores, such as cattle, have a four-part stomach, each with a special function. The largest stomach part is a p ...
Clot Formation in the Sipunculid Worm Themiste petricola: A
... rapidly activated, aggregate homotypically, and create an insoluble mass that can be seen macroscopically [15, 16]. The haemostatic significance of this mass was demonstrated experimentally by its ability to block coelomic fluid flow [6]. When coelomic fluid was allowed to flow through a thin glass ...
... rapidly activated, aggregate homotypically, and create an insoluble mass that can be seen macroscopically [15, 16]. The haemostatic significance of this mass was demonstrated experimentally by its ability to block coelomic fluid flow [6]. When coelomic fluid was allowed to flow through a thin glass ...
Human Systems and Homeostasis
... contrast, neurons develop extensions that transmit and receive messages from other neurons. Humans, like almost all multicellular organisms, are collections of specialized cells that work together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which is formed by the union of an egg and sperm. ...
... contrast, neurons develop extensions that transmit and receive messages from other neurons. Humans, like almost all multicellular organisms, are collections of specialized cells that work together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which is formed by the union of an egg and sperm. ...
pregnancy - Holy Family Catholic Regional Division No. 37
... entering the female; • Diaphragm – which fits over the cervix and prevents semen from entering the uterus • both of these methods are more reliable when used in conjunction with a spermicidal foam or jelly ...
... entering the female; • Diaphragm – which fits over the cervix and prevents semen from entering the uterus • both of these methods are more reliable when used in conjunction with a spermicidal foam or jelly ...
Unit One
... living things seem to need energy, which they get from the environment — sometimes as food, though plants can get their energy directly from sunlight. Because there are so many ways of eating we often say that living things exchange energy with their environment. Also, all living things we know abou ...
... living things seem to need energy, which they get from the environment — sometimes as food, though plants can get their energy directly from sunlight. Because there are so many ways of eating we often say that living things exchange energy with their environment. Also, all living things we know abou ...
Assignments Handbook - Independence High
... What is phenylketonuria? Phenylketonuria (commonly known as PKU) is an inherited disorder that increases the levels of a substance called phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylalanine (an amino acid) is a building block of proteins that is obtained through the diet. It is found in all proteins and in so ...
... What is phenylketonuria? Phenylketonuria (commonly known as PKU) is an inherited disorder that increases the levels of a substance called phenylalanine in the blood. Phenylalanine (an amino acid) is a building block of proteins that is obtained through the diet. It is found in all proteins and in so ...
View/Open - seafdec/aqd
... polysaccharide or sometimes a glycolipid) to which lymphocytes respond; also known as immunogen because it induces the immune response antioxidant – a substance that chemically protects other compound against oxidation; for example, vitamin E prevents oxidation and rancidity of fats antiserum – seru ...
... polysaccharide or sometimes a glycolipid) to which lymphocytes respond; also known as immunogen because it induces the immune response antioxidant – a substance that chemically protects other compound against oxidation; for example, vitamin E prevents oxidation and rancidity of fats antiserum – seru ...
Cnidarians (Phylum Cnidaria)
... • The endoderm cells line the gastrovascular cavity. These cells release digestive enzymes into the cavity to begin the digestion process. When the food is partially digested, it is engulfed by the endoderm cells, where digestion is completed within food vacuoles. Thus, digestion is both extracellul ...
... • The endoderm cells line the gastrovascular cavity. These cells release digestive enzymes into the cavity to begin the digestion process. When the food is partially digested, it is engulfed by the endoderm cells, where digestion is completed within food vacuoles. Thus, digestion is both extracellul ...
1 Properties of Matter
... primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower ...
... primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower ...
Phylum Porifera
... • Diversity of species: About 8000 species • Phylum Porifera – From Greek ‘poros’ meaning ‘passage’ or ‘pore’ – Sponges have tiny openings all over their body, hints the name ‘pore-bearers’ ...
... • Diversity of species: About 8000 species • Phylum Porifera – From Greek ‘poros’ meaning ‘passage’ or ‘pore’ – Sponges have tiny openings all over their body, hints the name ‘pore-bearers’ ...
Bio 20 A - Holy Trinity Academy
... Proteins are made from the elements C, O, H, and N. These elements link together to make an amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins for living things on earth. Six functions of proteins: 1) enzymes—are globular proteins, speed up reactions, ex. Amylase 2) hormones—so ...
... Proteins are made from the elements C, O, H, and N. These elements link together to make an amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins for living things on earth. Six functions of proteins: 1) enzymes—are globular proteins, speed up reactions, ex. Amylase 2) hormones—so ...
Fungi
... The tip of a fungal hypha binds with a suitable host cell Both lose their cell wall and their cytoplasm fuses as both organisms grow together The fungus recieves a long-term source of nutrients, which it absorbs from the ...
... The tip of a fungal hypha binds with a suitable host cell Both lose their cell wall and their cytoplasm fuses as both organisms grow together The fungus recieves a long-term source of nutrients, which it absorbs from the ...
Mark scheme
... a plant cell that has been placed in water a plant cell that has been placed in a strong sugar solution ...
... a plant cell that has been placed in water a plant cell that has been placed in a strong sugar solution ...
Chapter 27
... In animals, segmentation refers to a body composed of a series of _________________________________ that can move independently permitting great ______________ and _______________. Within the phylum Arthropoda, segments may look different and have different functions. A small change in a segment can ...
... In animals, segmentation refers to a body composed of a series of _________________________________ that can move independently permitting great ______________ and _______________. Within the phylum Arthropoda, segments may look different and have different functions. A small change in a segment can ...
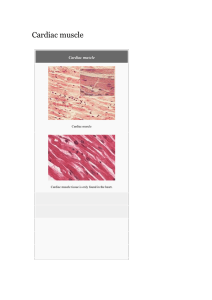
Cardiac muscle File
... Institute in Stockholm tested samples of heart muscle from people born before 1955 who had very little cardiac muscle around their heart, many showing with disabilities from this abnormality. By using DNA samples from many hearts, the researchers estimated that a 4-year-old renews about 20% of heart ...
... Institute in Stockholm tested samples of heart muscle from people born before 1955 who had very little cardiac muscle around their heart, many showing with disabilities from this abnormality. By using DNA samples from many hearts, the researchers estimated that a 4-year-old renews about 20% of heart ...
Respiratory Epithelium, Larynx and Trachea
... Airway (conducting part) It starts from nasal cavity, continues in the nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and terminal bronchioles. Its function is to clean, moisten and warm the inhaled air and conduct it to respiratory part. Respiratory unit ...
... Airway (conducting part) It starts from nasal cavity, continues in the nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and terminal bronchioles. Its function is to clean, moisten and warm the inhaled air and conduct it to respiratory part. Respiratory unit ...
1 ANATOMY RS#9 August 14, 2008 JR Churchill, Ph.D. 9:00
... The proteoglycan family of proteins is large and varied in structure and function. Grouping them together is similar to grouping all phosphorylated proteins together, however some general features make it convenient to consider them as a group. They are major constituents of cartilage, loose CT and ...
... The proteoglycan family of proteins is large and varied in structure and function. Grouping them together is similar to grouping all phosphorylated proteins together, however some general features make it convenient to consider them as a group. They are major constituents of cartilage, loose CT and ...
Albert - Brookings School District
... The Alveoli Alveoli are the tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles. Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli. They provide a huge surface area – 70-80 square meters – for efficient gas exchange. Alveoli have thin walls made out of single-layered epithelial tissue for maximum efficiency. T ...
... The Alveoli Alveoli are the tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles. Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli. They provide a huge surface area – 70-80 square meters – for efficient gas exchange. Alveoli have thin walls made out of single-layered epithelial tissue for maximum efficiency. T ...
The Lymphatic System
... excess tissue fluid called lymph. • Tissue fluid contains water, solutes (nutrients, electrolytes, oxygen), and cellular products (hormones, enzymes, wastes) TO PREVIOUS SLIDE ...
... excess tissue fluid called lymph. • Tissue fluid contains water, solutes (nutrients, electrolytes, oxygen), and cellular products (hormones, enzymes, wastes) TO PREVIOUS SLIDE ...
Human Anatomy and Histology course Lecturer: Anna Barlasov PhD
... Description: Consists of blood plasma (55%) and formed elements (45%): red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Location: Within blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins) and within the chambers of the heart. Function: ...
... Description: Consists of blood plasma (55%) and formed elements (45%): red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Location: Within blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins) and within the chambers of the heart. Function: ...
EXTRACELLULAR AND INTERNAL ENVIORNMENT
... materials to the cells, intercellular communication, as well as removal of metabolic waste. Plasma ...
... materials to the cells, intercellular communication, as well as removal of metabolic waste. Plasma ...
ANIMAL TISSUES
... Cells group together in the body to form tissues. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning. There are only four types of tissues that are dispers ...
... Cells group together in the body to form tissues. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning. There are only four types of tissues that are dispers ...
Respiratory System[1] - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
... Firstly the breathing system must inhale oxygen and secondly it must exhale carbon dioxide. It is designed to be able to perform both tasks using the same organs. One final important fact to remember is that breathing can be performed without humans having to think about it. Just imagine that as wel ...
... Firstly the breathing system must inhale oxygen and secondly it must exhale carbon dioxide. It is designed to be able to perform both tasks using the same organs. One final important fact to remember is that breathing can be performed without humans having to think about it. Just imagine that as wel ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.

















![Respiratory System[1] - missdannocksyear11biologyclass](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008654285_1-2b054e727f792a49d70ccbd4d097227d-300x300.png)