department of biology - Medgar Evers College
... Biology 403 is a one semester, 4 credit course that meets 3 hours per week for lecture and 3 hours per week for lab. The course is designed for Biology major students. The course will enable the students to learn about microorganisms, methods of their studies, mechanism of energy generation in diffe ...
... Biology 403 is a one semester, 4 credit course that meets 3 hours per week for lecture and 3 hours per week for lab. The course is designed for Biology major students. The course will enable the students to learn about microorganisms, methods of their studies, mechanism of energy generation in diffe ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... All proteins are made of 20 different amino acids linked in different orders Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell ...
... All proteins are made of 20 different amino acids linked in different orders Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell ...
M.Sc. (Prev.) ZOOLOGY Exam. –2014 Distribution of Marks Paper
... Study of sections of the arm of a starfish: water vascular system of starfish; IV. Permanent preparations and their study : 1. Preparation of cultures of Amoeba, Paramaecium and Euglena.Study of these protozoans using vital dyes. 2. Permanent preparations of Amoeba. Paramaecium and Euglena from cult ...
... Study of sections of the arm of a starfish: water vascular system of starfish; IV. Permanent preparations and their study : 1. Preparation of cultures of Amoeba, Paramaecium and Euglena.Study of these protozoans using vital dyes. 2. Permanent preparations of Amoeba. Paramaecium and Euglena from cult ...
Protein Synthesis
... which genes will be expressed (used to make a protein). This can be affected by the cell’s history and/or environment (g+e=p) Proteins may be overproduced, underproduced or produced at incorrect times ...
... which genes will be expressed (used to make a protein). This can be affected by the cell’s history and/or environment (g+e=p) Proteins may be overproduced, underproduced or produced at incorrect times ...
unit b1 – influences on life checklist
... advantageous characteristics to their offspring f gradual change – over a period of time the proportion of individuals with the advantageous characteristics in the population will increase compared with the proportion of individuals with poorly adapted characteristics, and the poorly adapted charact ...
... advantageous characteristics to their offspring f gradual change – over a period of time the proportion of individuals with the advantageous characteristics in the population will increase compared with the proportion of individuals with poorly adapted characteristics, and the poorly adapted charact ...
What are atoms and molecules?
... LIPIDS – What do they do They are a great source of STORED ENERGY so we have it in the future. They INSULATE the body to maintain normal body temperature and they CUSHION the internal organs for ...
... LIPIDS – What do they do They are a great source of STORED ENERGY so we have it in the future. They INSULATE the body to maintain normal body temperature and they CUSHION the internal organs for ...
Chapter 1 - The Science of Biology - holyoke
... data - the information gathered from observations quantitative data = numbers qualitative data = descriptive inference - a logical interpretation based on prior knowledge or experience hypothesis - a proposed scientific explanation ***Science is and ongoing process*** ...
... data - the information gathered from observations quantitative data = numbers qualitative data = descriptive inference - a logical interpretation based on prior knowledge or experience hypothesis - a proposed scientific explanation ***Science is and ongoing process*** ...
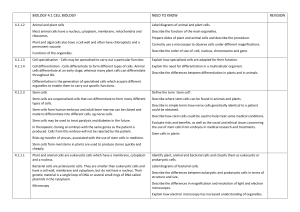
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Give examples of substances that diffuse into and out of cells. Calculate and compare surface area: volume ratios. Explain how the small intestine and lungs in mammals, and roots and leaves in plants, are adapted for exchange of substances. Describe and explain how an exchange surface is made more e ...
... Give examples of substances that diffuse into and out of cells. Calculate and compare surface area: volume ratios. Explain how the small intestine and lungs in mammals, and roots and leaves in plants, are adapted for exchange of substances. Describe and explain how an exchange surface is made more e ...
Cell Theory
... soh sie TOH sis). During exocytosis, a vesicle forms around a large particle within the cell. The vesicle carries the particle to the cell membrane. The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases the particle to the outside of the cell. ...
... soh sie TOH sis). During exocytosis, a vesicle forms around a large particle within the cell. The vesicle carries the particle to the cell membrane. The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane and releases the particle to the outside of the cell. ...
summary of b1 topic 1
... Viruses are not classified into any of the 5 kingdoms because viruses are non-living and the kingdoms only contain living organisms. Viruses are classed as non-living because they do not fulfil all of the 7 life processes. They can only reproduce. They take over a host cell, injecting its DNA which ...
... Viruses are not classified into any of the 5 kingdoms because viruses are non-living and the kingdoms only contain living organisms. Viruses are classed as non-living because they do not fulfil all of the 7 life processes. They can only reproduce. They take over a host cell, injecting its DNA which ...
Structure and Function in Living Systems Chapter 8: Systems in
... Ex: tendons and ligaments - bind other tissues together Tendons: muscles to bone and cartilage to internal skeleton Ligaments: bones to cartilage - unified ...
... Ex: tendons and ligaments - bind other tissues together Tendons: muscles to bone and cartilage to internal skeleton Ligaments: bones to cartilage - unified ...
Prepared by Ms. Bowie Biology 11 Exam Preparation Notes Page 1
... a. The info card is a 4”x6” index card (provided by your teacher). You are permitted to write any information you think might be important on ONE (1) side of the card (only). Your name should be written on the other side. The info on the card must be created originally by you (not simply a copy of s ...
... a. The info card is a 4”x6” index card (provided by your teacher). You are permitted to write any information you think might be important on ONE (1) side of the card (only). Your name should be written on the other side. The info on the card must be created originally by you (not simply a copy of s ...
Organs - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... tissue type; most contain all four types. The wall of the gut is an example. Individual organs are part of an organ system, a group of organs that work together (e.g., the digestive system). ...
... tissue type; most contain all four types. The wall of the gut is an example. Individual organs are part of an organ system, a group of organs that work together (e.g., the digestive system). ...
The questions below were presented in different
... Cardiac muscle cells are striated, reflecting organization of thin and thick filaments (actin and myosin), whereas smooth muscle cells are not. Cardiac muscle cells can be branched whereas smooth muscle cells are not. Cardiac muscle cells have more mitochondria than smooth muscle cells. Card ...
... Cardiac muscle cells are striated, reflecting organization of thin and thick filaments (actin and myosin), whereas smooth muscle cells are not. Cardiac muscle cells can be branched whereas smooth muscle cells are not. Cardiac muscle cells have more mitochondria than smooth muscle cells. Card ...
Cell
... Epithelial tissue: covers surfaces of the body. Inside the body, epithelial tissue serves as a lining or covering for internal organs. Forms a layer of skin outside the body. Connective tissue: Connects all parts of the body and provides support. Examples of connective tissue includes tendons, ligam ...
... Epithelial tissue: covers surfaces of the body. Inside the body, epithelial tissue serves as a lining or covering for internal organs. Forms a layer of skin outside the body. Connective tissue: Connects all parts of the body and provides support. Examples of connective tissue includes tendons, ligam ...
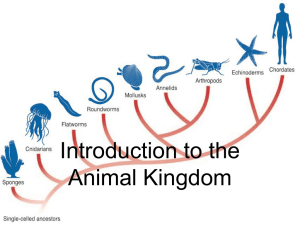
Zoology * Chapter 9 * Multicellular and Tissue Levels of Organization
... Stage in their life history is the _____________. Unlike hydrozoan medusae, scyphozoan medusae lack a ____________, the mesoglea contains amoeboid mesenchyme cells, ________________ occur in the gastrodermis as well as the epidermis, and ________________ are gastrodermal in origin. Many scyphozoans ...
... Stage in their life history is the _____________. Unlike hydrozoan medusae, scyphozoan medusae lack a ____________, the mesoglea contains amoeboid mesenchyme cells, ________________ occur in the gastrodermis as well as the epidermis, and ________________ are gastrodermal in origin. Many scyphozoans ...
powerpoint note presentation
... accelerated rapidly from 525-535 million years ago, during the Cambrian period. – Because so many animal body plans and new phyla appear in the fossils from such an evolutionarily short time span, biologists call this episode the Cambrian explosion. ...
... accelerated rapidly from 525-535 million years ago, during the Cambrian period. – Because so many animal body plans and new phyla appear in the fossils from such an evolutionarily short time span, biologists call this episode the Cambrian explosion. ...
Bio 102
... 2. Freeman, S., Quillin, K., & Allison, L. (2013). Biological Science (5th ed., Vol. 1). Benjamin Cummings . Freeman's Biological Science helps teach readers the fundamentals while introducing them to the excitement that drives the science. By presenting unifying concepts and methods of analysis, th ...
... 2. Freeman, S., Quillin, K., & Allison, L. (2013). Biological Science (5th ed., Vol. 1). Benjamin Cummings . Freeman's Biological Science helps teach readers the fundamentals while introducing them to the excitement that drives the science. By presenting unifying concepts and methods of analysis, th ...
What is Physiology? The Chemical Level Cells Tissues Types of
... Levels of Structural Organization in the Human Body ...
... Levels of Structural Organization in the Human Body ...
Understanding the Food Chain and Natural Selection
... The term “natural selection” was introduced by Charles Darwin in his 1859 book The Origin of Species. In the book, he described natural selection as the process by which species adapt to their environment. In the process, favorable heritable traits become more common in successive generations of a p ...
... The term “natural selection” was introduced by Charles Darwin in his 1859 book The Origin of Species. In the book, he described natural selection as the process by which species adapt to their environment. In the process, favorable heritable traits become more common in successive generations of a p ...
Big Idea 14 : Organization and Development of Living Organisms
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
Levels of Organization
... what you think are the 5 Levels – Data Collector will be the recorder. ...
... what you think are the 5 Levels – Data Collector will be the recorder. ...
Feedback Mechanisms and Types of Neurons
... Negative Feedback • *Most common mechanism for homeostasis – The results of the process stop the process from continuing (selflimiting) – Maintains conditions within a certain range ...
... Negative Feedback • *Most common mechanism for homeostasis – The results of the process stop the process from continuing (selflimiting) – Maintains conditions within a certain range ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.