Sue G feedback
... Essential Questions: 1. Can human body systems operate independently of one another? Why or why not. 2. How can we help our body systems work better? 3. Why is there an order to all systems? 4. What would happen if one step in a system is skipped or blocked? 5. What are some ways that people harm th ...
... Essential Questions: 1. Can human body systems operate independently of one another? Why or why not. 2. How can we help our body systems work better? 3. Why is there an order to all systems? 4. What would happen if one step in a system is skipped or blocked? 5. What are some ways that people harm th ...
Student Guide The Morphology and Function of Tissue Types Name
... Introduction: Histology is often a very difficult topic for students. You are expected to understand the morphology and function of various tissue types, and be able to identify these tissue types in a drawing or a prepared slide. Part 1: Flash Cards You will be given a “flash card” with information ...
... Introduction: Histology is often a very difficult topic for students. You are expected to understand the morphology and function of various tissue types, and be able to identify these tissue types in a drawing or a prepared slide. Part 1: Flash Cards You will be given a “flash card” with information ...
Chapter 4 - Los Angeles City College
... Senses stimuli and transmits signals from one part of the animal to another. Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. Neuron: Nerve cell. Structural and functional unit of nervous tissue. Consists of: Cell body : Contains cell’s nucleus. ...
... Senses stimuli and transmits signals from one part of the animal to another. Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its environment. Neuron: Nerve cell. Structural and functional unit of nervous tissue. Consists of: Cell body : Contains cell’s nucleus. ...
LAB 1: Scientific Method/Tools of Scientific Inquiry
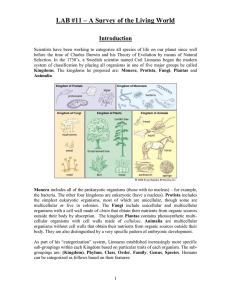
... LAB #11 – A Survey of the Living World Introduction Scientists have been working to categorize all species of life on our planet since well before the time of Charles Darwin and his Theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection. In the 1730’s, a Swedish scientist named Carl Linnaeus began the mo ...
... LAB #11 – A Survey of the Living World Introduction Scientists have been working to categorize all species of life on our planet since well before the time of Charles Darwin and his Theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection. In the 1730’s, a Swedish scientist named Carl Linnaeus began the mo ...
Human Body Structures and Systems gr5
... All self-replicating life forms are composed of cells—from single-celled bacteria to elephants, with their trillions of cells. Although a few giant cells, such as hens' eggs, can be seen with the naked eye, most cells are microscopic. It is at the cell level that many of the basic functions of organ ...
... All self-replicating life forms are composed of cells—from single-celled bacteria to elephants, with their trillions of cells. Although a few giant cells, such as hens' eggs, can be seen with the naked eye, most cells are microscopic. It is at the cell level that many of the basic functions of organ ...
Sample question
... compartments to allow more time for digestion of the grass. The earthworm has a tubular gut because it needs to be thin to burrow underground, but still be long enough to allow for digestion of food and absorption of nutrients. Having large storage compartments and folding like the cow and human wou ...
... compartments to allow more time for digestion of the grass. The earthworm has a tubular gut because it needs to be thin to burrow underground, but still be long enough to allow for digestion of food and absorption of nutrients. Having large storage compartments and folding like the cow and human wou ...
Organ Systems
... Which is the correct order from smallest to largest? A. Tissue, Cell, Organ, Organ System, Organism B. Cell, Tissue, Organ System, Organ, Organism C. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism D. Cell, Organ, Tissue, Organ System, Organism ...
... Which is the correct order from smallest to largest? A. Tissue, Cell, Organ, Organ System, Organism B. Cell, Tissue, Organ System, Organ, Organism C. Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism D. Cell, Organ, Tissue, Organ System, Organism ...
AS BIOLOGY UNITS
... 1.1.3 Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation During the cell cycle, genetic information is copied and passed to daughter cells. Microscopes can be used to view the different stages of the cycle. In multicellular organisms, stem cells are modified to produce many different types of ...
... 1.1.3 Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation During the cell cycle, genetic information is copied and passed to daughter cells. Microscopes can be used to view the different stages of the cycle. In multicellular organisms, stem cells are modified to produce many different types of ...
Binary fission
... *Letters in parentheses indicate phylogenetic status (B, Bacteria; A, Archaea). Representatives of either domain of prokaryotes are known in each category. Most eukaryotes are obligate aerobes, but facultative aerobes (for example, yeast) and obligate anaerobes (for example, certain protozoa and fun ...
... *Letters in parentheses indicate phylogenetic status (B, Bacteria; A, Archaea). Representatives of either domain of prokaryotes are known in each category. Most eukaryotes are obligate aerobes, but facultative aerobes (for example, yeast) and obligate anaerobes (for example, certain protozoa and fun ...
ARMT+Science Item Specs Grade7
... Describe how organisms reproduce using sexual and/or asexual methods. Describe how organisms are comprised of at least one cell. Describe how organisms use energy to undergo life processes. Describe how organisms exchange gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Describe how organisms res ...
... Describe how organisms reproduce using sexual and/or asexual methods. Describe how organisms are comprised of at least one cell. Describe how organisms use energy to undergo life processes. Describe how organisms exchange gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Describe how organisms res ...
Full Text - The International Journal of Developmental Biology
... on new molecular genetic aspects of early embryogenesis, especially gene structure and function in normogenesis, and including the close relationship of developmental biology to evolution, teratogenesis, carcinogenesis, and the influence of environmental factors on ontogenesis. Since the human genom ...
... on new molecular genetic aspects of early embryogenesis, especially gene structure and function in normogenesis, and including the close relationship of developmental biology to evolution, teratogenesis, carcinogenesis, and the influence of environmental factors on ontogenesis. Since the human genom ...
Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses
... chopping up the cell DNA, a process that shuts down the infected host cell – In this lytic infection, the virus then uses the materials of the host cell to make thousands of copies of its own DNA molecule ...
... chopping up the cell DNA, a process that shuts down the infected host cell – In this lytic infection, the virus then uses the materials of the host cell to make thousands of copies of its own DNA molecule ...
APBiology 12
... very sensitive to changes in body temperature. The rates of most enzyme-mediated reactions increase by a factor of 2 or 3 for every 10°C temperature increase, until proteins start to lose activity. o For example, the oxygen carrier hemoglobin becomes less effective at binding oxygen as temperature i ...
... very sensitive to changes in body temperature. The rates of most enzyme-mediated reactions increase by a factor of 2 or 3 for every 10°C temperature increase, until proteins start to lose activity. o For example, the oxygen carrier hemoglobin becomes less effective at binding oxygen as temperature i ...
Biology Cells Lecture B. Rife SOHI 2001
... A plant cell in a hypotonic solution, the cytoplasm and central vacuoles gain water, and plasma membrane pushes against the rigid cell wall. The resulting pressure, called turgor pressure, helps give internal support to the cell. An animal cell in a hypertonic solution will lose water and shrivel. A ...
... A plant cell in a hypotonic solution, the cytoplasm and central vacuoles gain water, and plasma membrane pushes against the rigid cell wall. The resulting pressure, called turgor pressure, helps give internal support to the cell. An animal cell in a hypertonic solution will lose water and shrivel. A ...
Structured Questions
... of a particular kind of organisms. Scientists try to classify them with the classification system that we use for the organisms on earth. One of the specimens has structures similar to a backbone. It has no limbs and looks like a snake and an eel. How can we determine whether it is a fish, an amphib ...
... of a particular kind of organisms. Scientists try to classify them with the classification system that we use for the organisms on earth. One of the specimens has structures similar to a backbone. It has no limbs and looks like a snake and an eel. How can we determine whether it is a fish, an amphib ...
A N N O T A T I O N S F R O M T H E L I T E R A T U R E
... resembling those of crocodiles instead of the unique system found in birds. Well-preserved remains of certain dinosaurs appear to indicate a non-avian respiratory system. For example, the theropod Sinosauropteryx (Compsognathidae) appears to have a vertical separation between the thoracic and abdomi ...
... resembling those of crocodiles instead of the unique system found in birds. Well-preserved remains of certain dinosaurs appear to indicate a non-avian respiratory system. For example, the theropod Sinosauropteryx (Compsognathidae) appears to have a vertical separation between the thoracic and abdomi ...
maximum mark: 60
... whereas (in the case of type 2) cells all over the body are dysfunctional ; and so cannot be replaced / much more difficult to replace them all ; use of stem cells may be preferable to transplants as less invasive / fewer side-effects / no need to wait for suitable donor ; use of patients own adult ...
... whereas (in the case of type 2) cells all over the body are dysfunctional ; and so cannot be replaced / much more difficult to replace them all ; use of stem cells may be preferable to transplants as less invasive / fewer side-effects / no need to wait for suitable donor ; use of patients own adult ...
Cells - Open Equal Free
... Salmonella grows in uncooked meat. Salmonella is one reason it is so important to cook meat. Salmonella can even live on a spoon or plate that touched raw meat or raw eggs earlier that day. Be careful, these guys would love to attack your cells too! ...
... Salmonella grows in uncooked meat. Salmonella is one reason it is so important to cook meat. Salmonella can even live on a spoon or plate that touched raw meat or raw eggs earlier that day. Be careful, these guys would love to attack your cells too! ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... cells then absorbs the digested matter. Extracelluar digestion increases the possible food supplies for organisms, as they are no longer limited to very small foods. Large amounts of organic matter could be ingested and then partially digested in order to be able to enter individual cells. Some exam ...
... cells then absorbs the digested matter. Extracelluar digestion increases the possible food supplies for organisms, as they are no longer limited to very small foods. Large amounts of organic matter could be ingested and then partially digested in order to be able to enter individual cells. Some exam ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.