Pre-AP Bio 8-29
... Endosymbiont Hypothesis • A. This hypothesis was proposed by Lynn Margulis in the 1960’s. • B. Define symbiosis and introduce common types of symbiotic relationships. ...
... Endosymbiont Hypothesis • A. This hypothesis was proposed by Lynn Margulis in the 1960’s. • B. Define symbiosis and introduce common types of symbiotic relationships. ...
DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS
... Carl Linnaeus, father of modern botany, was a Swedish naturalist who laid the foundation of modern classification and nomenclature in 1758. He devised a binomial system of nomenclature (naming system) in which an organism is given two names: ...
... Carl Linnaeus, father of modern botany, was a Swedish naturalist who laid the foundation of modern classification and nomenclature in 1758. He devised a binomial system of nomenclature (naming system) in which an organism is given two names: ...
Chapter One Vocab Biology Organism Organization Growth
... Remember biology = the study of life, but what is life exactly??? To be considered a living thing an organism must posses ALL of the characteristics of life! For each characteristic, list it, write a brief description, and sketch a picture to help you remember it. The first one is done for you. ...
... Remember biology = the study of life, but what is life exactly??? To be considered a living thing an organism must posses ALL of the characteristics of life! For each characteristic, list it, write a brief description, and sketch a picture to help you remember it. The first one is done for you. ...
Buzzle – Zoology Terms – Glossary of Biology Terms and Definitions
... Beta Diversity: A term of measurement that gauges the variety of organisms in a region. It is impacted by the turnover of species among habitats. Bilateral Symmetry: This type of symmetry is exhibited by most animals, and just means that if a line were drawn down the middle of the body, both sides w ...
... Beta Diversity: A term of measurement that gauges the variety of organisms in a region. It is impacted by the turnover of species among habitats. Bilateral Symmetry: This type of symmetry is exhibited by most animals, and just means that if a line were drawn down the middle of the body, both sides w ...
Bell Work: 4/8/13
... What is the function of this organ system? transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells breaking food down into nutrients that cells can use producing offspring ...
... What is the function of this organ system? transporting oxygen and nutrients to cells breaking food down into nutrients that cells can use producing offspring ...
Invasive alien plants on Irish roads – challenges
... Manage vegetation to promote resistance Early identification and early treatment reduce costs Accurate costing based on distribution, density, treatment Work with the biology/ecology of the species: let density effects do some of the work; knowing the age/timing of seed set can buy time; work down t ...
... Manage vegetation to promote resistance Early identification and early treatment reduce costs Accurate costing based on distribution, density, treatment Work with the biology/ecology of the species: let density effects do some of the work; knowing the age/timing of seed set can buy time; work down t ...
Science - New Charter Academy
... and enjoy their study of Science through A-Levels and beyond. The curriculum is delivered in eight specialist rooms. ...
... and enjoy their study of Science through A-Levels and beyond. The curriculum is delivered in eight specialist rooms. ...
Cells and Systems Quiz – Section 1 and 2 – Study Guide
... chloroplast, parts of the microscope, unicellular, multicellular, semi-permeable, selectively permeable, diffusion, osmosis, the five systems, enzymes, mechanical and chemical digestion, peristalsis, villi, alveoli, trachea, ureter, urethra, nephron, sweat glands, peripheral nervous system, central ...
... chloroplast, parts of the microscope, unicellular, multicellular, semi-permeable, selectively permeable, diffusion, osmosis, the five systems, enzymes, mechanical and chemical digestion, peristalsis, villi, alveoli, trachea, ureter, urethra, nephron, sweat glands, peripheral nervous system, central ...
Living Systems - Lonoke School District
... nature of structure and function. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, whole organisms, and ecosystems. • Big Idea: All organisms are composed of cells-the fundamental unit of life. Most organisms are single cells: other organisms ...
... nature of structure and function. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, whole organisms, and ecosystems. • Big Idea: All organisms are composed of cells-the fundamental unit of life. Most organisms are single cells: other organisms ...
1.1 Cells – structure and function
... For each of the following statements, say whether it is true or false. 1 All living things are made of many eukaryotic cells. 2 Plant cells do not contain mitochondria. 3 Animal cells do not have a large vacuole. 4 The cell membrane controls which substances enter and leave a cell. ...
... For each of the following statements, say whether it is true or false. 1 All living things are made of many eukaryotic cells. 2 Plant cells do not contain mitochondria. 3 Animal cells do not have a large vacuole. 4 The cell membrane controls which substances enter and leave a cell. ...
Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi
... • Like all living things, bacteria need to have a sources of food and a way to break that food down in order to survive. ...
... • Like all living things, bacteria need to have a sources of food and a way to break that food down in order to survive. ...
CANCER COURSE MODULE SIGN
... place, and are generally capped at maximum of twelve students (six, in the case of Module A2, as this has a laboratory component). ...
... place, and are generally capped at maximum of twelve students (six, in the case of Module A2, as this has a laboratory component). ...
Moore 1 Timothy Moore Life Science: Semester 1 Assessment 22
... membrane. Animal cells have only the cell membrane. Also, plants produce their own energy using chloroplasts. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts and get their energy from the food they ingest. Both plant and animal cells have nucleus which control the cells function and house the DNA. The mitocho ...
... membrane. Animal cells have only the cell membrane. Also, plants produce their own energy using chloroplasts. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts and get their energy from the food they ingest. Both plant and animal cells have nucleus which control the cells function and house the DNA. The mitocho ...
Homeostasis (Active and Passive Transport)
... solution would be hypotonic and the cell would be hypertonic Water would rush into the cell, causing it to swell and eventually burst This doesn’t often happen because cells in the body of multicellular organisms are protected from fresh water, and are instead bathed in isotonic fluids such as blood ...
... solution would be hypotonic and the cell would be hypertonic Water would rush into the cell, causing it to swell and eventually burst This doesn’t often happen because cells in the body of multicellular organisms are protected from fresh water, and are instead bathed in isotonic fluids such as blood ...
Cell and Human Body and Chemistry SC PASS Notes
... Mitosis – occurs in nucleus; cell reproduction; makes exact copy of cell; produces 2 identical daughter cells (look like parent cell) from 1 parent cell; use for growth, replacement, & asexual reproduction Genetic information (DNA) is passed from parent to offspring causing offspring to have similar ...
... Mitosis – occurs in nucleus; cell reproduction; makes exact copy of cell; produces 2 identical daughter cells (look like parent cell) from 1 parent cell; use for growth, replacement, & asexual reproduction Genetic information (DNA) is passed from parent to offspring causing offspring to have similar ...
Preface 1 PDF
... resulted in the Euglena chloroplast being among the first photosynthetic organelles whose genome was physically characterized and sequenced. The undeveloped plastids in dark-grown Euglena, the facile induction by light exposure of the enzymatic machinery required to transform the plastid into a phot ...
... resulted in the Euglena chloroplast being among the first photosynthetic organelles whose genome was physically characterized and sequenced. The undeveloped plastids in dark-grown Euglena, the facile induction by light exposure of the enzymatic machinery required to transform the plastid into a phot ...
Cells_and_Tissues_in_Health_and_Disease
... Basic Structure and Organization of Cells • Nucleus: contains genetic information; directs metabolic function of cells • Cytoplasm: surrounds nucleus; structures carry out directions of the nucleus • Cell: basic structural and functional unit of the body • Tissues: group of similar cells performing ...
... Basic Structure and Organization of Cells • Nucleus: contains genetic information; directs metabolic function of cells • Cytoplasm: surrounds nucleus; structures carry out directions of the nucleus • Cell: basic structural and functional unit of the body • Tissues: group of similar cells performing ...
CELL WALL - Winona ISD
... structure. 2. The cell is the basic unit of function. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... structure. 2. The cell is the basic unit of function. 3. All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
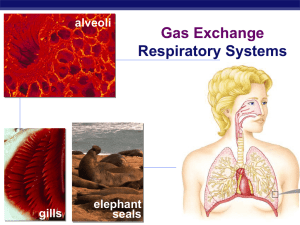
Gas Exchange print ppt
... Evolution of gas exchange structures Aquatic organisms external systems with lots of surface area exposed to aquatic environment ...
... Evolution of gas exchange structures Aquatic organisms external systems with lots of surface area exposed to aquatic environment ...
Human Body Introduction
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
Viruses & Bacteria
... between cells, concentrated in particular organ (spleen and lungs) – Natural killer cells – attack cells infected with pathogens, puncture cell membrane, water rushes into infected cell which swells & ...
... between cells, concentrated in particular organ (spleen and lungs) – Natural killer cells – attack cells infected with pathogens, puncture cell membrane, water rushes into infected cell which swells & ...
review for the biology regents exam
... • DIFFUSION: movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Requires no energy (passive transport) • ACTIVE TRANSPORT: requires energy, usually movement of molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration (against the natural flow of dif ...
... • DIFFUSION: movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Requires no energy (passive transport) • ACTIVE TRANSPORT: requires energy, usually movement of molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration (against the natural flow of dif ...
Minor Sheet - College of Arts and Sciences
... Biology, 300 Aronoff Laboratory, 318 W. 12th Ave., Columbus, OH 43210-1293; 614-292-8088; https://eeob.osu.edu/ The minor in evolution and ecology focuses on the descent and interrelationships of organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. These two disciplines provide an understanding ...
... Biology, 300 Aronoff Laboratory, 318 W. 12th Ave., Columbus, OH 43210-1293; 614-292-8088; https://eeob.osu.edu/ The minor in evolution and ecology focuses on the descent and interrelationships of organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. These two disciplines provide an understanding ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.