Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells make up the
... organ and muscle tissue), and the organisms survive based on products that the cells make. For example, cells in the pancreas make insulin, which is necessary to ensure that the blood glucose level doesn’t skyrocket. Without insulin, the blood glucose can reach a level that is lethal. So, without th ...
... organ and muscle tissue), and the organisms survive based on products that the cells make. For example, cells in the pancreas make insulin, which is necessary to ensure that the blood glucose level doesn’t skyrocket. Without insulin, the blood glucose can reach a level that is lethal. So, without th ...
CxVirus(NoTP)
... • Carry and directly transfer cancer causing genes by infecting target cells? • Be present in the germ line as provirus copies in the host DNA From infection in times past Reactivated by carcinogenic events? • Be inserted into the host cell genome and misregulate endogenous host genes? • Infect host ...
... • Carry and directly transfer cancer causing genes by infecting target cells? • Be present in the germ line as provirus copies in the host DNA From infection in times past Reactivated by carcinogenic events? • Be inserted into the host cell genome and misregulate endogenous host genes? • Infect host ...
Class 10th CBSE how do organisms Reproduction
... temperature were to be increased by global warming, most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would servive and grow further, variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time. ...
... temperature were to be increased by global warming, most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would servive and grow further, variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time. ...
1. What is true of all fungi? They are a. eukaryotic, heterotrophic
... d. by consuming living, rather than dead, prey. e. by using enzymes to digest their food. 12. Assuming that all of the following events occur, what is the correct sequence in which the following processes occur during the development of an individual animal? 1. gastrulation 2. metamorphosis 3. ferti ...
... d. by consuming living, rather than dead, prey. e. by using enzymes to digest their food. 12. Assuming that all of the following events occur, what is the correct sequence in which the following processes occur during the development of an individual animal? 1. gastrulation 2. metamorphosis 3. ferti ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
... Fermentation by fungi produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. Humans use fungi to ferment food sources producing bread, alcohol and cheese. Fungi are used for medicines. It was discovered that fungi produce a chemical which affects bacterial growth, now used by humans as antibiotics. 16.4 Animals are a ...
LC Biology Sample Paper 6 HL Solutions
... (iii) Genetic screening: is the testing of a persons DNA to find the presence of altered or defective genes. (3) In favour: It may help in the location and early detection of defective genes which cause diseases like cancers, which on early detection can receive gene therapy to prevent. (3) Against: ...
... (iii) Genetic screening: is the testing of a persons DNA to find the presence of altered or defective genes. (3) In favour: It may help in the location and early detection of defective genes which cause diseases like cancers, which on early detection can receive gene therapy to prevent. (3) Against: ...
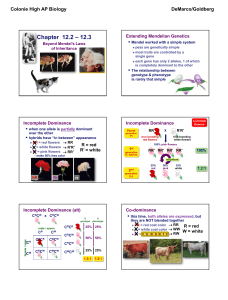
Lecture 030 - Beyond Mendel
... Some phenotypes determined by additive effects of 2 or more genes on a single character ...
... Some phenotypes determined by additive effects of 2 or more genes on a single character ...
Science Year 8 Learn Sheet DC4 – Respiration
... because your cells need more oxygen and glucose for respiration. Breathing is the movement of muscles in the diaphragm and attached to the ribs. These movements change the volume of the chest ...
... because your cells need more oxygen and glucose for respiration. Breathing is the movement of muscles in the diaphragm and attached to the ribs. These movements change the volume of the chest ...
paramedics - anatomy and physiology.indb
... All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing cells through cell replication and division. The human body is composed of billions of cells which are specially adapted for t ...
... All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing cells through cell replication and division. The human body is composed of billions of cells which are specially adapted for t ...
Excretion - JLooby Biology
... plants and animals In excess it lowers the pH (CO2 forms a weak acid – carbonic acid which dissolves in water) Lower pH can affect enzyme activity ...
... plants and animals In excess it lowers the pH (CO2 forms a weak acid – carbonic acid which dissolves in water) Lower pH can affect enzyme activity ...
Vital Functions for Human Life
... Vital Functions for Human Life In this section, you will be introduced to the major organ systems of the body. To put these systems in context, we will first discuss vital functions of life. Within any organism, there are a multitude of functions taking place at any given time. Humans, for example, ...
... Vital Functions for Human Life In this section, you will be introduced to the major organ systems of the body. To put these systems in context, we will first discuss vital functions of life. Within any organism, there are a multitude of functions taking place at any given time. Humans, for example, ...
Cells Unit
... The Circulatory System Purpose: to deliver oxygenated blood to the various cells and organ systems in your body so they can undergo cellular respiration Major Organs and Their Functions Heart – the major muscle of the circulatory system -- pumps blood through its four chambers (two ventricles and t ...
... The Circulatory System Purpose: to deliver oxygenated blood to the various cells and organ systems in your body so they can undergo cellular respiration Major Organs and Their Functions Heart – the major muscle of the circulatory system -- pumps blood through its four chambers (two ventricles and t ...
Contents - Beck-Shop
... The range is the spread of the values – from the smallest number of petals you counted, to the largest number. The range for the number of petals on the daisy flowers is 17 to 21. • The median is the middle value in your results. The median number of petals on the daisy flowers is 19. • The mode i ...
... The range is the spread of the values – from the smallest number of petals you counted, to the largest number. The range for the number of petals on the daisy flowers is 17 to 21. • The median is the middle value in your results. The median number of petals on the daisy flowers is 19. • The mode i ...
lecture_ch03_for website_updated 11_12_14
... You can think of a cell as a car factory. The control center holds the directions for making the car. There are assembly lines for constructing the engine and frame of the car. After the main structure of the car is built, the finishing touches are added (paint, leather seats, chrome bumpers). La ...
... You can think of a cell as a car factory. The control center holds the directions for making the car. There are assembly lines for constructing the engine and frame of the car. After the main structure of the car is built, the finishing touches are added (paint, leather seats, chrome bumpers). La ...
Organ Systems of the Body
... Regional – all structures in one part of the body (such as the abdomen or leg) Systemic – gross anatomy of the body studied by system Surface – study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin ...
... Regional – all structures in one part of the body (such as the abdomen or leg) Systemic – gross anatomy of the body studied by system Surface – study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin ...
Human Body Orientation
... 3. A ______ is the basic structural and functional component of life a. Humans are composed of 60-100 _____________ cells b. ______________, growth, responsiveness, repair, and replication are carried on at the cellular level 4. Cells are composed of organelles and cytoplasm surrounded by a plasma _ ...
... 3. A ______ is the basic structural and functional component of life a. Humans are composed of 60-100 _____________ cells b. ______________, growth, responsiveness, repair, and replication are carried on at the cellular level 4. Cells are composed of organelles and cytoplasm surrounded by a plasma _ ...
Biology 11 final review
... UNIT VI: VERTEBRATES The Rat – know the organs and their function. Be able to answer any of the questions from the lab. ...
... UNIT VI: VERTEBRATES The Rat – know the organs and their function. Be able to answer any of the questions from the lab. ...
3 Cells - Dr Magrann
... own energy (ATP). Cells have hundreds of mitochondria. Function of mitochondria is to make most of the cell’s ATP, which is cellular energy (ATP is an energy source). Some ATP is made in the cytosol, but most is made in the mitochondria. NOTE: Mitochondria must have OXYGEN to convert nutrients to AT ...
... own energy (ATP). Cells have hundreds of mitochondria. Function of mitochondria is to make most of the cell’s ATP, which is cellular energy (ATP is an energy source). Some ATP is made in the cytosol, but most is made in the mitochondria. NOTE: Mitochondria must have OXYGEN to convert nutrients to AT ...
09 - Animal Form & Function Sum13
... Re-read today’s lecture, highlight all vocabulary you do not understand, and look up terms. ...
... Re-read today’s lecture, highlight all vocabulary you do not understand, and look up terms. ...
Annexure `AAB-CD-01b` Course Title: ANATOMY AND
... To discuss the human body and its function. To analyze the structural aspect of systems of the body. To describe the concept of fundamental of human body organs. To analyze the functional aspects of Human body. ...
... To discuss the human body and its function. To analyze the structural aspect of systems of the body. To describe the concept of fundamental of human body organs. To analyze the functional aspects of Human body. ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.