Advanced Cell Biology BI735
... understanding of these experimental approaches and their limitations. In this course, you will read original research papers that have led to our current understanding of the cytoskeleton, nuclear import/export, protein quality control, membrane trafficking and more. In addition, you will read curre ...
... understanding of these experimental approaches and their limitations. In this course, you will read original research papers that have led to our current understanding of the cytoskeleton, nuclear import/export, protein quality control, membrane trafficking and more. In addition, you will read curre ...
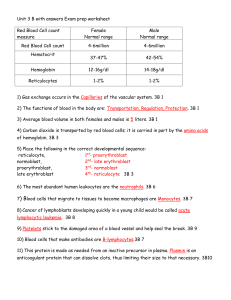
Red Blood Cell count measure Female Normal range Male Normal
... 1st- proerythroblast normoblast, 2nd- late erythroblast proerythroblast, 3rd- normoblast late erythroblast 4th- reticulocyte 3B 3 6) The most abundant human leukocytes are the neutrophils. 3B 6 7) Blood cells that migrate to tissues to become macrophages are Monocytes. 3B 7 8) Cancer of lymphoblasts ...
... 1st- proerythroblast normoblast, 2nd- late erythroblast proerythroblast, 3rd- normoblast late erythroblast 4th- reticulocyte 3B 3 6) The most abundant human leukocytes are the neutrophils. 3B 6 7) Blood cells that migrate to tissues to become macrophages are Monocytes. 3B 7 8) Cancer of lymphoblasts ...
Student Packet 16 Plant Animal Cells L.14.3
... Activity 1 - Cell Structure Vocabulary: cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE usin ...
... Activity 1 - Cell Structure Vocabulary: cell wall, centriole, chloroplast, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, nucleus, organelle, plasma membrane, plastid, ribosome, vacuole, vesicle Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE usin ...
1 Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -in multicellular organisms, cells can’t obtain nutrients or pass wastes directly with their environment -so: specialized systems, like a circulatory system, are used for the transport of materials -plants also have transport systems— exchange gases with stomatal openings; nutrients are absorbed thr ...
... -in multicellular organisms, cells can’t obtain nutrients or pass wastes directly with their environment -so: specialized systems, like a circulatory system, are used for the transport of materials -plants also have transport systems— exchange gases with stomatal openings; nutrients are absorbed thr ...
Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -ex: some bacteria that attach to solid objects form colonies called biofilms -a biofilm may contain several unrelated types of bacteria that require similar environments -in some colonies individual cells take on specialized roles -ex: volvox is one of many types of colonial algae -it’s a colony sh ...
... -ex: some bacteria that attach to solid objects form colonies called biofilms -a biofilm may contain several unrelated types of bacteria that require similar environments -in some colonies individual cells take on specialized roles -ex: volvox is one of many types of colonial algae -it’s a colony sh ...
100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the
... 100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents Exam TOPIC 1 1.The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as homeostasis. 2.Metabolism- the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3.Organic molecules contain bo ...
... 100 Important Facts you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents Exam TOPIC 1 1.The ability of an organism to maintain internal stability is known as homeostasis. 2.Metabolism- the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of an organism. 3.Organic molecules contain bo ...
Chapter 1 - SharpSchool
... cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
... cells will kill bacteria that may enter your body through your cut. The blood cells use energy to do their work! ...
BIOLOGY, BIOTECHNOLOGY Handouts and ppt
... BME Department of Applied Biotechnology and Food Science ...
... BME Department of Applied Biotechnology and Food Science ...
File
... 4) Multi-cellular: made of many cells 5) Unicellular: single-celled; a living thing made of only one cell 6) Permeable: able to pass through 7) Organism: an individual living thing (can be unicellular or multi-cellular) 8) Offspring: the young of a person, animal, or plant 9) Parents: animals (inclu ...
... 4) Multi-cellular: made of many cells 5) Unicellular: single-celled; a living thing made of only one cell 6) Permeable: able to pass through 7) Organism: an individual living thing (can be unicellular or multi-cellular) 8) Offspring: the young of a person, animal, or plant 9) Parents: animals (inclu ...
Chapter 7. The Cell: Basic Unit of Life
... Cell Theory All organisms are made up of cells The cell is the basic living unit of ...
... Cell Theory All organisms are made up of cells The cell is the basic living unit of ...
Notes 3-3
... Structure of Proteins Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids 20 different amino acids can form thousands of different proteins (just like 26 letters of the alphabet can form thousands of words) Similar to letters and words, the order of amino acids will determine which protein it is ...
... Structure of Proteins Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids 20 different amino acids can form thousands of different proteins (just like 26 letters of the alphabet can form thousands of words) Similar to letters and words, the order of amino acids will determine which protein it is ...
anatomy of the body
... Nuclear membrane has pores to allow substances passage Chromatin genetic material (long threads of chromosomes) are inside nucleoplasm Nucleolus - site of ribosome formation Cytoplasm Is the watery solution of minerals, gases, organic molecules and cell organelles that is found between the c ...
... Nuclear membrane has pores to allow substances passage Chromatin genetic material (long threads of chromosomes) are inside nucleoplasm Nucleolus - site of ribosome formation Cytoplasm Is the watery solution of minerals, gases, organic molecules and cell organelles that is found between the c ...
2.1-3
... Bluish-shiny white rubbery substance Chondrocytes sit in spaces called lacunae No blood vessels or nerves so repair is very slow Reduces friction at joints as articular cartilage ...
... Bluish-shiny white rubbery substance Chondrocytes sit in spaces called lacunae No blood vessels or nerves so repair is very slow Reduces friction at joints as articular cartilage ...
Test Review Mrs. Benham
... 6. What is the Cell Wall? It is the tough, usually flexible layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. 7. What is a Vacuole? Membrane-bound organelle found mainly in plant cells, but also in some ...
... 6. What is the Cell Wall? It is the tough, usually flexible layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. 7. What is a Vacuole? Membrane-bound organelle found mainly in plant cells, but also in some ...
Document
... The Cell Theory Emerges In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes ...
... The Cell Theory Emerges In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes ...
Cell - Del Mar College
... The Cell Theory Emerges In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes ...
... The Cell Theory Emerges In 1839, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the basic concepts of the modern cell theory • All organisms consists of one or more cells • A cell is the smallest unit with the properties of life • Each new cell arises from division of another, preexisting cell • Each cell passes ...
Cells The cell theory: All living things are made up of cells. Cells are
... vesicles to move proteins around the cell. Some eukaryotic cells also have lysosomes or peroxisomes to digest waste, vacuoles for storing water or other things, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and centrioles for splitting the cell during mitosis. Cell walls can also be found surrounding some types ...
... vesicles to move proteins around the cell. Some eukaryotic cells also have lysosomes or peroxisomes to digest waste, vacuoles for storing water or other things, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and centrioles for splitting the cell during mitosis. Cell walls can also be found surrounding some types ...
What You Absolutely Must Know to Pass the NYS Living
... G. RNA carries the genetic code to ribosomes. The ribosomes then synthesize protein (see page 2 for more about proteins). H. Changes to DNA are called mutations. They can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells (sperm or egg). I. All cells in the body contain the same genes. Only some ...
... G. RNA carries the genetic code to ribosomes. The ribosomes then synthesize protein (see page 2 for more about proteins). H. Changes to DNA are called mutations. They can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells (sperm or egg). I. All cells in the body contain the same genes. Only some ...
Solutions - jfindlay.ca
... 8. During prophase, the nuclear membrane dissolves. It reforms during telophase. Explain why this action is important for cell division. ...
... 8. During prophase, the nuclear membrane dissolves. It reforms during telophase. Explain why this action is important for cell division. ...
EOC Review All Content
... • Bacteria only • One circular chromosome • Includes: chromosome, ribosomes, and plasma membrane ...
... • Bacteria only • One circular chromosome • Includes: chromosome, ribosomes, and plasma membrane ...
8.L.5- Energy in Living Organisms - NHCS
... Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some of its energy as thermal energy. All organisms are composed of cells-a group of organelles working together. Most organisms are single cells; other organis ...
... Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some of its energy as thermal energy. All organisms are composed of cells-a group of organelles working together. Most organisms are single cells; other organis ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... the surface area of a cell refers to the total area of the outside of the cell membrane a cell with a large surface area will have more membrane in contact with the ECF, so will better be able to pull in nutrients and get rid of waste calculating surface area involves adding up the area of all sides ...
... the surface area of a cell refers to the total area of the outside of the cell membrane a cell with a large surface area will have more membrane in contact with the ECF, so will better be able to pull in nutrients and get rid of waste calculating surface area involves adding up the area of all sides ...
Organization of the Body
... Organ systems are a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function in the body. There are ten organ systems in the human ...
... Organ systems are a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function in the body. There are ten organ systems in the human ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.