Post-doctoral Research Associate in Structural Virology
... structural-virology/rg61). We use molecular biology, X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy/tomography, and focused ion beam milling to determine three-dimensional structures of viruses and study their interactions with infected cells. We aim to provide structural information for developmen ...
... structural-virology/rg61). We use molecular biology, X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy/tomography, and focused ion beam milling to determine three-dimensional structures of viruses and study their interactions with infected cells. We aim to provide structural information for developmen ...
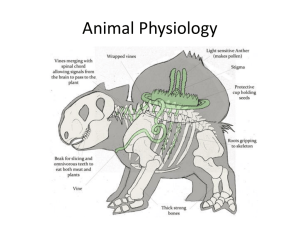
Animal Physiology Powerpoint
... around 1 billion years ago – Probably the first multicellular organisms ...
... around 1 billion years ago – Probably the first multicellular organisms ...
Biochemistry Review
... 55. What is the difference between an essential and nonessential amino acid? Essential aa must be obtained through food because the body cannot make them. Nonessential can be made by the body. 56. How does our body use the protein we eat? Breaks the proteins apart into the individual amino acids and ...
... 55. What is the difference between an essential and nonessential amino acid? Essential aa must be obtained through food because the body cannot make them. Nonessential can be made by the body. 56. How does our body use the protein we eat? Breaks the proteins apart into the individual amino acids and ...
BIOL 105 S 2014 QZM2 QA 140207.1
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
ARMT+Science Item Specs Grade7
... Even on a windy day, most plants can remain upright. Which structure plays the greatest role in providing a plant with this type of support? A ...
... Even on a windy day, most plants can remain upright. Which structure plays the greatest role in providing a plant with this type of support? A ...
RNA Polymerase II: Reading in Loops to get Different Tails Abstract
... a message that can be recognized by the proteins that properly export it to the cytosol and so that it can be efficiently translated by the ribosomes or mediate its turnover [1,2]. But what happens with the RNA polymerase after a first round of transcription? It is necessary to recycle the RNA polym ...
... a message that can be recognized by the proteins that properly export it to the cytosol and so that it can be efficiently translated by the ribosomes or mediate its turnover [1,2]. But what happens with the RNA polymerase after a first round of transcription? It is necessary to recycle the RNA polym ...
Cell activity
... All living things are made of cells. Some organisms, for example, bacteria, are composed of only one cell, but humans are composed of millions of cells, most of which are specialised for a particular job. Cytoplasm. In which most of the cell’s chemical processes take place ...
... All living things are made of cells. Some organisms, for example, bacteria, are composed of only one cell, but humans are composed of millions of cells, most of which are specialised for a particular job. Cytoplasm. In which most of the cell’s chemical processes take place ...
Schoolnet
... 56. A student used the dimmest setting on a light microscope to observe a euglena and an amoeba. The student shined a narrow beam of light at the top of the cover slip. She observed that the euglena swam up toward the light but the amoeba did not. She knew the amoeba was alive because it slowly cha ...
... 56. A student used the dimmest setting on a light microscope to observe a euglena and an amoeba. The student shined a narrow beam of light at the top of the cover slip. She observed that the euglena swam up toward the light but the amoeba did not. She knew the amoeba was alive because it slowly cha ...
VJJ Class - 6 Mark Question File
... organism and the insertion of that gene into the DNA of another organism Advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering to produce GM organisms, – a beta carotene in golden rice to reduce vitamin A deficiency in humans – b the production of human insulin by genetically modified bacteria – c the ...
... organism and the insertion of that gene into the DNA of another organism Advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering to produce GM organisms, – a beta carotene in golden rice to reduce vitamin A deficiency in humans – b the production of human insulin by genetically modified bacteria – c the ...
Unit 3 - Body Systems
... Each system of the body includes an organ that performs an important function for living. Students understand core concepts and principles of science and use measurement and observation tools to assist in categorizing, representing and interpreting the natural and designed world. Scientific kn ...
... Each system of the body includes an organ that performs an important function for living. Students understand core concepts and principles of science and use measurement and observation tools to assist in categorizing, representing and interpreting the natural and designed world. Scientific kn ...
APES-Chapter-19-PPT-Risk-Toxicology-and-Human
... Chemical Hazards: harmful chemicals in the air, water, soil, food (human body contains about 500 synthetic chemicals whose health effects are unknown) ...
... Chemical Hazards: harmful chemicals in the air, water, soil, food (human body contains about 500 synthetic chemicals whose health effects are unknown) ...
1.1 Modern Cell Theory- All organisms (living things) are composed
... of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Many organisms are single-celled and that one cell must carry out all the basic functions of life. Other organisms are multicellular and the cells that form these organisms can be organized at various levels to carry ...
... of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Many organisms are single-celled and that one cell must carry out all the basic functions of life. Other organisms are multicellular and the cells that form these organisms can be organized at various levels to carry ...
1. Which phrase is an example of autotrophic
... weeks, and then it grew slower. (4) The plant grew slowest during the first three weeks, and then it grew faster ...
... weeks, and then it grew slower. (4) The plant grew slowest during the first three weeks, and then it grew faster ...
Sue G feedback
... and be able to present it to the class. In addition, they will be able to “connect” their system to at least one other system and explain the benefits/necessity of being “connected.” Finally, students will provide three do’s and don’ts of how to keep their systems working without breaking down. Whic ...
... and be able to present it to the class. In addition, they will be able to “connect” their system to at least one other system and explain the benefits/necessity of being “connected.” Finally, students will provide three do’s and don’ts of how to keep their systems working without breaking down. Whic ...
Cell organization and Diffusion
... 2 An organ is a collection of several different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function in the body, e.g. heart pumps blood around the body, the stomach collects the food you eat and continues the digestive process (any two examples). An organ system is a number of organs which ...
... 2 An organ is a collection of several different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function in the body, e.g. heart pumps blood around the body, the stomach collects the food you eat and continues the digestive process (any two examples). An organ system is a number of organs which ...
1 A. Biology: Glossary
... biofilm colony of prokaryotes that is stuck to a surface such as a rock or a host’s tissue biogeochemical cycle interconnected pathways through which water or a chemical element such as carbon is continuously recycled through the biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere biogeography study of ho ...
... biofilm colony of prokaryotes that is stuck to a surface such as a rock or a host’s tissue biogeochemical cycle interconnected pathways through which water or a chemical element such as carbon is continuously recycled through the biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere biogeography study of ho ...
Presentation - JigCell
... require two orders of magnitude in additional complexity. • We hope our current vision for tools can supply one order of magnitude. • The other order of magnitude is an open problem. ...
... require two orders of magnitude in additional complexity. • We hope our current vision for tools can supply one order of magnitude. • The other order of magnitude is an open problem. ...
EOG Review Human Body and Genetics SI
... 5. The stomach and the intestines are parts of the digestive system. The digestive system breaks food down into small particles of nutrients that body cells can use. Food enters the digestive system through the mouth and travels down the esophagus to the stomach and the intestines, where it is diges ...
... 5. The stomach and the intestines are parts of the digestive system. The digestive system breaks food down into small particles of nutrients that body cells can use. Food enters the digestive system through the mouth and travels down the esophagus to the stomach and the intestines, where it is diges ...
PowerPoint - New Mexico FFA
... For this activity have students mash two creatures together to create an new animal. After they create (draw or Photoshop) their creature, have them name and scientific name it and describe its special characteristics. Have them explain where it lives, what it eats, what eats it,. Have students des ...
... For this activity have students mash two creatures together to create an new animal. After they create (draw or Photoshop) their creature, have them name and scientific name it and describe its special characteristics. Have them explain where it lives, what it eats, what eats it,. Have students des ...
Week 4 Evolution Ideas and Evidence
... Mutations which increase an animals fitness are beneficial while mutations which decrease it are harmful. Mutations which have no af fect on fitness are neutral Mutation rates themselves are quite low and thus do not change a population very quickly by themselves But with natural selection, th ...
... Mutations which increase an animals fitness are beneficial while mutations which decrease it are harmful. Mutations which have no af fect on fitness are neutral Mutation rates themselves are quite low and thus do not change a population very quickly by themselves But with natural selection, th ...
Chapter 35. - Cloudfront.net
... “typical” plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
... “typical” plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.