Document
... – Protection. Forms boundary of individual, barrier to external dangers and valuable internal materials – Sensing. Can gather information about environment: temperature, pressure, light, damage to integument – Communication. Since visible to others, can send signals with skin color or structures (ha ...
... – Protection. Forms boundary of individual, barrier to external dangers and valuable internal materials – Sensing. Can gather information about environment: temperature, pressure, light, damage to integument – Communication. Since visible to others, can send signals with skin color or structures (ha ...
Investigating the Human Body - On-site student
... Our nervous system receives and transmits information about everything that goes on inside us and in our environment. It makes sure that all of our body systems work together. The nervous system allows us to think and make decisions, carry out different actions and ...
... Our nervous system receives and transmits information about everything that goes on inside us and in our environment. It makes sure that all of our body systems work together. The nervous system allows us to think and make decisions, carry out different actions and ...
Section 26.2 Summary – pages 698-705
... Sponges passively filter food particles from the water when the particles flow through the sponge. Cnidarians actively seek food with tentacles that capture or paralyze the prey and take it to the cnidarian’s mouth for ingestion. ...
... Sponges passively filter food particles from the water when the particles flow through the sponge. Cnidarians actively seek food with tentacles that capture or paralyze the prey and take it to the cnidarian’s mouth for ingestion. ...
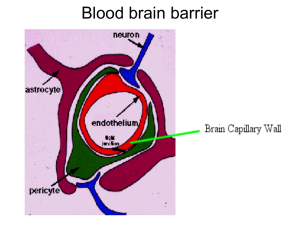
Blood brain barrier - Selam Higher Clinic
... The uptake can be further enhanced by specifically targeting the delivery system to receptors on the brain endothelium surface that are capable of receptor mediated endocytosis. This method is more selective than the tight junction disruption, especially if brain specific targeting technology is use ...
... The uptake can be further enhanced by specifically targeting the delivery system to receptors on the brain endothelium surface that are capable of receptor mediated endocytosis. This method is more selective than the tight junction disruption, especially if brain specific targeting technology is use ...
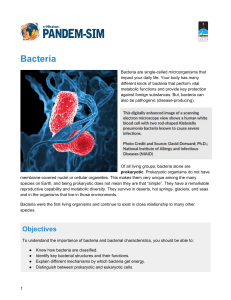
Bacteria - Pandem-Sim
... bladder. Some organisms can be identified by their motility (movement) pattern in cultures. 4) plasma membrane—a membrane surrounding the cytoplasm just inside the cell wall. The plasma membrane provides support and allows movement into and out of the cell. Its main function is providing the selec ...
... bladder. Some organisms can be identified by their motility (movement) pattern in cultures. 4) plasma membrane—a membrane surrounding the cytoplasm just inside the cell wall. The plasma membrane provides support and allows movement into and out of the cell. Its main function is providing the selec ...
Using food and controlling growth - Delivery guide
... ‘These draft qualifications have not yet been accredited by Ofqual. They are published (along with specimen assessment materials, summary brochures and sample resources) to enable teachers to have early sight of our proposed approach. Further changes may be required and no assurance can be given at ...
... ‘These draft qualifications have not yet been accredited by Ofqual. They are published (along with specimen assessment materials, summary brochures and sample resources) to enable teachers to have early sight of our proposed approach. Further changes may be required and no assurance can be given at ...
Presentation
... increase in population. For instance, the food supply in an area may suddenly become abundant or the living space for a species may suddenly expand. By reproducing asexually in great numbers, some animals can gain a competitive edge by taking advantage of the favorable environ- ...
... increase in population. For instance, the food supply in an area may suddenly become abundant or the living space for a species may suddenly expand. By reproducing asexually in great numbers, some animals can gain a competitive edge by taking advantage of the favorable environ- ...
26–1 Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... they live on or inside the bodies of other animals. Others are many meters long and live in the depths of the sea. They may walk, swim, crawl, burrow, or fly—or not move at all. As you will see, each major group, or phylum, has its own typical body plan. ...
... they live on or inside the bodies of other animals. Others are many meters long and live in the depths of the sea. They may walk, swim, crawl, burrow, or fly—or not move at all. As you will see, each major group, or phylum, has its own typical body plan. ...
Export To Word
... B. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, reproduction, and homeostasis. C. Life can be organized in a functional and structural hierarchy ranging from cells to the biosphere. D. Most multicellular organisms are composed of organ systems whose structures reflect their ...
... B. Processes in a cell can be classified broadly as growth, maintenance, reproduction, and homeostasis. C. Life can be organized in a functional and structural hierarchy ranging from cells to the biosphere. D. Most multicellular organisms are composed of organ systems whose structures reflect their ...
Human Body Systems Lesson Guide
... different solutions is to rubber band a test tube to the side of a bottle of liquid. This test tube becomes the holder for the pipette. Students are reminded to only use the attached pipette when ...
... different solutions is to rubber band a test tube to the side of a bottle of liquid. This test tube becomes the holder for the pipette. Students are reminded to only use the attached pipette when ...
20_Lecture_Presentation
... However, as organisms increase in size, the surface area – is too small for the corresponding volume and – too far away from the deepest cells of the body. – In these organisms, evolutionary adaptations – consist of extensively branched or folded surfaces, which increase the area of these surfaces ...
... However, as organisms increase in size, the surface area – is too small for the corresponding volume and – too far away from the deepest cells of the body. – In these organisms, evolutionary adaptations – consist of extensively branched or folded surfaces, which increase the area of these surfaces ...
ORGANIZATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
... like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different level of organization of the human body. Atoms are a nonliving unit of the body. But cells and organs are living units. How do these different living units relate to each other? Where do body systems, like the digestiv ...
... like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different level of organization of the human body. Atoms are a nonliving unit of the body. But cells and organs are living units. How do these different living units relate to each other? Where do body systems, like the digestiv ...
Classifying living things helps us understand the diversity of life.
... Organizing things according to their similarities and differences is called classification. You used a classification system to sort living and non-living things in Chapter 1. You found that living things share the same characteristics and needs. But how could you further classify all the thousands ...
... Organizing things according to their similarities and differences is called classification. You used a classification system to sort living and non-living things in Chapter 1. You found that living things share the same characteristics and needs. But how could you further classify all the thousands ...
Appendix A: Four Corners Statements 1) I like to be the organizer of
... 2) The scientific name for a platelet is a ______________________ . They make up around ________ % of total blood volume. The are very small in size, only ___________ in diameter. 3) Platelets are not cells, but instead are considered ________________________ since they do not have a ______________ ...
... 2) The scientific name for a platelet is a ______________________ . They make up around ________ % of total blood volume. The are very small in size, only ___________ in diameter. 3) Platelets are not cells, but instead are considered ________________________ since they do not have a ______________ ...
Maintaining a Balance #6
... from plant. Takes heat with it. Leaf shape: - Thinnest where 2 surfaces come together, lose most heat from this section. Heat shock proteins: - Produce these @ 400C. Protect enzymes & other proteins from denaturing. Leaf orientation: - Drooping leaves to minimise surface exposure to sun (parallel to ...
... from plant. Takes heat with it. Leaf shape: - Thinnest where 2 surfaces come together, lose most heat from this section. Heat shock proteins: - Produce these @ 400C. Protect enzymes & other proteins from denaturing. Leaf orientation: - Drooping leaves to minimise surface exposure to sun (parallel to ...
Review for Midterm and Final
... small and large subunit. mRNA has triplets called__________that are bonded to the tRNA’s________ __________ in the process of ________________. Each tRNA carries a specific _________ _________ which through the process of dehydration synthesis forms a ___________________. Protein synthesis occurs in ...
... small and large subunit. mRNA has triplets called__________that are bonded to the tRNA’s________ __________ in the process of ________________. Each tRNA carries a specific _________ _________ which through the process of dehydration synthesis forms a ___________________. Protein synthesis occurs in ...
NEPHRON 1 The nephron – the functional unit of the kidney
... kidneys and the nephrons are the functional units of these anatomical structures. The paper will illustrate the anatomical structures that make up the nephron and their physiological roles in the function of the kidney (Netter, 2014). As mentioned above, the nephron is the functional unit of the kid ...
... kidneys and the nephrons are the functional units of these anatomical structures. The paper will illustrate the anatomical structures that make up the nephron and their physiological roles in the function of the kidney (Netter, 2014). As mentioned above, the nephron is the functional unit of the kid ...
XVIII. Biology, High School - Massachusetts Department of
... resistant or susceptible to arthritis. The allele for having resistance to arthritis (a) is recessive to the allele for being susceptible to arthritis (A). ...
... resistant or susceptible to arthritis. The allele for having resistance to arthritis (a) is recessive to the allele for being susceptible to arthritis (A). ...
Organization in Plants and Animals
... are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different level of organization of the human body. Atoms are a nonliving unit of the body. But cells and organs are living units. How do these different living units relate to each other? Where do body system ...
... are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different level of organization of the human body. Atoms are a nonliving unit of the body. But cells and organs are living units. How do these different living units relate to each other? Where do body system ...
Points to take note for Biology - Learning Made Simple Singapore
... Light dependent and light independent stages - Light dependent and light independent stages of photosynthesis are not that important. If you still want to know more just in case, see below brief points. - In light dependent stage, water molecules are split by light into hydrogen and oxygen. This is ...
... Light dependent and light independent stages - Light dependent and light independent stages of photosynthesis are not that important. If you still want to know more just in case, see below brief points. - In light dependent stage, water molecules are split by light into hydrogen and oxygen. This is ...
Marine Biology - Hartnell College
... main steps: observation, hypothesis, experiment, and conclusion. Typically the method is initiated with a question. It also usually includes predicting the results of an experiment. Hermit crabs are decapod crustaceans. As the name implies, decapods (Greek deca- ten) have ten legs. The front three p ...
... main steps: observation, hypothesis, experiment, and conclusion. Typically the method is initiated with a question. It also usually includes predicting the results of an experiment. Hermit crabs are decapod crustaceans. As the name implies, decapods (Greek deca- ten) have ten legs. The front three p ...
2.01 structure of cells.
... Cytology is the study of cells, and cytologists are scientists that study cells. Cytologists have discovered that all cells are similar. Cells are all composed chiefly of molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. 2.01 STRUCTURE OF CELLS. In 1655, the English sc ...
... Cytology is the study of cells, and cytologists are scientists that study cells. Cytologists have discovered that all cells are similar. Cells are all composed chiefly of molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. 2.01 STRUCTURE OF CELLS. In 1655, the English sc ...
Untitled
... in order to get air out, the intrapulmonary pressure must increase above atmospheric pressure. To increase pressure in the alveoli, we can decrease the volume of the space. How? The lung’s natural recoil. If you want to get air into the alveoli, decrease the pressure by increasing the alveolar volum ...
... in order to get air out, the intrapulmonary pressure must increase above atmospheric pressure. To increase pressure in the alveoli, we can decrease the volume of the space. How? The lung’s natural recoil. If you want to get air into the alveoli, decrease the pressure by increasing the alveolar volum ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.