Olympiads | Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education
... The % composition of inner mitochondrial membrane is likely to be: a. 40:30:20 b. 42:33:9 c. 43:33:15 d. 76:24:0 ...
... The % composition of inner mitochondrial membrane is likely to be: a. 40:30:20 b. 42:33:9 c. 43:33:15 d. 76:24:0 ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
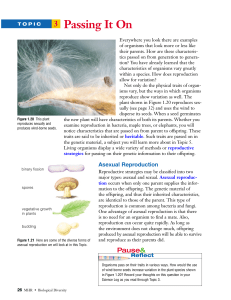
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
Pre-Course Assignment
... Homeostasis is the condition in which the body’s internal environment remains relatively constant (within limits) An organism is said to be in Homeostasis when it’s internal environment: (1) Contains the optimum concentration of gases, nutrients, ions and water (2) Has an optimal temperature (3) Has ...
... Homeostasis is the condition in which the body’s internal environment remains relatively constant (within limits) An organism is said to be in Homeostasis when it’s internal environment: (1) Contains the optimum concentration of gases, nutrients, ions and water (2) Has an optimal temperature (3) Has ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Beating cilia producing water current. Respiratory organs that increase surface area available for diffusion. Bring external environment close to internal fluid. Atmospheric Pressure and Partial Pressures One atmosphere is 760 mm Hg. Partial Pressure is fraction contributed by a gas. Raven - J ...
... Beating cilia producing water current. Respiratory organs that increase surface area available for diffusion. Bring external environment close to internal fluid. Atmospheric Pressure and Partial Pressures One atmosphere is 760 mm Hg. Partial Pressure is fraction contributed by a gas. Raven - J ...
national unit specification: general information
... This unit introduces you to the main body systems and how as a sports coach these apply to your understanding of the body and its uses, and limitations, in the coaching environment. The unit looks at how these affect performance and it will give you a better understanding of how to increase the part ...
... This unit introduces you to the main body systems and how as a sports coach these apply to your understanding of the body and its uses, and limitations, in the coaching environment. The unit looks at how these affect performance and it will give you a better understanding of how to increase the part ...
Life Processes
... 2. Why molecular movement needed for life? A. Living organisms have organs, tissues, cells, and so on. Because of the effects of the environment this organized, ordered nature of living structures is likely to keep breaking down over time. If order breaks down, the organism will no longer be alive. ...
... 2. Why molecular movement needed for life? A. Living organisms have organs, tissues, cells, and so on. Because of the effects of the environment this organized, ordered nature of living structures is likely to keep breaking down over time. If order breaks down, the organism will no longer be alive. ...
Developmental Issues - Core Constellations
... some of the fundamentals of the Neo-Reichian approach to body psychotherapy, which is also the foundation of the somatic aspects of Core Energetics. Evolutionary theory teaches that after the joining of sperm and egg during conception, we then go though all the complex developmental stages of all th ...
... some of the fundamentals of the Neo-Reichian approach to body psychotherapy, which is also the foundation of the somatic aspects of Core Energetics. Evolutionary theory teaches that after the joining of sperm and egg during conception, we then go though all the complex developmental stages of all th ...
document
... •They contain a nucleus and are alive •Phloem cells transport water and sugars (sucrose) around the plant •Transport it is bi-directional, both up and down the plant •Movement of materials in the phloem is called translocation ...
... •They contain a nucleus and are alive •Phloem cells transport water and sugars (sucrose) around the plant •Transport it is bi-directional, both up and down the plant •Movement of materials in the phloem is called translocation ...
Instructions regarding INBO Theory Test Paper:
... 30. (2 points) A glucose-fed yeast cell growing in an aerobic environment consumes 1.8 g of glucose per unit time. If these cells are moved to anaerobic environment, how many moles of glucose the cells will consume to generate ATP at the same rate? (Write the answer in decimal form.) Answer: _______ ...
... 30. (2 points) A glucose-fed yeast cell growing in an aerobic environment consumes 1.8 g of glucose per unit time. If these cells are moved to anaerobic environment, how many moles of glucose the cells will consume to generate ATP at the same rate? (Write the answer in decimal form.) Answer: _______ ...
Question Bank Kingdom Animalia
... (i) They are acellular or non-cellular animals. Sometimes these are described as unicellular animals. However, this is not true as a protozoan cell is a complete animal carrying on all the essential functions while a cell in other phyla is merely a specialized unit performing a specific function. (i ...
... (i) They are acellular or non-cellular animals. Sometimes these are described as unicellular animals. However, this is not true as a protozoan cell is a complete animal carrying on all the essential functions while a cell in other phyla is merely a specialized unit performing a specific function. (i ...
Track 3
... (2 marks) c. Which cell became plasmolysed? __________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) d. Name one structure present in plant cells, which is absent in animal cells. ___________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) e. Durin ...
... (2 marks) c. Which cell became plasmolysed? __________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) d. Name one structure present in plant cells, which is absent in animal cells. ___________________________________________________________________________ (1 mark) e. Durin ...
Grade 12, University Preparation Biology Version A
... Biochemistry is the chemistry of life. In order to understand the metabolic processes that occur in our bodies, we must have a strong understanding of Biochemistry. Biochemists study the elements, compounds and chemical reactions that are controlled by enzymes and take place in all living organisms. ...
... Biochemistry is the chemistry of life. In order to understand the metabolic processes that occur in our bodies, we must have a strong understanding of Biochemistry. Biochemists study the elements, compounds and chemical reactions that are controlled by enzymes and take place in all living organisms. ...
Microvascular Endothelial Cells
... • Response of Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1)-induced chemotaxis in monocytic cells: • Calcein-prelabeled cells (top chamber) were incubated with 25 nM MCP-1 (bottom chamber) • Bottom fluorescence was measured at varying time points • Data on the graph are representative for a typical e ...
... • Response of Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1)-induced chemotaxis in monocytic cells: • Calcein-prelabeled cells (top chamber) were incubated with 25 nM MCP-1 (bottom chamber) • Bottom fluorescence was measured at varying time points • Data on the graph are representative for a typical e ...
Unit 2 - Cells and Systems Learning Pack (Science In Action 8
... A cell is the basic unit of life, because their individual cells carry out all the functions carried out by living things. Two scientists (Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann) who studied cells combined their observations to make a hypothesis … all living things are made up of cells. Rudolf Virc ...
... A cell is the basic unit of life, because their individual cells carry out all the functions carried out by living things. Two scientists (Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann) who studied cells combined their observations to make a hypothesis … all living things are made up of cells. Rudolf Virc ...
Teacher Edition
... As a class, discuss what a Level-3 response would include. A complete and correct response for Analysis Question 4 will include specific examples from the activity about how scientists and doctors use the microscope to diagnose diseases. You may develop a Level-3 exemplar with the class or share wit ...
... As a class, discuss what a Level-3 response would include. A complete and correct response for Analysis Question 4 will include specific examples from the activity about how scientists and doctors use the microscope to diagnose diseases. You may develop a Level-3 exemplar with the class or share wit ...
Anatomy & Physiology
... Characteristics of Living Organisms 1) Responsiveness: respond to changes in the environment ...
... Characteristics of Living Organisms 1) Responsiveness: respond to changes in the environment ...
Tree of Life - Methow Naturalist
... Kingdom Fungi (Greek ‘sponge’)- 75,000 species in 6 phyla have been identified; total may number more than a million. One of the 6 phyla of Fungi is lichens, which are mostly fungal with an algae or cyanobacteria symbiont (lives inside the fungus). Fungi are now thought to have diverged from other l ...
... Kingdom Fungi (Greek ‘sponge’)- 75,000 species in 6 phyla have been identified; total may number more than a million. One of the 6 phyla of Fungi is lichens, which are mostly fungal with an algae or cyanobacteria symbiont (lives inside the fungus). Fungi are now thought to have diverged from other l ...
chapter 40 - Biology Junction
... internal temperature, sensing and responding to environmental stimuli, and all other animal activities require fuel in the form of chemical energy. The concept of bioenergetics—how organisms obtain, process, and use energy resources—is a connecting theme in the comparative study of animals. Concep ...
... internal temperature, sensing and responding to environmental stimuli, and all other animal activities require fuel in the form of chemical energy. The concept of bioenergetics—how organisms obtain, process, and use energy resources—is a connecting theme in the comparative study of animals. Concep ...
Body Organization
... • Tissue is a group of similar cells that performs the same function. –Muscle tissue: contract, or shorten, to make parts of your body move. –Nervous tissue: directs and controls the processes, and carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and other parts of the body. –Connective ...
... • Tissue is a group of similar cells that performs the same function. –Muscle tissue: contract, or shorten, to make parts of your body move. –Nervous tissue: directs and controls the processes, and carries electrical messages back and forth between the brain and other parts of the body. –Connective ...
25.4 Absorption of Water and Mineral Salts by
... allows some molecules to pass through but not others. o The cell surface membrane in plants is an example of a partially permeable membrane. • Gases (e.g. oxygen) and smaller molecules (e.g. sugar) diffuse into the plants cells through the membrane. ...
... allows some molecules to pass through but not others. o The cell surface membrane in plants is an example of a partially permeable membrane. • Gases (e.g. oxygen) and smaller molecules (e.g. sugar) diffuse into the plants cells through the membrane. ...
Pengaruh Medium Kultur Bebas Serum terhadap Perkembangan
... 1Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Syiah Kuala University, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 1Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Syiah Kuala University, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 2Faculty of Veterinarian, Institute of Agriculture of Bogor (IPB) Bogo ...
... 1Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Syiah Kuala University, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 1Department of Biology, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Syiah Kuala University, Darussalam, Banda Aceh 2Faculty of Veterinarian, Institute of Agriculture of Bogor (IPB) Bogo ...
SET1 - CBSE
... 4. In any question exclusively on diagram no marks on any description. But in questions on descriptions, same value points may be marked on the diagrams as a subsitute. 5. All awarded marks are to be written in the left hand margin at the end of the question or its part. 6. Place a tick (v’) in red ...
... 4. In any question exclusively on diagram no marks on any description. But in questions on descriptions, same value points may be marked on the diagrams as a subsitute. 5. All awarded marks are to be written in the left hand margin at the end of the question or its part. 6. Place a tick (v’) in red ...
What is a Cell?
... Level 5: Organism • Entire living things that carry out all basic life functions. Meaning… they are made of cells, share similar chemicals, can take in and use energy, grow and develop, reproduce, and sense and respond to changes in their surroundings. They’re ALIVE! ...
... Level 5: Organism • Entire living things that carry out all basic life functions. Meaning… they are made of cells, share similar chemicals, can take in and use energy, grow and develop, reproduce, and sense and respond to changes in their surroundings. They’re ALIVE! ...
to the syllabus for Biology 18, Spring
... 1. Describe some of the earliest contributors to the field of Marine Biology: early cultures, explorers and researchers that began the field of Marine Biology. 2. Explain the origin of the present sea floor shape and the movement of continents to their present position. 3. Review the properties of w ...
... 1. Describe some of the earliest contributors to the field of Marine Biology: early cultures, explorers and researchers that began the field of Marine Biology. 2. Explain the origin of the present sea floor shape and the movement of continents to their present position. 3. Review the properties of w ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.