Cell Membrane
... Lipid bilayer – phospholipids and proteins Selectively permeable: allows only certain substances in and out Diffusion: movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Osmosis: diffusion of water Isotonic – dynamic equilibrium – equal movement Hypertonic – wat ...
... Lipid bilayer – phospholipids and proteins Selectively permeable: allows only certain substances in and out Diffusion: movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Osmosis: diffusion of water Isotonic – dynamic equilibrium – equal movement Hypertonic – wat ...
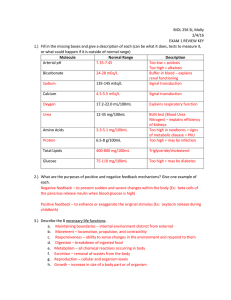
Components, Characteristics, functions of blood investigation 1
... 1. Formed elements - the actual cellular components of blood ...
... 1. Formed elements - the actual cellular components of blood ...
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
... water will cross the membrane into the cell, as the cell contains a strong solution in the cytoplasm. Animal cells do not have a strong cell wall to stop them swelling too much so if too muc ...
... water will cross the membrane into the cell, as the cell contains a strong solution in the cytoplasm. Animal cells do not have a strong cell wall to stop them swelling too much so if too muc ...
LAB 09 – Cellular Responses to Stimuli
... DNA, is located in the membrane bound nucleus. The membrane allows for separation between the nucleus with its critical genetic material and the cytoplasm of the cell. In a prokaryotic cell, the genetic information is in a region defined as nucleoid but it is not partitioned by a membrane from the r ...
... DNA, is located in the membrane bound nucleus. The membrane allows for separation between the nucleus with its critical genetic material and the cytoplasm of the cell. In a prokaryotic cell, the genetic information is in a region defined as nucleoid but it is not partitioned by a membrane from the r ...
B2 Revision - Tonypandy Community College
... •Scientists have to control the growth carefully otherwise they will produce very quickly. As they grow the microorganisms use up the nutrients in the culture medium and produce waste products and other substances. – this process is called FERMENTATION •We use fermentation for making wine and bear b ...
... •Scientists have to control the growth carefully otherwise they will produce very quickly. As they grow the microorganisms use up the nutrients in the culture medium and produce waste products and other substances. – this process is called FERMENTATION •We use fermentation for making wine and bear b ...
Name__________________________________________
... ATP to light Light to chemical Heat to electrical Chemical to chemical ...
... ATP to light Light to chemical Heat to electrical Chemical to chemical ...
Cell Membrane Proteins.
... except as parts of glycoprotein molecules,but they play a major role in nutrition of the cell. Most human cells do not maintain large stores of carbohydrates; the amount usually averages about 1per cent of their total mass but increases to as much as 3 per cent in muscle cells and, occasionally, 6 p ...
... except as parts of glycoprotein molecules,but they play a major role in nutrition of the cell. Most human cells do not maintain large stores of carbohydrates; the amount usually averages about 1per cent of their total mass but increases to as much as 3 per cent in muscle cells and, occasionally, 6 p ...
... (Spontaneous Generation does not occur). 4. Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. 5. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. 6. All energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells. The Living Cell (20:00) T ...
Clinical pathology
... certain diseases particularly some nutritional diseases , the survival time of erythrocyte is shortened like ( iron, vitamin B12, folic acid ). Erythrocyte breakdown This occurs in three ways : 1. The cell may be fragmented into pieces enough for the reticuloendothelial system to take up 2. When the ...
... certain diseases particularly some nutritional diseases , the survival time of erythrocyte is shortened like ( iron, vitamin B12, folic acid ). Erythrocyte breakdown This occurs in three ways : 1. The cell may be fragmented into pieces enough for the reticuloendothelial system to take up 2. When the ...
Lymphatic System Test
... ______ 6. A phagocytic cell that protects the body by eating invading cells is called a: a. macrophage b. erythrocyte c. antigen ______ 7. Intercellular or interstitial fluid is a thin, watery fluid formed when plasma diffuses into tissue spaces and is called: a. platelets b. pus c. lymph ______ 8. ...
... ______ 6. A phagocytic cell that protects the body by eating invading cells is called a: a. macrophage b. erythrocyte c. antigen ______ 7. Intercellular or interstitial fluid is a thin, watery fluid formed when plasma diffuses into tissue spaces and is called: a. platelets b. pus c. lymph ______ 8. ...
The Cell
... 30,000 or so scales of skin flake off your body every minute. Right now, they’re collecting on the pages of this book, on your clothes, on whatever piece of furniture you’re sitting on, and so on. Over the course of a year, you lose about a pound of the stuff. Once your skin leaves your body, it’s k ...
... 30,000 or so scales of skin flake off your body every minute. Right now, they’re collecting on the pages of this book, on your clothes, on whatever piece of furniture you’re sitting on, and so on. Over the course of a year, you lose about a pound of the stuff. Once your skin leaves your body, it’s k ...
Chapter 5 Tissues
... 2. Bone-most rigid connective tissue -hardness is due to mineral salts between cells -internally support body structures -protects vital parts in the cranial and thoracic cavities -attachment for muscles -contains red marrow, forms blood cells osteocytes-bone cells 3.Blood-transports materials betwe ...
... 2. Bone-most rigid connective tissue -hardness is due to mineral salts between cells -internally support body structures -protects vital parts in the cranial and thoracic cavities -attachment for muscles -contains red marrow, forms blood cells osteocytes-bone cells 3.Blood-transports materials betwe ...
Diversity if Life Jeopardy Questions
... 1 Living things are classified using this ancient language. LATIN 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% ...
... 1 Living things are classified using this ancient language. LATIN 5 The diversity of life increases as these two factors increase. HUMIDITY AND TEMPERATURE. 1 Plants are not found in deep ocean areas because of a lack of this. LIGHT 2 85% of all plants on Earth are found here. OCEAN 3 More than 20% ...
Unit 3B: Cell Transport Homework Packet Name: ______KEY
... D. Water moves only into the cell 2. Which of the following statements tells how facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion? A. Particles move through cell membranes without the use of energy by cells. B. Particles tend to move from high concentration to lower concentration. C. Particles mo ...
... D. Water moves only into the cell 2. Which of the following statements tells how facilitated diffusion differs from simple diffusion? A. Particles move through cell membranes without the use of energy by cells. B. Particles tend to move from high concentration to lower concentration. C. Particles mo ...
TEKS Presentation Organisms and the Enviornment
... contract to pull ribs up and out. The DIAPHRAGM muscle contracts to pull down the lungs. Tissue expands to suck in air. BREATH OUT -- you get rid of other gases that your body does not need. Rib muscles relax. The Diaphragm muscle relaxes. Tissue returns to resting position and forces air out. ...
... contract to pull ribs up and out. The DIAPHRAGM muscle contracts to pull down the lungs. Tissue expands to suck in air. BREATH OUT -- you get rid of other gases that your body does not need. Rib muscles relax. The Diaphragm muscle relaxes. Tissue returns to resting position and forces air out. ...
animal tissues and organ systems
... that interact and provide specific functions Organs – made of 2 or more different interacting tissues Organ systems – 2 or more organs joined physically or functionally ...
... that interact and provide specific functions Organs – made of 2 or more different interacting tissues Organ systems – 2 or more organs joined physically or functionally ...
1. Living Things - The Physics Teacher.ie
... Sensitivity is the ability to detect and respond to stimuli or changes in the environment. 4. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves. 5. Reproduction Reproduction is the formation of new individ ...
... Sensitivity is the ability to detect and respond to stimuli or changes in the environment. 4. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves. 5. Reproduction Reproduction is the formation of new individ ...
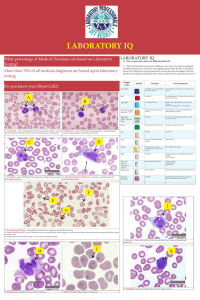
LABORATORY IQ
... Q. Why so many tubes drawn for different blood test? A. Well, you’ll find that each one has a different color of cap. The tubes are designed for different blood tests. Some have anticoagulant agents inside the tube so the blood doesn’t clot. Others have special preservatives. Some tubes get centrif ...
... Q. Why so many tubes drawn for different blood test? A. Well, you’ll find that each one has a different color of cap. The tubes are designed for different blood tests. Some have anticoagulant agents inside the tube so the blood doesn’t clot. Others have special preservatives. Some tubes get centrif ...
Chapter 43.
... proteins which constantly carry bits of cellular material from the cytosol to the cell surface “snapshot” of what is going on inside cell give the surface of cells a unique label or “fingerprint” MHC protein ...
... proteins which constantly carry bits of cellular material from the cytosol to the cell surface “snapshot” of what is going on inside cell give the surface of cells a unique label or “fingerprint” MHC protein ...
Cells
... A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is the name of this whip-like projection? A. a cilium B. a villus C. a flagellum D. a pilus 3. Which of the following organ ...
... A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is the name of this whip-like projection? A. a cilium B. a villus C. a flagellum D. a pilus 3. Which of the following organ ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE MIDTERM REVIEW Units 1
... 1. One of the largest steps in the evolution of life is the development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. The theory of endosymbiosis explains how some steps in this process may have occurred. Which of the following is evidence for this theory? a. Mitochondria have DNA similar to eukaryote ...
... 1. One of the largest steps in the evolution of life is the development of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells. The theory of endosymbiosis explains how some steps in this process may have occurred. Which of the following is evidence for this theory? a. Mitochondria have DNA similar to eukaryote ...
Vertebrate Form and Function Homeostasis: The Foundation of
... Exchange materials (eg. nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, wastes) with surrounding environment Perform chemical reactions that provide energy for the cell Synthesize needed cellular components Sense and respond to changes in surrounding environment (receptors) Reproduce (divide) Cell physiology, bi ...
... Exchange materials (eg. nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, wastes) with surrounding environment Perform chemical reactions that provide energy for the cell Synthesize needed cellular components Sense and respond to changes in surrounding environment (receptors) Reproduce (divide) Cell physiology, bi ...
Animal Systems
... ________________________ acquire energy from organic molecules made by other organisms __________________________________ harvests the chemical energy from food which is stored as ______; this energy is then used for _______ or lost as _________ Metabolic rate Total amount of ___________ and anim ...
... ________________________ acquire energy from organic molecules made by other organisms __________________________________ harvests the chemical energy from food which is stored as ______; this energy is then used for _______ or lost as _________ Metabolic rate Total amount of ___________ and anim ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.