Physiology of Respiratory system
... The respiratory system is made up of a gas-exchanging organ (the lungs) and a "pump" that ventilates the lungs. The pump consists of the chest wall; the respiratory muscles, which increase and decrease the size of the thoracic cavity; the areas in the brain that control the muscles; and the tracts a ...
... The respiratory system is made up of a gas-exchanging organ (the lungs) and a "pump" that ventilates the lungs. The pump consists of the chest wall; the respiratory muscles, which increase and decrease the size of the thoracic cavity; the areas in the brain that control the muscles; and the tracts a ...
Biology Topic - The characteristics of life
... a) Topic: Organisation by cells Cells have the effect of organising the structures and chemicals within themselves. A random mixing of chemicals would result in chaos within the organism and would not serve the need to stay alive. b) Topic: Continuity and survival of living organisms Another feature ...
... a) Topic: Organisation by cells Cells have the effect of organising the structures and chemicals within themselves. A random mixing of chemicals would result in chaos within the organism and would not serve the need to stay alive. b) Topic: Continuity and survival of living organisms Another feature ...
functions
... 2. Function correlates with structure in the tissues of organisms • Life is characterized by hierarchical levels of organization, each with emergent properties. • Animals are multicellular organisms with their specialized cells grouped into tissues. • In most animals, combinations of various tissue ...
... 2. Function correlates with structure in the tissues of organisms • Life is characterized by hierarchical levels of organization, each with emergent properties. • Animals are multicellular organisms with their specialized cells grouped into tissues. • In most animals, combinations of various tissue ...
1 - Wsfcs
... 35. Different types of organisms are made of different numbers of cells. What is the range in the number of cells that organisms can be made of, from the very smallest organism to the very largest? A. From 1 cell to about 100 cells B. From 1 cell to many millions of cells C. From about 100 cells to ...
... 35. Different types of organisms are made of different numbers of cells. What is the range in the number of cells that organisms can be made of, from the very smallest organism to the very largest? A. From 1 cell to about 100 cells B. From 1 cell to many millions of cells C. From about 100 cells to ...
pH and Acidosis - SupremeFulvic.com
... Acidosis leads to partial lipid breakdown and destructive oxidative cascades accelerating free radical damage of cell walls and intracellular membrane structures. In this process, many healthy cells are destroyed. Acidosis is the first step towards premature aging and accelerated oxidative cascades ...
... Acidosis leads to partial lipid breakdown and destructive oxidative cascades accelerating free radical damage of cell walls and intracellular membrane structures. In this process, many healthy cells are destroyed. Acidosis is the first step towards premature aging and accelerated oxidative cascades ...
explanation - mbhsbiologystaar
... discussed the lac and trp operons in your Biology class and remembered that the genes that code for the breakdown of lactose or the synthesis of tryptophan can be turned on and off as the cell needs those things to be done. • If not, here are some other things you might have known: – Genes are on li ...
... discussed the lac and trp operons in your Biology class and remembered that the genes that code for the breakdown of lactose or the synthesis of tryptophan can be turned on and off as the cell needs those things to be done. • If not, here are some other things you might have known: – Genes are on li ...
Cell Biology - Hardin County Schools
... In 1858, after using microscopes much better than Hooke’s first microscope, Rudolf Virchow developed the hypothesis that cells only come from other cells. For example, bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, divide in half (after they grow some) to make new bacteria. In the same way, your body ...
... In 1858, after using microscopes much better than Hooke’s first microscope, Rudolf Virchow developed the hypothesis that cells only come from other cells. For example, bacteria, which are single-celled organisms, divide in half (after they grow some) to make new bacteria. In the same way, your body ...
Respiratory System
... Lower Respiratory Tract Larynx [voicebox] -walls made of cartilage -Thyroid cartilage [adam’s apple] -Epiglottic cartilage- covered with mucous membrane -epiglottis blocks opening to trachea [glottis] when swallowing False Vocal cords- musc/conn. tissue; same function as epiglottis True Vocal cord ...
... Lower Respiratory Tract Larynx [voicebox] -walls made of cartilage -Thyroid cartilage [adam’s apple] -Epiglottic cartilage- covered with mucous membrane -epiglottis blocks opening to trachea [glottis] when swallowing False Vocal cords- musc/conn. tissue; same function as epiglottis True Vocal cord ...
Loose connective tissue
... When collagen bundles are present without apparent orientation, called dense irregular connective tissue. When oriented in parallel arrays, called dense regular connective tissue. Elastic tissue - bundles of thick, parallel elastic fibers. Small amount of loose connective tissue around each bundle. ...
... When collagen bundles are present without apparent orientation, called dense irregular connective tissue. When oriented in parallel arrays, called dense regular connective tissue. Elastic tissue - bundles of thick, parallel elastic fibers. Small amount of loose connective tissue around each bundle. ...
Life Science Semester 1 Final Exam Review Sheet
... Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Parts and functions of cells Compare and contrast chart: animal, plant cells Anatomy of a cell Cell treasure hunt Structures of Life video clip Summarize organelle functions: 3 words per organelle Cell analogy Edible Cell Lab A visit to Cellville Organelle flashcards ...
... Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Parts and functions of cells Compare and contrast chart: animal, plant cells Anatomy of a cell Cell treasure hunt Structures of Life video clip Summarize organelle functions: 3 words per organelle Cell analogy Edible Cell Lab A visit to Cellville Organelle flashcards ...
Chapter 36 - Key Concepts
... What are the types of asexual reproduction and under what conditions is it an advantage? Which animals have external fertilization and which have internal? How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ in humans? ...
... What are the types of asexual reproduction and under what conditions is it an advantage? Which animals have external fertilization and which have internal? How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ in humans? ...
COURSE 120 ANAT. ( HISTOLOGY) ( I ) Basic Information Course
... (1) First continuous assessment: Comprehensive exam (i.e. all topics studied from the start of the academic year are included). (2) Mid-year exam: comprehensive exam: * One third of questions are related to topics included in the first continuous assessment. * Two thirds of questions are related to ...
... (1) First continuous assessment: Comprehensive exam (i.e. all topics studied from the start of the academic year are included). (2) Mid-year exam: comprehensive exam: * One third of questions are related to topics included in the first continuous assessment. * Two thirds of questions are related to ...
AP Bio Wording - Biology with Radjewski
... functions to be performed away from the rest of the cell and Allowed specialization of tissues ...
... functions to be performed away from the rest of the cell and Allowed specialization of tissues ...
Revised NEW Item Specifications October 2007 Biology
... • Recognize and apply the definition of passive transport. (The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of osmosis. (The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion. (The spontaneou ...
... • Recognize and apply the definition of passive transport. (The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of osmosis. (The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion. (The spontaneou ...
Revised NEW Item Specifications October 2007 Biology
... • Recognize and apply the definition of passive transport. (The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of osmosis. (The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion. (The spontaneou ...
... • Recognize and apply the definition of passive transport. (The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of osmosis. (The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane.) • Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion. (The spontaneou ...
Microvascular Endothelial Cells
... EC are cultivated at desired cell density onto the top of high concentrated Matrigel (4-8 mg/ml Any drug/growth factors can be applied into the gel Monitoring of “branches” by eye or imaging software * Molecular Cell- and Tumour Biology * Summer 2013 * Naples* ...
... EC are cultivated at desired cell density onto the top of high concentrated Matrigel (4-8 mg/ml Any drug/growth factors can be applied into the gel Monitoring of “branches” by eye or imaging software * Molecular Cell- and Tumour Biology * Summer 2013 * Naples* ...
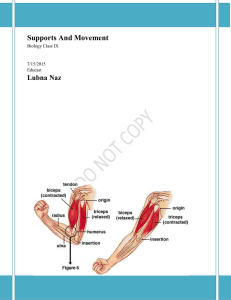
Supports And Movement
... Movement involves 3 basic mechanisms. They are amoeboid, ciliary and muscular. Amoeboid movement is typically found in amoeba, a unicellular animal. Amoeba moves by producing pseudopodia, which are cytoplasmic projections. This involves change in the shape of the cell body and streaming movement of ...
... Movement involves 3 basic mechanisms. They are amoeboid, ciliary and muscular. Amoeboid movement is typically found in amoeba, a unicellular animal. Amoeba moves by producing pseudopodia, which are cytoplasmic projections. This involves change in the shape of the cell body and streaming movement of ...
Biological Classification of Mustard Plant
... These cells have a membrane bound nucleus; and hereditary material is found inside the nucleus. These cells have membrane bound organelles. Ribosomes are of large size and are present in endoplasmic reticulum free in cytoplasm. Cellulose is present in cell wall of plant cells. The cell wall of most ...
... These cells have a membrane bound nucleus; and hereditary material is found inside the nucleus. These cells have membrane bound organelles. Ribosomes are of large size and are present in endoplasmic reticulum free in cytoplasm. Cellulose is present in cell wall of plant cells. The cell wall of most ...
1 - Corwith-Wesley-LuVerne High School
... i Stops blood flow ii Protect area from bacteria etc. d Granulation tissue forms pink tissue with many new capillaries e Phagocytes clean up debris f Surface epithelium begins to regenerate g Forms a scar F Developmental aspects of cells & tissue 1 Most cells continue to divide until puberty (except ...
... i Stops blood flow ii Protect area from bacteria etc. d Granulation tissue forms pink tissue with many new capillaries e Phagocytes clean up debris f Surface epithelium begins to regenerate g Forms a scar F Developmental aspects of cells & tissue 1 Most cells continue to divide until puberty (except ...
Animal Structure and Function Review
... 30. Compare and contrast B and T cells. (include structure, function, where they mature, and what they give rise to). What is the difference between cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells. 31. Explain the treatment one would get if they were bit by a poisonous snake. 32. Explain why vaccinations work. ...
... 30. Compare and contrast B and T cells. (include structure, function, where they mature, and what they give rise to). What is the difference between cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells. 31. Explain the treatment one would get if they were bit by a poisonous snake. 32. Explain why vaccinations work. ...
2015 COB Generic MIH (2)_new
... The Company of Biologists is a UK based charity and not-for-profit publisher run by biologists for biologists. The Company aims to promote research and study across all branches of biology through the publication of its five journals. Development ...
... The Company of Biologists is a UK based charity and not-for-profit publisher run by biologists for biologists. The Company aims to promote research and study across all branches of biology through the publication of its five journals. Development ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.