Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... 18. Why do muscle cells need more mitochondria than skin cells? Muscle cells require a lot of energy for contraction and movement. While a skin cell still requires mitochondria for cellular respiration (converting glucose to useable ATP energy), they do not require as much energy to perform their fu ...
... 18. Why do muscle cells need more mitochondria than skin cells? Muscle cells require a lot of energy for contraction and movement. While a skin cell still requires mitochondria for cellular respiration (converting glucose to useable ATP energy), they do not require as much energy to perform their fu ...
Introduction to Animals Worksheet
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
... Introduction to Animals Worksheet Circle the correct response. 1. Animals are [ heterotrophs / autotrophs ] 2. [ All / Most ] animals are multicellular. 3. The cells in the skin of your hand are [ bigger than / the same size as ] the cells in your heart. 4. Organisms that have 2 copies of each chrom ...
Exam Review Notes
... It protects the cell by holding extra water and only allowing in what is needed. Enables plants to make carbohydrate through the process of photosynthesis. ...
... It protects the cell by holding extra water and only allowing in what is needed. Enables plants to make carbohydrate through the process of photosynthesis. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... the inner surfaces of the tubular and hollow structures within the body. Epithelial cells rest on an extracellular protein layer called the basement membrane. ...
... the inner surfaces of the tubular and hollow structures within the body. Epithelial cells rest on an extracellular protein layer called the basement membrane. ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... o A Cell Membrane- the boundary of the cell which allows chemicals to move in and out o Cytoplasm- the watery gel inside the cell where the chemical reactions happen o A Nucleus- contains the genetic information and controls the cell in all it does Plant cells also contain chloroplasts, where phot ...
... o A Cell Membrane- the boundary of the cell which allows chemicals to move in and out o Cytoplasm- the watery gel inside the cell where the chemical reactions happen o A Nucleus- contains the genetic information and controls the cell in all it does Plant cells also contain chloroplasts, where phot ...
Science and technology in the environment
... • Digestion – the process that changes food into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the cells • Absorption – transfer of nutrients from digestive system to bloodstream • Elimination – the removal of an unabsorbed food remain from the body • Solid material = feces • Liquid material = urine ...
... • Digestion – the process that changes food into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the cells • Absorption – transfer of nutrients from digestive system to bloodstream • Elimination – the removal of an unabsorbed food remain from the body • Solid material = feces • Liquid material = urine ...
Review Guide for Living Environment Written Assessment
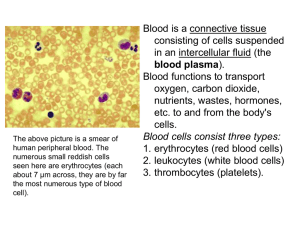
... III. Immunity and Disease 1. Blood and its components Define each part of the blood and know the function of each: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Especially review and outline the functions of your white blood cells!!! Describe the 3 major functions of the blood. Des ...
... III. Immunity and Disease 1. Blood and its components Define each part of the blood and know the function of each: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Especially review and outline the functions of your white blood cells!!! Describe the 3 major functions of the blood. Des ...
An Introduction to Cells
... • More solute molecules, lower concentration of water molecules • Membrane must be freely permeable to water, selectively permeable to solutes • Water molecules diffuse across membrane toward solution with more solutes • Volume increases on the side with more solutes • Osmotic pressure • Is the forc ...
... • More solute molecules, lower concentration of water molecules • Membrane must be freely permeable to water, selectively permeable to solutes • Water molecules diffuse across membrane toward solution with more solutes • Volume increases on the side with more solutes • Osmotic pressure • Is the forc ...
PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... Blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. ...
... Blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. ...
Chapter 23
... (hyaluronidase), released by the acrosome of the sperm. It then passes through the egg cell membrane into the cytoplasm. During this process, the sperm cell loses its tail, and the nucleus in its head swells. The egg cell then divides unequally to form a relatively large cell and a tiny second polar ...
... (hyaluronidase), released by the acrosome of the sperm. It then passes through the egg cell membrane into the cytoplasm. During this process, the sperm cell loses its tail, and the nucleus in its head swells. The egg cell then divides unequally to form a relatively large cell and a tiny second polar ...
Biology Second Semester Exam Review Answers Bacteria and
... Name: _________________________ Hour: _____ ...
... Name: _________________________ Hour: _____ ...
Unit 3 cell - Kowenscience.com
... and can move past one another in a fluid manner…also allows proteins to move and change in this layer thus scientist explain cell membrane and call it a Fluid Mosaic Model ...
... and can move past one another in a fluid manner…also allows proteins to move and change in this layer thus scientist explain cell membrane and call it a Fluid Mosaic Model ...
Document
... Contrast inorganics such as H2O, O2, CO2, and NH3 with organics Structure and function of: nucleus, plasma membrane,cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes ...
... Contrast inorganics such as H2O, O2, CO2, and NH3 with organics Structure and function of: nucleus, plasma membrane,cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes ...
function
... – All are made of one or more cells. – All need energy for metabolism. • Metabolism: All of the chemical processes in an organism that build up or break down materials. – All respond to their environment. ...
... – All are made of one or more cells. – All need energy for metabolism. • Metabolism: All of the chemical processes in an organism that build up or break down materials. – All respond to their environment. ...
Glucose plasma membrane homeostasis organism
... 22. The concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is lower than inside the cell. 23. When a cell is place in this solution, water will enter the cell by osmosis, resulting in turgor pressure. 24. The concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is the same as the concentration ...
... 22. The concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is lower than inside the cell. 23. When a cell is place in this solution, water will enter the cell by osmosis, resulting in turgor pressure. 24. The concentration of dissolved substances outside the cell is the same as the concentration ...
Biology Common Mid
... 13. Ovalbumin is a protein found in eggs. Which of the following best describes the molecular structure of ovalbumin? a. A group of six carbon atoms joined in a ring b. A chain of amino acids folded and twisted into a molecule. c. A set of three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol. d. A s ...
... 13. Ovalbumin is a protein found in eggs. Which of the following best describes the molecular structure of ovalbumin? a. A group of six carbon atoms joined in a ring b. A chain of amino acids folded and twisted into a molecule. c. A set of three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol. d. A s ...
Science Cumulative Review 1 Unicellular and Multicellular
... c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in a multicellular organism are specialized while cells in a unicellular organism are generalized. b. Cells in a unicellular organism are specialized while cells in a mul ...
... c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in a multicellular organism are specialized while cells in a unicellular organism are generalized. b. Cells in a unicellular organism are specialized while cells in a mul ...
Unit 2 - Glow Blogs
... Animal storage carbohydrate located in the liver and muscle tissues Liver A large organ with many important functions including a role in blood glucose control Target organ An organ with receptor molecules on its cell surface that recognise a specific hormone ...
... Animal storage carbohydrate located in the liver and muscle tissues Liver A large organ with many important functions including a role in blood glucose control Target organ An organ with receptor molecules on its cell surface that recognise a specific hormone ...
Sickle Cell Anemia - Woodcliff Lake School
... This recessive genetic disease (ss) illustrates the point that a change in DNA can have major consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of th ...
... This recessive genetic disease (ss) illustrates the point that a change in DNA can have major consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of th ...
B2 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... An organism’s surroundings, made of factors like air, water, soil and other organisms Protein molecule made by cells which speeds up the rate of a reaction Development of a new species over time as a result of natural selection Period of time after exercise when a greater amount of oxygen is needed ...
... An organism’s surroundings, made of factors like air, water, soil and other organisms Protein molecule made by cells which speeds up the rate of a reaction Development of a new species over time as a result of natural selection Period of time after exercise when a greater amount of oxygen is needed ...
Immunology - Bosna Sema
... contacts with them and this triggers phagocyte to engulf. It will wrap around the bacteria. Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and ...
... contacts with them and this triggers phagocyte to engulf. It will wrap around the bacteria. Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL AS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE 2.1 What is a cell
... 1. Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. 2. Animals and most plants are also multicellular organisms. (mammal, bird, reptile, amphibian, fish) 3. Examples of multicellular organisms: a. Hydra - animal b. Spirogyra – plant (contains chloroplast) c. mosses d. ferns e. flowering pl ...
... 1. Multicellular organisms are made up of more than one cell. 2. Animals and most plants are also multicellular organisms. (mammal, bird, reptile, amphibian, fish) 3. Examples of multicellular organisms: a. Hydra - animal b. Spirogyra – plant (contains chloroplast) c. mosses d. ferns e. flowering pl ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
... • Robert Hooke (1635-1703) – invented the term cell; studied dead plant cells such as cork. ...
Intro: Signal Fusion within the Cell
... – Identify global or emergent network properties – Virtual knockouts; evaluate drug targets in silico ...
... – Identify global or emergent network properties – Virtual knockouts; evaluate drug targets in silico ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.