B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... • Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries to respiring cells • Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells to capillaries • Capillaries - smallest vessel that carries blood between cells/ one cell thick • Substances move by diffusion down a concentraBon gradient = the diffusion ...
... • Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries to respiring cells • Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells to capillaries • Capillaries - smallest vessel that carries blood between cells/ one cell thick • Substances move by diffusion down a concentraBon gradient = the diffusion ...
Biology_Review-1
... a)Natural : Because of memory T cells and Memory B cells, we are protected from getting sick twicw from the same disease b) Artificial : Men made vaccin made from dead organism , triggers a secondary immune response and create Memory B and T cell for soecific desease. ...
... a)Natural : Because of memory T cells and Memory B cells, we are protected from getting sick twicw from the same disease b) Artificial : Men made vaccin made from dead organism , triggers a secondary immune response and create Memory B and T cell for soecific desease. ...
LS.3 Cellular Organization
... 1. Diffusion is the movement of substances from ___. 2. The diffusion of water across a membrane is called ______________. 3. Cellular transport that does not require energy is called _____________________. 4. Which way would the salt move in the cell below ...
... 1. Diffusion is the movement of substances from ___. 2. The diffusion of water across a membrane is called ______________. 3. Cellular transport that does not require energy is called _____________________. 4. Which way would the salt move in the cell below ...
Cells_and_Tissues_in_Health_and_Disease
... – Two types of nucleic acid combined with protein – Nuclear membrane: double-layered; with pores; separates nucleus from cytoplasm • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): in chromosomes in the nucleus, contains genetic information • Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in nucleoli; component of messenger, transfer, ribos ...
... – Two types of nucleic acid combined with protein – Nuclear membrane: double-layered; with pores; separates nucleus from cytoplasm • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): in chromosomes in the nucleus, contains genetic information • Ribonucleic acid (RNA): in nucleoli; component of messenger, transfer, ribos ...
UPcellprepro.10131154
... Cell Division NotesMassengale Cell Growth and Division PPT Animal Cell Mitosis Plant Cell ...
... Cell Division NotesMassengale Cell Growth and Division PPT Animal Cell Mitosis Plant Cell ...
08 - Cell Diversity
... Applications of tissue culture Plant Breeding Micropropagation is the growth of large numbers of plants from very small pieces of tissue or cells. 1. The cells are taken from the carrot. 2. The cells are grown on a suitable medium. 3. A 'callus' of cells grows. 4. The callus is put in a different m ...
... Applications of tissue culture Plant Breeding Micropropagation is the growth of large numbers of plants from very small pieces of tissue or cells. 1. The cells are taken from the carrot. 2. The cells are grown on a suitable medium. 3. A 'callus' of cells grows. 4. The callus is put in a different m ...
From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization Life’s Organization
... down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissue performs a specific function necessary for the stomach to work properly and break down food. Muscle tissue contracts and breaks up food. Epithelial tissue lines the stomach. Nervous ti ...
... down food. It is made of all four types of tissue: muscle, epithelial, nervous, and connective. Each type of tissue performs a specific function necessary for the stomach to work properly and break down food. Muscle tissue contracts and breaks up food. Epithelial tissue lines the stomach. Nervous ti ...
HumanBodyVocabulary
... 18. Thalamus: A large ovoid mass of gray matter situated in the posterior part of the forebrain that relays sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex 19. Hypothalamus: The part of the brain that lies below the thalamus, forming the major portion of the ventral region of the diencephalon and functionin ...
... 18. Thalamus: A large ovoid mass of gray matter situated in the posterior part of the forebrain that relays sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex 19. Hypothalamus: The part of the brain that lies below the thalamus, forming the major portion of the ventral region of the diencephalon and functionin ...
Unit 2 - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellular can live in a wide variety of environments; by specializing the ...
... The disadvantage of being unicellular -Unicellular organisms have to be able to move, eat, reproduce and respond to environments. Because they depend on cell membranes they can only live in watery, food rich environments. Multi-cellular can live in a wide variety of environments; by specializing the ...
Cells - P5 GE Science 2011
... • Some other living things are made up of only one cell. • These are single-cell organisms, such as bacteria, yeast and paramecium. • The cells can only be seen under a microscope. ...
... • Some other living things are made up of only one cell. • These are single-cell organisms, such as bacteria, yeast and paramecium. • The cells can only be seen under a microscope. ...
Chapter 1
... Cell Structure and Function The Cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life. Cells are covered by a membrane and have DNA and cytoplasm. Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, so they weren’t discovered until the mid 1600’s, after microscopes were invented. Robe ...
... Cell Structure and Function The Cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the processes necessary for life. Cells are covered by a membrane and have DNA and cytoplasm. Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, so they weren’t discovered until the mid 1600’s, after microscopes were invented. Robe ...
Diffusion: Allowing Earthworms to Breathe
... pass through the cell’s plasma membrane. Oxygen is small enough to pass through the membrane without any facilitation by proteins, it is non-polar and it is able to dissolve in the inner lipid layer. Earthworms – as well as most living things – are constantly using oxygen for chemical reactions with ...
... pass through the cell’s plasma membrane. Oxygen is small enough to pass through the membrane without any facilitation by proteins, it is non-polar and it is able to dissolve in the inner lipid layer. Earthworms – as well as most living things – are constantly using oxygen for chemical reactions with ...
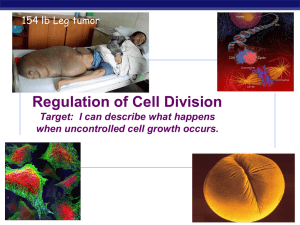
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs ...
... Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs ...
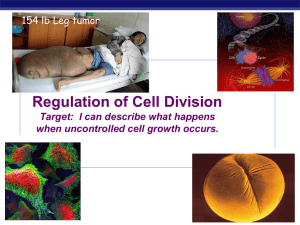
Chapter 12. Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs ...
... Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs ...
High School Biology-Honors
... 2. Structure and Function of Cells Broad Concept: All living things are composed of cells. Life processes in a cell are based on molecular interactions. 2.1 Relate cell parts/organelles to their functions. 2.2 Differentiate between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, in terms of their general st ...
... 2. Structure and Function of Cells Broad Concept: All living things are composed of cells. Life processes in a cell are based on molecular interactions. 2.1 Relate cell parts/organelles to their functions. 2.2 Differentiate between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, in terms of their general st ...
PPT
... • One drop of blood has 250 million RBC’s • Adult human has total of 25 trillion RBC’s—1/3 of all cells in the body • Each RBC lives about 120 days and travels 700 miles. Membrane rupture or other damage is noticed by phagocytes which then engulf the cell • One percent of RBC’s are replaced each day ...
... • One drop of blood has 250 million RBC’s • Adult human has total of 25 trillion RBC’s—1/3 of all cells in the body • Each RBC lives about 120 days and travels 700 miles. Membrane rupture or other damage is noticed by phagocytes which then engulf the cell • One percent of RBC’s are replaced each day ...
Cells Power point
... material, in their cell walls while most animals do not. •Animals have a limited growth scheme. Once they have attained a particular size and shape, they change very little after maturity. On the other hand, maximum size and shape of plants within a given species is variable and depends on the envir ...
... material, in their cell walls while most animals do not. •Animals have a limited growth scheme. Once they have attained a particular size and shape, they change very little after maturity. On the other hand, maximum size and shape of plants within a given species is variable and depends on the envir ...
Biology Review Answers
... glucose to provide energy to all life processes Breaks down glucose (sometimes with O2 and others without it), transfers energy to a small energy transferring compound called ATP • Think of Respiration like burning the cake. Energy is released from the bonds of glucose to be stored as ATP. All pl ...
... glucose to provide energy to all life processes Breaks down glucose (sometimes with O2 and others without it), transfers energy to a small energy transferring compound called ATP • Think of Respiration like burning the cake. Energy is released from the bonds of glucose to be stored as ATP. All pl ...
Warm Up Question: - Nick Williams` San Marin Science
... • Multicellular-Having or consisting of many cells or more than one cell to perform all vital functions. ...
... • Multicellular-Having or consisting of many cells or more than one cell to perform all vital functions. ...
Downloaded - MsOttoliniBiology
... • REASON #2: Surface area of membrane doesn’t increase as quickly as cell volume Too little membrane not enough exchange of materials (nutrient absorption and waste removal) between cell and environment Cells need a: • (Large surface area) for more materials to pass in and out of the cell… • (Smal ...
... • REASON #2: Surface area of membrane doesn’t increase as quickly as cell volume Too little membrane not enough exchange of materials (nutrient absorption and waste removal) between cell and environment Cells need a: • (Large surface area) for more materials to pass in and out of the cell… • (Smal ...
Biology Study Guide - Jackson School District
... Directions: Complete the following study guide by using your textbook and/or notes. If you have any questions I am available after school for extra help. Chapter 1 1. What is biology?Biology Study Guide.doc ...
... Directions: Complete the following study guide by using your textbook and/or notes. If you have any questions I am available after school for extra help. Chapter 1 1. What is biology?Biology Study Guide.doc ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.