Chapter 21 - Human Anatomy
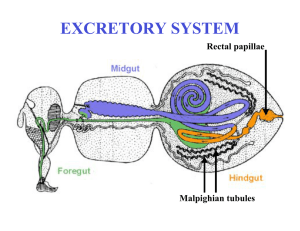
... from the blood to form filtrate 2. Reabsorption of water and valuable solutes back into the blood 3. Secretion of certain substances, such as ions and drugs, into the filtrate 4. Excretion of urine from the kidneys to the outside ...
... from the blood to form filtrate 2. Reabsorption of water and valuable solutes back into the blood 3. Secretion of certain substances, such as ions and drugs, into the filtrate 4. Excretion of urine from the kidneys to the outside ...
prenatal development
... division, the sorting out of the genetic material, begins, and unfolds over the course of 2 cellular divisions that result in 4 gametes. SITINOR/FEM3101/FEBRUARI 2013/PJJ ...
... division, the sorting out of the genetic material, begins, and unfolds over the course of 2 cellular divisions that result in 4 gametes. SITINOR/FEM3101/FEBRUARI 2013/PJJ ...
Excretory system - Faculty Support Site
... 1. Intermediary metabolism (glycogen to glucose; glycerol production) 2. Contain MFO or cytochrome P450 enzymes (similar to vertebrate liver) 3. Take precursors from the hemolymph and produce the female specific protein or vitellogenin and put it into the hemolymph 4. Takes wastes out of hemolymph a ...
... 1. Intermediary metabolism (glycogen to glucose; glycerol production) 2. Contain MFO or cytochrome P450 enzymes (similar to vertebrate liver) 3. Take precursors from the hemolymph and produce the female specific protein or vitellogenin and put it into the hemolymph 4. Takes wastes out of hemolymph a ...
CHAPTER 15
... R & L bronchi Contain cartilage, smooth muscle R is wider, shorter, more vertical Divide into secondary and tertiary bronchi Bronchioles Lungs (alveolar ducts and ...
... R & L bronchi Contain cartilage, smooth muscle R is wider, shorter, more vertical Divide into secondary and tertiary bronchi Bronchioles Lungs (alveolar ducts and ...
biology - Textbooks Online
... are animal species and out of which 750,000 belong to insect species alone. There are 350,000 species of plants including algae, fungi, mosses and higher forms of plants. Thus the existence of different forms of a species or genus and diverse adaptations for, varied surroundings are referred to as “ ...
... are animal species and out of which 750,000 belong to insect species alone. There are 350,000 species of plants including algae, fungi, mosses and higher forms of plants. Thus the existence of different forms of a species or genus and diverse adaptations for, varied surroundings are referred to as “ ...
Integumentary System PowerPoint
... Contains hard keratin; tougher, more durable than soft keratin of skin & individual cells do not flake off. ...
... Contains hard keratin; tougher, more durable than soft keratin of skin & individual cells do not flake off. ...
Human Regulation and Reproduction
... manner. By moving certain ions into a cell, it is possible to change the potential difference (voltage) and cause an impulse to be transmitted. Research Most of our knowledge of nervous impulse transmission comes from the work of two scientists, Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley, who conducted experime ...
... manner. By moving certain ions into a cell, it is possible to change the potential difference (voltage) and cause an impulse to be transmitted. Research Most of our knowledge of nervous impulse transmission comes from the work of two scientists, Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley, who conducted experime ...
Body Organization and Homeostasis
... Body Organization and Homeostasis The bell rings—lunchtime! You hurry down the noisy halls to the cafeteria. The unmistakable aroma of hot pizza makes your mouth water. At last, you balance your tray of pizza and salad while you pay the cashier. You look around the cafeteria for your friends. Then, ...
... Body Organization and Homeostasis The bell rings—lunchtime! You hurry down the noisy halls to the cafeteria. The unmistakable aroma of hot pizza makes your mouth water. At last, you balance your tray of pizza and salad while you pay the cashier. You look around the cafeteria for your friends. Then, ...
6_1_ 6_3 Digestion and Infectious Diseases PP-2
... Antibiotics take advantage of the differences between our cells and bacteria. Can you some of those differences? • Prokaryotes: Cell wall, nucleoid (free floating DNA), no nucleus • Antibiotics are chemicals produced by microorganisms, ...
... Antibiotics take advantage of the differences between our cells and bacteria. Can you some of those differences? • Prokaryotes: Cell wall, nucleoid (free floating DNA), no nucleus • Antibiotics are chemicals produced by microorganisms, ...
Anatomy2_Final_Study_Guide1
... Know the primary components of the lymphatic system. Know the primary functions of the lymphatic and immune systems. Know the principle ducts and trunks of the lymphatic system. Know where each duct drains. Know the sequence of fluid flow in the lymphatic system. Know the primary and secondary lymph ...
... Know the primary components of the lymphatic system. Know the primary functions of the lymphatic and immune systems. Know the principle ducts and trunks of the lymphatic system. Know where each duct drains. Know the sequence of fluid flow in the lymphatic system. Know the primary and secondary lymph ...
molecular physiology
... Endothelial layer of capillaries: The endothelium is fenestrated i.e. contains holes of about 70-90 nm and is freely permeable to water, small solutes such as sodium, urea and glucose and even very small proteins but not all since this layer express negatively charged glycoproteins (sialoproteins) o ...
... Endothelial layer of capillaries: The endothelium is fenestrated i.e. contains holes of about 70-90 nm and is freely permeable to water, small solutes such as sodium, urea and glucose and even very small proteins but not all since this layer express negatively charged glycoproteins (sialoproteins) o ...
Critical Content/Concept Web
... 1. Cells are the basic unit of life 9-10.B.1.2.2 Develop models to explain concepts or systems. 9-10.B.3.3.1 Identify the particular structures that underlie the cellular functions. 9-10.B.3.3.2 Explain cell functions involving chemical reactions. 9-10.B.3.2.2 Explain how organisms use the continuou ...
... 1. Cells are the basic unit of life 9-10.B.1.2.2 Develop models to explain concepts or systems. 9-10.B.3.3.1 Identify the particular structures that underlie the cellular functions. 9-10.B.3.3.2 Explain cell functions involving chemical reactions. 9-10.B.3.2.2 Explain how organisms use the continuou ...
Brief Contents
... 5.4 Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane 76 Water balance between cells and their surroundings is crucial to organisms 76 Transport proteins can facilitate diffusion across membranes 77 ...
... 5.4 Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane 76 Water balance between cells and their surroundings is crucial to organisms 76 Transport proteins can facilitate diffusion across membranes 77 ...
EXAMPLE Histology Compendium
... intracellular organelles. These include granules, but no nucleus. ...
... intracellular organelles. These include granules, but no nucleus. ...
Study Guide for AHSGE Biology Edition
... A cell is the smallest unit that is alive and can carry on all the processes of life Cells make up organisms (living things) ...
... A cell is the smallest unit that is alive and can carry on all the processes of life Cells make up organisms (living things) ...
B1 Revision Mind Maps
... What does phase one drug testing involve and why is it necessary? Test drug on cells, tissues or animals Safety testing - check for toxicity and interaction with other drugs. What is involved in phase two drugs ...
... What does phase one drug testing involve and why is it necessary? Test drug on cells, tissues or animals Safety testing - check for toxicity and interaction with other drugs. What is involved in phase two drugs ...
Binary fission
... Binary fission • In prokaryotes, growth = increase in number of cells • Generation time is the time required for 1 bacterium to become 2 bacteria • E. coli generation time is ~ 20 min ...
... Binary fission • In prokaryotes, growth = increase in number of cells • Generation time is the time required for 1 bacterium to become 2 bacteria • E. coli generation time is ~ 20 min ...
الشريحة 1
... Copper Cu: It is carried & transported by plasma protein ceruloplasmin. It catalyses the oxidation of Fe++ to Fe+++, a reaction that must occur before transferrin can combine and transport iron. ...
... Copper Cu: It is carried & transported by plasma protein ceruloplasmin. It catalyses the oxidation of Fe++ to Fe+++, a reaction that must occur before transferrin can combine and transport iron. ...
WHRHS BIOLOGY K PROFICIENCIES
... 46. Explain how Watson and Crick derived the DNA model. Discuss the importance of polymers to life. 47. Describe DNA replication. 48. Describe the 3 types of RNA and state function of each. 49. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 50. Explain how the order of nucleotides in DNA codes for different amin ...
... 46. Explain how Watson and Crick derived the DNA model. Discuss the importance of polymers to life. 47. Describe DNA replication. 48. Describe the 3 types of RNA and state function of each. 49. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. 50. Explain how the order of nucleotides in DNA codes for different amin ...
File - thebiotutor.com
... A: Levels of organisation Levels of Organisation Students will be assessed on their ability to: 2.1 describe the levels of organisation within organisms: organelles, cells, tissues, organs and systems. ...
... A: Levels of organisation Levels of Organisation Students will be assessed on their ability to: 2.1 describe the levels of organisation within organisms: organelles, cells, tissues, organs and systems. ...
Functions of hormones
... 1. The innermost layer contains the cell bodies of two types of cells: the numerous and tiny granule cells, and the larger Golgi cells. 2. Incoming (mossy) fibers enter the granular layer and form excitatory synapses with the granule cells and the cells of the deep cerebellar nuclei. 3. The granule ...
... 1. The innermost layer contains the cell bodies of two types of cells: the numerous and tiny granule cells, and the larger Golgi cells. 2. Incoming (mossy) fibers enter the granular layer and form excitatory synapses with the granule cells and the cells of the deep cerebellar nuclei. 3. The granule ...
The Science of Candy!
... Add some candy and allow the color to dissolve. You may test as many colors as you like, but be sure to only use one color of candy in each water puddle. Dip the edge of the coffee filter (or paper towel or napkin) into the colored water. It works best if you fold the paper so that you can dip ...
... Add some candy and allow the color to dissolve. You may test as many colors as you like, but be sure to only use one color of candy in each water puddle. Dip the edge of the coffee filter (or paper towel or napkin) into the colored water. It works best if you fold the paper so that you can dip ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.