SCIENCE BOOKLET GRADE 7
... 2. Which statement correctly tells why the cells of unicellular and multicellular organisms divide? A. The cells of unicellular organisms divide to reproduce; those of multicellular organisms divide to replace cells and to grow. B. The cells of unicellular organisms divide to replace cells and to gr ...
... 2. Which statement correctly tells why the cells of unicellular and multicellular organisms divide? A. The cells of unicellular organisms divide to reproduce; those of multicellular organisms divide to replace cells and to grow. B. The cells of unicellular organisms divide to replace cells and to gr ...
Scaling up Delivery Guide
... lump. The learners must firstly do the task on their own – then they must do it as part of a production line (e.g. with one one tearing off plasticine from the large ball into appropriate sizes, one rolling the pieces into balls and the final one squaring them off ). Talk about the division of labou ...
... lump. The learners must firstly do the task on their own – then they must do it as part of a production line (e.g. with one one tearing off plasticine from the large ball into appropriate sizes, one rolling the pieces into balls and the final one squaring them off ). Talk about the division of labou ...
Conservation Biology
... scientists think that we are in the midst of the sixth mass extinction. This extinction event is unlike past mass extinction events in that humans are largely responsible for such species loss. In this course, we will investigate how we can apply biological principles to reverse the trends in specie ...
... scientists think that we are in the midst of the sixth mass extinction. This extinction event is unlike past mass extinction events in that humans are largely responsible for such species loss. In this course, we will investigate how we can apply biological principles to reverse the trends in specie ...
Teaching Evolution to Students with Compromised
... were asked to evaluate their confidence in their understanding of evolution, specifically. We gathered additional information on students’ sources of information about evolution (options included their high school courses, church or religion, family, or the media). Furthermore, the survey asked abo ...
... were asked to evaluate their confidence in their understanding of evolution, specifically. We gathered additional information on students’ sources of information about evolution (options included their high school courses, church or religion, family, or the media). Furthermore, the survey asked abo ...
connective tissue
... 3. Bone tissue—Bones are living structures that grow and are able to repair ...
... 3. Bone tissue—Bones are living structures that grow and are able to repair ...
An Introduction to Studying the Human Body
... regions, and relative positions. • 1-9 Identify the major body cavities and their subdivisions, and describe the functions of each. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... regions, and relative positions. • 1-9 Identify the major body cavities and their subdivisions, and describe the functions of each. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Multicellular Organisms
... Cells, tissues and organs LI: 1. Explain what is meant by the term “specialisation of cells” 2. Give details of how the structure of an animal cell or plant cell can relate to its function. 3. Describe the levels of organisation found in animals and plants. National 4/5 Biology Course Unit 2 ...
... Cells, tissues and organs LI: 1. Explain what is meant by the term “specialisation of cells” 2. Give details of how the structure of an animal cell or plant cell can relate to its function. 3. Describe the levels of organisation found in animals and plants. National 4/5 Biology Course Unit 2 ...
Kingdom Animalia
... to transport oxygen and nutrients to the cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide and wastes are transported away from the cells. Sponges and cnidarians have no circulatory systems, so nutrients and gases are exchanged directly with the environment by diffusion across cell membranes. Arthropods and s ...
... to transport oxygen and nutrients to the cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide and wastes are transported away from the cells. Sponges and cnidarians have no circulatory systems, so nutrients and gases are exchanged directly with the environment by diffusion across cell membranes. Arthropods and s ...
Homeostasis revision
... organisms are known as osmoconformers. They can maintain body concentration within their normal tolerance limits which is either above (hypertonic) or below (hypotonic) their environment. These organisms are known as osmoregulators. ...
... organisms are known as osmoconformers. They can maintain body concentration within their normal tolerance limits which is either above (hypertonic) or below (hypotonic) their environment. These organisms are known as osmoregulators. ...
Earthworm Biology - UFDC Image Array 2
... soils containing large quantities of organic matter, but the new grower should purchase breeding stock from a reputable grower or distributor. Breeder worms may be purchased in lots as small as 1,000 worms. (One 8-foot by 3-foot by 1-foot deep bin, however, may contain 100,000 worms or more.) ...
... soils containing large quantities of organic matter, but the new grower should purchase breeding stock from a reputable grower or distributor. Breeder worms may be purchased in lots as small as 1,000 worms. (One 8-foot by 3-foot by 1-foot deep bin, however, may contain 100,000 worms or more.) ...
gce marking scheme
... glucose broken down by enzyme; Products/oxygen affect/detected by electrode; (not: measured by) electric signal generated/chemical to electrical; greater conc. glucose the greater the signal; enzyme activity/ rate of diffusion of glucose affected; change rate of reaction; ...
... glucose broken down by enzyme; Products/oxygen affect/detected by electrode; (not: measured by) electric signal generated/chemical to electrical; greater conc. glucose the greater the signal; enzyme activity/ rate of diffusion of glucose affected; change rate of reaction; ...
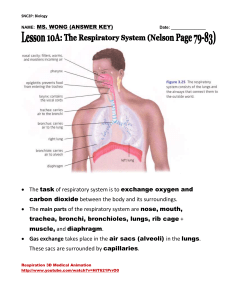
Lesson 10a: Respiratory System
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gYSIWceGMxY&NR=1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mf8xTqfspp4&feature=related ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gYSIWceGMxY&NR=1 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mf8xTqfspp4&feature=related ...
Create an Invertebrate
... insects. mutualism: One of the three types of symbiotic relationships in which the interaction of two different species derive benefit from the association with one another and in fact is necessary for both organism's survival. *Example: Termites and the protozoa living within the termite's stomach. ...
... insects. mutualism: One of the three types of symbiotic relationships in which the interaction of two different species derive benefit from the association with one another and in fact is necessary for both organism's survival. *Example: Termites and the protozoa living within the termite's stomach. ...
File
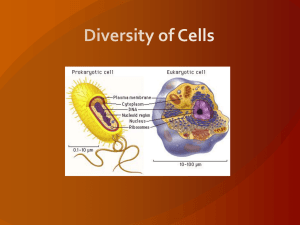
... 2.3 Eukaryotic Evolution and Diversity About 2 billion years ago, eukaryotes evolved and this led to an increase in the diversity of life on Earth. These organisms are more complex than prokaryotes. They include more genes, allowing for greater cellular diversity in terms of size, shape, mobility, a ...
... 2.3 Eukaryotic Evolution and Diversity About 2 billion years ago, eukaryotes evolved and this led to an increase in the diversity of life on Earth. These organisms are more complex than prokaryotes. They include more genes, allowing for greater cellular diversity in terms of size, shape, mobility, a ...
ANNELIDS Annelida Read the passage below, which covers topics
... Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. ...
Chapter 9
... • 1910—Morgan and others noted parallel inheritance of ‘genes’ with chromosomes, suggesting that genes were ‘on’ the chromosomes ...
... • 1910—Morgan and others noted parallel inheritance of ‘genes’ with chromosomes, suggesting that genes were ‘on’ the chromosomes ...
File
... 5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have specific characteristics. Which of the following statements describes the characteristics of the cells that make up a tissue? F. The cells have similar structures and similar ...
... 5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have specific characteristics. Which of the following statements describes the characteristics of the cells that make up a tissue? F. The cells have similar structures and similar ...
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet
... 3. Sperm production in humans is controlled by two hormones, P and Q. As levels of P rise, sperm production increases. As levels of Q rise, sperm production decreases. Which of the graphs below shows the changes in hormone levels of a man whose sperm production is decreasing? ...
... 3. Sperm production in humans is controlled by two hormones, P and Q. As levels of P rise, sperm production increases. As levels of Q rise, sperm production decreases. Which of the graphs below shows the changes in hormone levels of a man whose sperm production is decreasing? ...
HCCS - HCC Learning Web
... Calculate renal plasma clearance etc. Structure of ureters and urine bladder, urethra. LAB: Buffer system by the kidneys. Medical terminology, normal VS abnormal kidneys function test, disorders associated with kidneys. ...
... Calculate renal plasma clearance etc. Structure of ureters and urine bladder, urethra. LAB: Buffer system by the kidneys. Medical terminology, normal VS abnormal kidneys function test, disorders associated with kidneys. ...
Chapter 12
... • May look, act like fungi, but at cellular and molecular levels are completely unrelated • Fungi and water molds are good examples of convergent evolution: independent development of similar characteristics • Slime molds: organisms composed of ameboid cells; live on soil, leaf litter, decaying vege ...
... • May look, act like fungi, but at cellular and molecular levels are completely unrelated • Fungi and water molds are good examples of convergent evolution: independent development of similar characteristics • Slime molds: organisms composed of ameboid cells; live on soil, leaf litter, decaying vege ...
B2 Revision Pack F1
... 1.2 Describe the function of the components of a plant cell including chloroplast, large vacuole, cell wall, cell membrane, mitochondria, cytoplasm and nucleus 1.3 Describe the function of the components of an animal cell including cell membrane, mitochondria, cytoplasm and nucleus 1.4 Describe how ...
... 1.2 Describe the function of the components of a plant cell including chloroplast, large vacuole, cell wall, cell membrane, mitochondria, cytoplasm and nucleus 1.3 Describe the function of the components of an animal cell including cell membrane, mitochondria, cytoplasm and nucleus 1.4 Describe how ...
explanation - mbhsbiologystaar
... community as the most ancient life-forms on Earth. Yet, these primitive cells share many common characteristics with the more modern eukaryotes. However, one significant difference between these two cell types is that only eukaryotes contain The correct answer is • A membrane-bound compartments to c ...
... community as the most ancient life-forms on Earth. Yet, these primitive cells share many common characteristics with the more modern eukaryotes. However, one significant difference between these two cell types is that only eukaryotes contain The correct answer is • A membrane-bound compartments to c ...
chapter 12 (13)
... - The scientific classification of organisms is known as taxonomy. - More than 200 years ago Carolus Linnaeus proposed the first classification scheme. - Today, the tree of life is divided into three domains based on genetic and biochemical data: a. Bacteria, b. Archaea, and c. Eukarya - Members of ...
... - The scientific classification of organisms is known as taxonomy. - More than 200 years ago Carolus Linnaeus proposed the first classification scheme. - Today, the tree of life is divided into three domains based on genetic and biochemical data: a. Bacteria, b. Archaea, and c. Eukarya - Members of ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.