Solutions - Vanier College
... d) They should all have about the same number of mitochondria 26. How would you distinguish a bacterium from an archaen and a eukaryote? a) Only the bacterium would be unicellular. b) Only the bacterium would lack a nucleus. c) Only the bacterium would be able to survive in extreme temperatures. d) ...
... d) They should all have about the same number of mitochondria 26. How would you distinguish a bacterium from an archaen and a eukaryote? a) Only the bacterium would be unicellular. b) Only the bacterium would lack a nucleus. c) Only the bacterium would be able to survive in extreme temperatures. d) ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... All living things take in and use energy – A plant uses sunlight and carbon dioxide to make sugars – A bear hunts and eats a fish in order to survive – You yawn to take in more oxygen when you are tired ...
... All living things take in and use energy – A plant uses sunlight and carbon dioxide to make sugars – A bear hunts and eats a fish in order to survive – You yawn to take in more oxygen when you are tired ...
Five Kingdoms of Living Things Created by Stella Thalluri 2014 www.beaconmedia.com.au
... Note: The recent discovery of Bacteria which is part of God's creation that live in extreme environment are placed under the Archaea. Bacteria and Archaea come under Monera. ...
... Note: The recent discovery of Bacteria which is part of God's creation that live in extreme environment are placed under the Archaea. Bacteria and Archaea come under Monera. ...
Groups of Living Things Ppt
... These bacteria are thought to be the ancestors of eukaryotic organisms. ▪ Examples include bacteria that live in hot springs. ▪ Bacteria cells are prokaryotic (no nucleus or organelles). The majority of bacteria are going to be unicellular; however, some bacteria form cooperative groups called colon ...
... These bacteria are thought to be the ancestors of eukaryotic organisms. ▪ Examples include bacteria that live in hot springs. ▪ Bacteria cells are prokaryotic (no nucleus or organelles). The majority of bacteria are going to be unicellular; however, some bacteria form cooperative groups called colon ...
5 Levels of Organization Notes
... LEVEL FOUR: ORGAN SYSTEMS Each organ in your body is part of an organ system, a group of organs that work together to perform a major function. For example, your heart is part of your circulatory system, which carries oxygen and other materials throughout your body. Besides the heart, blood vessels ...
... LEVEL FOUR: ORGAN SYSTEMS Each organ in your body is part of an organ system, a group of organs that work together to perform a major function. For example, your heart is part of your circulatory system, which carries oxygen and other materials throughout your body. Besides the heart, blood vessels ...
Evolution Practice Test - Miami Beach Senior High
... 23. In several species of birds, the males show off their bright colors and long feathers. The dull-colored females usually pick the brightest colored males for mates. Male offspring inherit their father's bright colors and long feathers. Compared to earlier generations, future generations of these ...
... 23. In several species of birds, the males show off their bright colors and long feathers. The dull-colored females usually pick the brightest colored males for mates. Male offspring inherit their father's bright colors and long feathers. Compared to earlier generations, future generations of these ...
How a Cell Functions
... Many of life's failures are experienced by people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. ...
... Many of life's failures are experienced by people who did not realize how close they were to success when they gave up. ...
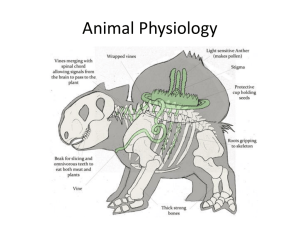
Animal Physiology Powerpoint
... the tree of life is the best possible fit for all the probabilities – New fossils are still being discovered and they often rewrite the tree of life – The “missing link” between humans and chimpanzees was sought for a long time ...
... the tree of life is the best possible fit for all the probabilities – New fossils are still being discovered and they often rewrite the tree of life – The “missing link” between humans and chimpanzees was sought for a long time ...
Analog VLSI and Biological Systems
... built the world's most energy-efficient and low-power neural amplifier, developed very efficient wireless recharging links, and successfully stimulated the brain of a zebra finch bird wirelessly. We are researching the development of ultra-low-power analog decoding algorithms for compression, decodi ...
... built the world's most energy-efficient and low-power neural amplifier, developed very efficient wireless recharging links, and successfully stimulated the brain of a zebra finch bird wirelessly. We are researching the development of ultra-low-power analog decoding algorithms for compression, decodi ...
Enzymes and the Digestive system…
... • What does the ultrastructure of a cell tell us about its function? ...
... • What does the ultrastructure of a cell tell us about its function? ...
ScienceWorld 7
... cannot make their own food. Therefore, they have to obtain nutrients from other sources. They do this by growing on things they can use as a source of nutrients, such as dead plants or animals. Chemicals released from fungi break down the remains of the plant or animal into simpler substances that c ...
... cannot make their own food. Therefore, they have to obtain nutrients from other sources. They do this by growing on things they can use as a source of nutrients, such as dead plants or animals. Chemicals released from fungi break down the remains of the plant or animal into simpler substances that c ...
grade 7 natural science term one: life and living contents topic 1
... Biodiversity refers to the large variety of plants, animals and micro-organisms in their habitats. ...
... Biodiversity refers to the large variety of plants, animals and micro-organisms in their habitats. ...
Chapter 42.
... Form follows function Veins thinner-walled blood travels back to heart at low velocity & pressure blood flows due to skeletal muscle contractions when we move ...
... Form follows function Veins thinner-walled blood travels back to heart at low velocity & pressure blood flows due to skeletal muscle contractions when we move ...
Human Body Orientation
... 2. ____________ of our bodies, as well as materials such as blood, food, urine, etc., within our bodies. What tissues are involved? 3. _______________ – the ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and react to them. What system is most involved? 4. _______________ – the breakdown of in ...
... 2. ____________ of our bodies, as well as materials such as blood, food, urine, etc., within our bodies. What tissues are involved? 3. _______________ – the ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and react to them. What system is most involved? 4. _______________ – the breakdown of in ...
1 Properties of Matter
... Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support and allow for movement. Recognize that bones pro ...
... Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support and allow for movement. Recognize that bones pro ...
01st lecture
... is a staining method for microscopic preparates. Cells are stained with chrystal violet and iodine, decolorized with alcohol and investigated under microscope. Cell walls colored violet-blue are identified as Gram-positive, Gram-negative cells remain pink. ...
... is a staining method for microscopic preparates. Cells are stained with chrystal violet and iodine, decolorized with alcohol and investigated under microscope. Cell walls colored violet-blue are identified as Gram-positive, Gram-negative cells remain pink. ...
Biological Concepts: Diversity (Pillsbury)
... This four credit-hour course will examine the diversity of life on Earth. We will cover all major organismal groups including bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. A central theme in the class is evolution as a force driving diversity. Particular emphasis will be placed on how these organi ...
... This four credit-hour course will examine the diversity of life on Earth. We will cover all major organismal groups including bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. A central theme in the class is evolution as a force driving diversity. Particular emphasis will be placed on how these organi ...
Course Expectations
... The structure of a neuron and how it functions. The difference between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is the control center for the body. The anatomical structure of the spinal cord. The major regions of the brain and their functions. T ...
... The structure of a neuron and how it functions. The difference between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is the control center for the body. The anatomical structure of the spinal cord. The major regions of the brain and their functions. T ...
Unit 3 cell - Kowenscience.com
... DNA is coiled into very compact chromosomes, made of both DNA and proteins. Chromatid – each chromosome consists of two identical halves called chromatids (= copies ...
... DNA is coiled into very compact chromosomes, made of both DNA and proteins. Chromatid – each chromosome consists of two identical halves called chromatids (= copies ...
a13 AnimalDiversity
... 7. Write the name of a species of Bony Fish. 8. Name and describe the organs that fish use to get oxygen into their bodies and remove carbon dioxide from their bodies. What do these structures look like close up? ...
... 7. Write the name of a species of Bony Fish. 8. Name and describe the organs that fish use to get oxygen into their bodies and remove carbon dioxide from their bodies. What do these structures look like close up? ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.