Structure and Function in Living Systems Chapter 8: Systems in
... Because multicellular organisms are large, many of their cells are far away from one another or from the outside of the organism where oxygen can be obtained and wastes such as carbon dioxide can be released. Therefore, multicellular organisms must have specialized cells to efficiently perform the t ...
... Because multicellular organisms are large, many of their cells are far away from one another or from the outside of the organism where oxygen can be obtained and wastes such as carbon dioxide can be released. Therefore, multicellular organisms must have specialized cells to efficiently perform the t ...
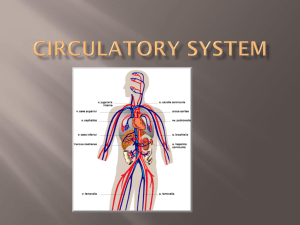
Circulatory System - Madison County Schools
... Branch into small, flexible arteries then to capillaries. ...
... Branch into small, flexible arteries then to capillaries. ...
Cell Biology Overview
... functions as a boundary to separate the cells interior from the external environment, supports the shape of the cell, and contains identification markers for other cells. There are five ways that materials pass through the cell membrane: 1) diffusion - a passive mechanism that involves movement from ...
... functions as a boundary to separate the cells interior from the external environment, supports the shape of the cell, and contains identification markers for other cells. There are five ways that materials pass through the cell membrane: 1) diffusion - a passive mechanism that involves movement from ...
Pg. 387 1-9 - Cobb Learning
... Opening: • Name the three types of muscles and tell me if they are voluntary or involuntary. ...
... Opening: • Name the three types of muscles and tell me if they are voluntary or involuntary. ...
SIA Worksheet
... c. The circulatory system delivers less carbon dioxide to the muscular system, resulting in stiffening of the muscles. d. The skeletal system produces more blood cells that circulate through the blood vessels, increasing the warmth of the body ...
... c. The circulatory system delivers less carbon dioxide to the muscular system, resulting in stiffening of the muscles. d. The skeletal system produces more blood cells that circulate through the blood vessels, increasing the warmth of the body ...
Outline
... __________ two centrioles that are functional during animal cell division Endoplasmic reticulum Provides passage for the ___________ of substances in the cytoplasm Mitochondria Serve as sites of cellular respiration and energy production Store ATP Golgi apparatus Manufactures ____________ and packag ...
... __________ two centrioles that are functional during animal cell division Endoplasmic reticulum Provides passage for the ___________ of substances in the cytoplasm Mitochondria Serve as sites of cellular respiration and energy production Store ATP Golgi apparatus Manufactures ____________ and packag ...
Biology Final Review Sheet
... Ø Compare & Contrast cellular respiration & fermentation (similarities & differences). Include which is an aerobic & which is an anaerobic process & which produces more ATP? Ø What are three differences bet ...
... Ø Compare & Contrast cellular respiration & fermentation (similarities & differences). Include which is an aerobic & which is an anaerobic process & which produces more ATP? Ø What are three differences bet ...
8.1 and 8.2 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. Oxygen is essential for survival because the cells of the body obtain energy through cellular respiration, which requires oxygen. 2. Breathing - the movement of gases between the external environment Cellular respiration - the breakdown of glucose within cells of the body producing ATP, a compoun ...
... 1. Oxygen is essential for survival because the cells of the body obtain energy through cellular respiration, which requires oxygen. 2. Breathing - the movement of gases between the external environment Cellular respiration - the breakdown of glucose within cells of the body producing ATP, a compoun ...
Biology/Life Science Review - St. Joseph School (Garden City)
... • All cells have three basic components: Cell Membrane, Nucleus (DNA), Cytoplasm and Ribosomes ...
... • All cells have three basic components: Cell Membrane, Nucleus (DNA), Cytoplasm and Ribosomes ...
Importance of Cell Division
... Asexual reproduction is the process of producing offspring from only one parent, this results in the production of offspring that are genetically identical. Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an o ...
... Asexual reproduction is the process of producing offspring from only one parent, this results in the production of offspring that are genetically identical. Genetically identical means that every cell that is produced has identical copies of a single, identical set of chromosomes. When cells in an o ...
Review for Final Exam - 2015
... In the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight, plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and water from the ground. They produce oxygen (released into the air) and food (glucose) for themselves. b. What is a tropism? ...
... In the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight, plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and water from the ground. They produce oxygen (released into the air) and food (glucose) for themselves. b. What is a tropism? ...
Sex Differentiation
... Same set of genes Different expression pattern Common expression of essential genes : housekeeping genes Differential expression of cell-specific genes Cellular differentiation is the process of turning on and off of specific genes ...
... Same set of genes Different expression pattern Common expression of essential genes : housekeeping genes Differential expression of cell-specific genes Cellular differentiation is the process of turning on and off of specific genes ...
HERE
... cell membranes and fills the cells with water. The plant’s cell membranes push against their cell walls, and the cells become firm, as shown on the right in the figure below. ...
... cell membranes and fills the cells with water. The plant’s cell membranes push against their cell walls, and the cells become firm, as shown on the right in the figure below. ...
Midterm Studyguide Avery L
... A. Metabolic Rates in Ectotherms vs. Endotherms Endotherms generate their heat internally and their body temperature does not rely on the outside temperature (hypothermia is so deadly because of how it affects the internal temperature due to outside temperature). Ectotherms, on the other hand, rely ...
... A. Metabolic Rates in Ectotherms vs. Endotherms Endotherms generate their heat internally and their body temperature does not rely on the outside temperature (hypothermia is so deadly because of how it affects the internal temperature due to outside temperature). Ectotherms, on the other hand, rely ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... – When organisms grow, they increase in size (unicellular) or number of cells (multicellular). Changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime are called development. ...
... – When organisms grow, they increase in size (unicellular) or number of cells (multicellular). Changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime are called development. ...
Press Release - MWM
... essential to successfully reprogram adult stem cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. In 2009 the research group of Professor Hans Schöler of the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster succeeded for the first time in converting adult human cells into iPS cells usin ...
... essential to successfully reprogram adult stem cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. In 2009 the research group of Professor Hans Schöler of the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Molecular Biomedicine in Münster succeeded for the first time in converting adult human cells into iPS cells usin ...
Organization of Living Things
... Your heart is an organ made up of cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue contracts, making the heart pump. The nerve tissue brings messages that tell the heart how fast to beat. The blood tissue is carried from the heart to other organs of the body. ...
... Your heart is an organ made up of cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. The cardiac muscle tissue contracts, making the heart pump. The nerve tissue brings messages that tell the heart how fast to beat. The blood tissue is carried from the heart to other organs of the body. ...
Summary of Human systems Human Body Systems Overview
... antibodies to fight disease). A vaccine is simply a cocktail of heat killed pathogens (a bacteria, etc.) that cannot cause disease because it is dead but can be recognized as foreign by the body. The B cells will then make antibodies against that pathogen which will circulate in the bloodstream for ...
... antibodies to fight disease). A vaccine is simply a cocktail of heat killed pathogens (a bacteria, etc.) that cannot cause disease because it is dead but can be recognized as foreign by the body. The B cells will then make antibodies against that pathogen which will circulate in the bloodstream for ...
Q14. How do the golgi bodies and lysosomes work together? Q15
... Q15. What is the function of smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum? Q16. How does the cell make golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum? Q17. What is the structure and function of a lysosome? Q18. How do lysosomes and vesicles assist each other by working together? Q19. Do plant cells have lysoso ...
... Q15. What is the function of smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum? Q16. How does the cell make golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum? Q17. What is the structure and function of a lysosome? Q18. How do lysosomes and vesicles assist each other by working together? Q19. Do plant cells have lysoso ...
Practice Exam
... Prokaryotic cells do not contain DNA; eukaryotic cells do Prokaryotic cells do not contain membrane-bound organelles; eukaryotic cells do Eukaryotic cells are smaller than prokaryotic cells All prokaryotic cells are photosynthetic whereas only some eukaryotic cells are. ...
... Prokaryotic cells do not contain DNA; eukaryotic cells do Prokaryotic cells do not contain membrane-bound organelles; eukaryotic cells do Eukaryotic cells are smaller than prokaryotic cells All prokaryotic cells are photosynthetic whereas only some eukaryotic cells are. ...
Unit 2 Test
... 34. Kidney cells are placed in a hypotonic solution of pure water. What do you expect will happen to the cells? a. stay the same size b. shrink c. swell d. dissolve 35. Which of the following statements summarize the differences between active and passive transport? a. Only active transport require ...
... 34. Kidney cells are placed in a hypotonic solution of pure water. What do you expect will happen to the cells? a. stay the same size b. shrink c. swell d. dissolve 35. Which of the following statements summarize the differences between active and passive transport? a. Only active transport require ...
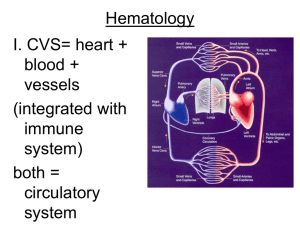
Hematology
... • Hematocrit- shows % of solid elements • Centrifuged tube shows parts • (refer to plate) ...
... • Hematocrit- shows % of solid elements • Centrifuged tube shows parts • (refer to plate) ...
8838083
... function. The parasympathetic nervous system is the dominant neuronal pathway in the control of airway smooth muscle tone. Stimulation of cholinergic nerves causes bronchoconstriction, mucus secretion, and bronchial vasodilation. Although abnormalities of the cholinergic innervation have been sugges ...
... function. The parasympathetic nervous system is the dominant neuronal pathway in the control of airway smooth muscle tone. Stimulation of cholinergic nerves causes bronchoconstriction, mucus secretion, and bronchial vasodilation. Although abnormalities of the cholinergic innervation have been sugges ...
2015 1st Semester Exam Review Key
... Biosphere: All of the earth where organisms survive Biome: Large sections of the planet with common ecosystems Niche: The role or job or an organism in the environment Habitat: The place where an organism lives. Community: A group of different populations Population: a group of organisms of the same ...
... Biosphere: All of the earth where organisms survive Biome: Large sections of the planet with common ecosystems Niche: The role or job or an organism in the environment Habitat: The place where an organism lives. Community: A group of different populations Population: a group of organisms of the same ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.