Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Nail root- grows new nail Cuticle- protects nail root Lunula- white half-moon at base- thick layer of cells ...
... Nail root- grows new nail Cuticle- protects nail root Lunula- white half-moon at base- thick layer of cells ...
abbey secondary school
... 11Briefly explain what are the changes occurs in blood as it pass through different parts of the body. ...
... 11Briefly explain what are the changes occurs in blood as it pass through different parts of the body. ...
BIOLOGY Specification
... a. define as nuclear division that leads to two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes so are genetically identical to each other and the parental cell b. recall the role of mitosis in growth of tissues by increasing cell number, repair of tissues, replacement of worn out cells and ...
... a. define as nuclear division that leads to two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes so are genetically identical to each other and the parental cell b. recall the role of mitosis in growth of tissues by increasing cell number, repair of tissues, replacement of worn out cells and ...
Cell Physiology
... • The tubules and vesicles interconnect with one another • The space inside the tubules and vesicles is filled with endoplasmic matrix (a watery fluid medium) • Mainly conduction system: substances enter the space and conducted to other parts of the cell • Vast surface area and multiple enzyme syste ...
... • The tubules and vesicles interconnect with one another • The space inside the tubules and vesicles is filled with endoplasmic matrix (a watery fluid medium) • Mainly conduction system: substances enter the space and conducted to other parts of the cell • Vast surface area and multiple enzyme syste ...
Intermediate Filament Cytoskeleton, Vol 78. Methods in Cell Biology Brochure
... comprehensive resource of methodology essentials, describing a variety of essential tools and assays for studying intermediate filaments. The book provides user-friendly advice and protocols covering all aspects of intermediate filaments including protein isolation and structure, protein and gene re ...
... comprehensive resource of methodology essentials, describing a variety of essential tools and assays for studying intermediate filaments. The book provides user-friendly advice and protocols covering all aspects of intermediate filaments including protein isolation and structure, protein and gene re ...
CELLS AND HEREDITY
... organisms have a contractile vacuole which pumps excess water out of the cell. Freshwater fish remove excess water through their gills. In a HYPERTONIC solution, cells can shrivel up because more water flows out of the cell than into it. Drinking seawater is dangerous to humans because the ocean is ...
... organisms have a contractile vacuole which pumps excess water out of the cell. Freshwater fish remove excess water through their gills. In a HYPERTONIC solution, cells can shrivel up because more water flows out of the cell than into it. Drinking seawater is dangerous to humans because the ocean is ...
EOC Warm-up Review Part I and II
... 16. The image to the right represents a cell with a semipermeable membrane. The process of osmosis would explain the net movement of water into a cell if the initial percentage of – A. protein was 35% inside the cell and 30% outside the cell. B. water was 95% inside the cell and 90% outside the cell ...
... 16. The image to the right represents a cell with a semipermeable membrane. The process of osmosis would explain the net movement of water into a cell if the initial percentage of – A. protein was 35% inside the cell and 30% outside the cell. B. water was 95% inside the cell and 90% outside the cell ...
The Institute of Marine Research (IMR) (http://www
... This is a permanent position based at Matre Aquaculture Research Station and focusing on fish welfare or environmental conditions in fish pens. We are seeking an innovative and creative scientist with good cooperative and communication skills and profiled qualifications in fish physiology, fishery b ...
... This is a permanent position based at Matre Aquaculture Research Station and focusing on fish welfare or environmental conditions in fish pens. We are seeking an innovative and creative scientist with good cooperative and communication skills and profiled qualifications in fish physiology, fishery b ...
Evolution of Systems for Exchange
... Single-celled organisms exchange gases directly across cell membrane. However, the slow diffusion rate of oxygen/carbon dioxide limits size. Simple animals lack specialized exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans Earthworms have a series of thin-walled blood vessels know ...
... Single-celled organisms exchange gases directly across cell membrane. However, the slow diffusion rate of oxygen/carbon dioxide limits size. Simple animals lack specialized exchange surfaces have flattened, tubular, or thin shaped body plans Earthworms have a series of thin-walled blood vessels know ...
Role of intestinal mucins in innate host defense
... responses against a plethora of microorganisms, including commensals and pathogens. In this review, we present a comprehensive overview on mucin biology, its properties, classification and gene assembly. We also consider the structure of the mucin gene, its proteins and its role in innate host defen ...
... responses against a plethora of microorganisms, including commensals and pathogens. In this review, we present a comprehensive overview on mucin biology, its properties, classification and gene assembly. We also consider the structure of the mucin gene, its proteins and its role in innate host defen ...
Scientific Method Web Resources
... We are Getting Nerdy! Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...
... We are Getting Nerdy! Mel and Gerdy are two life science teachers with a true passion for curriculum design. We LOVE creating time-saving, fun and engaging activities for our classrooms & we’re excited to be sharing them with you. We look forward to hearing your feedback on this product. ...
CELLS AND HEREDITY
... 1. All organisms are composed of cells. (Schleiden and Schwann) 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. (Schleiden and Schwann) 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. (Virchow) The virus does not fit this theory. It is a packet of nucleic acid wrapped in a protein coa ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of cells. (Schleiden and Schwann) 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. (Schleiden and Schwann) 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. (Virchow) The virus does not fit this theory. It is a packet of nucleic acid wrapped in a protein coa ...
Animal Systems
... ________________________ acquire energy from organic molecules made by other organisms __________________________________ harvests the chemical energy from food which is stored as ______; this energy is then used for _______ or lost as _________ Metabolic rate Total amount of ___________ and anim ...
... ________________________ acquire energy from organic molecules made by other organisms __________________________________ harvests the chemical energy from food which is stored as ______; this energy is then used for _______ or lost as _________ Metabolic rate Total amount of ___________ and anim ...
Cell
... • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the b ...
... • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the b ...
Body System Structures Function
... bloodstream. Digestion occurs as food passes through a series of digestive organs and is broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive ...
... bloodstream. Digestion occurs as food passes through a series of digestive organs and is broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive ...
Cell Organelles and Biotechnology
... cell at some time in the distant past. The larger cell would have gained the ability to make its own food, and have a greater ability to break down foods by cellular respiration. The smaller bacterial cells would have gained the food-gathering ability of the larger cells. We have some evidence for t ...
... cell at some time in the distant past. The larger cell would have gained the ability to make its own food, and have a greater ability to break down foods by cellular respiration. The smaller bacterial cells would have gained the food-gathering ability of the larger cells. We have some evidence for t ...
Daily Tasks 11-16 through 11-24
... Organization in the Human Body -Lesson 15, pgs. 169172 Guided Practice- Notes (1-5) ...
... Organization in the Human Body -Lesson 15, pgs. 169172 Guided Practice- Notes (1-5) ...
BIOL 105 QZ 6 Q NS SS ES LS 130510.3
... D) create turbulence in the air to trap small particulates in mucus. E) provide an opening to the outside of the body. ...
... D) create turbulence in the air to trap small particulates in mucus. E) provide an opening to the outside of the body. ...
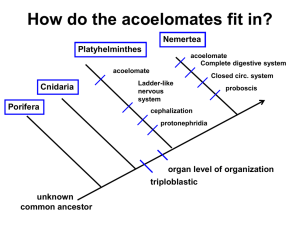
Notes on Invertebrates
... • Cilia at anterior end draw food into mouth. • Very complex for a pseudocoelomate Phylum: Nematoda. • Roundworms • Freshwater, marine, tissues and fluids of plants and animals. • Causes diseases such as elephantiasis, river blindness • Function as decomposers, parasites (Trichinella in pork). Caeno ...
... • Cilia at anterior end draw food into mouth. • Very complex for a pseudocoelomate Phylum: Nematoda. • Roundworms • Freshwater, marine, tissues and fluids of plants and animals. • Causes diseases such as elephantiasis, river blindness • Function as decomposers, parasites (Trichinella in pork). Caeno ...
Major Divisions of Life
... Guinea worm (Dracunculus medinensis): • transmitted by infected copepods in drinking water • larvae move into the body cavity • female adult migrates to the subcutaneous tissue, causes an ulcer/blister, and releases eggs through hole when host comes in ...
... Guinea worm (Dracunculus medinensis): • transmitted by infected copepods in drinking water • larvae move into the body cavity • female adult migrates to the subcutaneous tissue, causes an ulcer/blister, and releases eggs through hole when host comes in ...
A Journey Through the Cell: Part One—Cells: An Introduction
... cells. The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings, but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. ● Understand that the genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. The code used is virtually ...
... cells. The cells in similar tissues and organs in other animals are similar to those in human beings, but differ somewhat from cells found in plants. ● Understand that the genetic information encoded in DNA molecules provides instructions for assembling protein molecules. The code used is virtually ...
Fall Exam Review 2016
... cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, nucleus, Golgi body, and ribosome. 2. Draw a plant cell and label the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and nucleus. 3. Create a chart for the following organelles, which includes a brief ...
... cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, nucleus, Golgi body, and ribosome. 2. Draw a plant cell and label the following organelles: cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and nucleus. 3. Create a chart for the following organelles, which includes a brief ...
Middle School Science glossary
... capillaries) which provide a continuous flow of blood to your body, supplying the tissues with oxygen and nutrients climate- the long-term weather conditions for a region, generally determined by several years of records comet- a small body composed of ice and rock that travels in an elliptical orbi ...
... capillaries) which provide a continuous flow of blood to your body, supplying the tissues with oxygen and nutrients climate- the long-term weather conditions for a region, generally determined by several years of records comet- a small body composed of ice and rock that travels in an elliptical orbi ...
C1B – Chemistry - Tavistock College Science Department
... A palisade cell is tall with a large surface area It's found on the top side of a leaf - ideal for good absorption of carbon dioxide and light - both are needed for photosynthesis They're packed with chloroplasts, which contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which is needed for photosynthesis 4) The ...
... A palisade cell is tall with a large surface area It's found on the top side of a leaf - ideal for good absorption of carbon dioxide and light - both are needed for photosynthesis They're packed with chloroplasts, which contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which is needed for photosynthesis 4) The ...
PHS 398 (Rev. 9/04), Biographical Sketch Format Page
... characterization experiments this project demands. Focusing this powerful technology towards the task of identifying new interacting proteins and post-translational modifications will require technical and computational expertise, and biological insight. My graduate and post-graduate work in each of ...
... characterization experiments this project demands. Focusing this powerful technology towards the task of identifying new interacting proteins and post-translational modifications will require technical and computational expertise, and biological insight. My graduate and post-graduate work in each of ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.