Document
... The translocated bcl-2 gene is now under the control of an active immunoglobulin promoter that drives high levels of constitutive expression. Bcl-2 is pro-survival (anti-apoptotic) and is homologous to CED-9 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Quite early in the study of Bcl-2 it was found to localise to the ...
... The translocated bcl-2 gene is now under the control of an active immunoglobulin promoter that drives high levels of constitutive expression. Bcl-2 is pro-survival (anti-apoptotic) and is homologous to CED-9 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Quite early in the study of Bcl-2 it was found to localise to the ...
Keystone Review Packet #1 File - Dallastown Area School District
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
Part 1 Answers
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
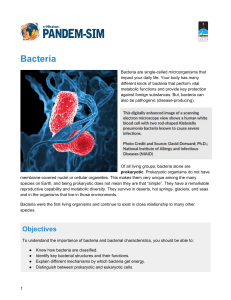
Bacteria - Pandem-Sim
... membrane-covered nuclei or cellular organelles. This makes them very unique among the many species on Earth, and being prokaryotic does not mean they are that “simple”. They have a remarkable reproductive capability and metabolic diversity. They survive in deserts, hot springs, glaciers, and seas an ...
... membrane-covered nuclei or cellular organelles. This makes them very unique among the many species on Earth, and being prokaryotic does not mean they are that “simple”. They have a remarkable reproductive capability and metabolic diversity. They survive in deserts, hot springs, glaciers, and seas an ...
Biology inside cover Mod2.indd
... bacterium which is about 0.25 µm in size. A human red blood cell is about 7.5 µm in diameter. ...
... bacterium which is about 0.25 µm in size. A human red blood cell is about 7.5 µm in diameter. ...
MCAS Review Booklet
... chloroplast, cytoskeleton, centriole, cilium, flagellum, pseudopod) to their functions. Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport). 7-2 Cell Structure (p. 173-183) 7-3 Movement through the Membrane (p. 184-189) ...
... chloroplast, cytoskeleton, centriole, cilium, flagellum, pseudopod) to their functions. Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport). 7-2 Cell Structure (p. 173-183) 7-3 Movement through the Membrane (p. 184-189) ...
Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
... Discussion of the necessary life functions and how each organ system plays several functions to support the living organism Discuss homeostasis and the diseases state that develops when homeostatic mechanisms are out of balance Discuss anatomical landmarks, divide the body into sections and planes a ...
... Discussion of the necessary life functions and how each organ system plays several functions to support the living organism Discuss homeostasis and the diseases state that develops when homeostatic mechanisms are out of balance Discuss anatomical landmarks, divide the body into sections and planes a ...
get Assignment File
... “Anatomy” and watch animations, then take quizzes based on the animation ...
... “Anatomy” and watch animations, then take quizzes based on the animation ...
SI 10/19/08 Exam 2 Review 1. Which of the following phylogenetic
... 26. Which of the following is the best description of human evolution: a. Humans did not evolve from gorillas b. Humans did not evolve from chimps c. Humans did not evolve from any extant (still living) primates d. Last common ancestor (a primate) was 5-7 million years ago e. All of the above are co ...
... 26. Which of the following is the best description of human evolution: a. Humans did not evolve from gorillas b. Humans did not evolve from chimps c. Humans did not evolve from any extant (still living) primates d. Last common ancestor (a primate) was 5-7 million years ago e. All of the above are co ...
Keystone Review Packet Spring 2017
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
... Evolution is a theory, but remember, theories although they can’t be proven as fact, are supported by wide bodies of evidence, experimental research and unify a variety of observations. Science assigns importance to theories and they are used to make predictions about new situations. Evolution is su ...
Interaction of Systems - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... For example, heart disease could affect organs in systems outside the circulatory system. Heart disease may affect the excretory system or respiratory system because these systems work closely with the circulatory system. For example, eating does not just involve the digestive system, it also involv ...
... For example, heart disease could affect organs in systems outside the circulatory system. Heart disease may affect the excretory system or respiratory system because these systems work closely with the circulatory system. For example, eating does not just involve the digestive system, it also involv ...
4a. Inhalation Expos..
... • Many volatile compounds associated with toxic endpoints • Boiling point a major determining factor in degree of exposure • Odor or immediate irritation sometimes serves as warning • But many (such as phosgene) do not present such warnings until very toxic levels have been experienced ...
... • Many volatile compounds associated with toxic endpoints • Boiling point a major determining factor in degree of exposure • Odor or immediate irritation sometimes serves as warning • But many (such as phosgene) do not present such warnings until very toxic levels have been experienced ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is a red blood cells protein involved in the transport of gases. External respiration •Hb combines with O2 to form HbO2. •HCO3- forms H2CO3 which breaks down into H2O and CO2. Internal respiration •HbO2 releases O2 into cells. •Hb combines with CO2. •CO2 combines with water to form H ...
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is a red blood cells protein involved in the transport of gases. External respiration •Hb combines with O2 to form HbO2. •HCO3- forms H2CO3 which breaks down into H2O and CO2. Internal respiration •HbO2 releases O2 into cells. •Hb combines with CO2. •CO2 combines with water to form H ...
Name Notes Page ______ 1 Bacteria Objectives
... o Methanogens take their name from methane, the natural gas they produce. These Archaea die if they are exposed to oxygen. They may live in the dense mud of swamps and marshes, and in the guts of animals such as cows and termites. o Halophiles live in very salty lakes and ponds. Some halophiles die ...
... o Methanogens take their name from methane, the natural gas they produce. These Archaea die if they are exposed to oxygen. They may live in the dense mud of swamps and marshes, and in the guts of animals such as cows and termites. o Halophiles live in very salty lakes and ponds. Some halophiles die ...
Quantitative Biology Minor Worksheet
... 2) At least two of the courses used to fulfill the Quantitative Biology minor must not be used to fulfill course the requirements of another major, minor or certificate. 3) Students must earn a “C” or better in all required courses. A course taken on a P/F basis will not count toward the minor. 4) A ...
... 2) At least two of the courses used to fulfill the Quantitative Biology minor must not be used to fulfill course the requirements of another major, minor or certificate. 3) Students must earn a “C” or better in all required courses. A course taken on a P/F basis will not count toward the minor. 4) A ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is a red blood cells protein involved in the transport of gases. External respiration •Hb combines with O2 to form HbO2. •HCO3- forms H2CO3 which breaks down into H2O and CO2. Internal respiration •HbO2 releases O2 into cells. •Hb combine with CO2. •CO2 combine with water to form H2C ...
... Hemoglobin (Hb) is a red blood cells protein involved in the transport of gases. External respiration •Hb combines with O2 to form HbO2. •HCO3- forms H2CO3 which breaks down into H2O and CO2. Internal respiration •HbO2 releases O2 into cells. •Hb combine with CO2. •CO2 combine with water to form H2C ...
PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
7 A - Reigate School
... embryo travels to the uterus where it sinks into the soft lining (implantation). The woman is now pregnant. Once it has developed all its organs (after about 10 weeks) it is called a foetus. It takes about 40 weeks (9 months) for a fertilised egg cell to grow into a baby ready to be born. This time ...
... embryo travels to the uterus where it sinks into the soft lining (implantation). The woman is now pregnant. Once it has developed all its organs (after about 10 weeks) it is called a foetus. It takes about 40 weeks (9 months) for a fertilised egg cell to grow into a baby ready to be born. This time ...
Biology 20 Year Review
... survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when members cannot interbreed 9. What is Pangea? How does it show evidence of evolu ...
... survive and reproduce. The others die without leaving offspring (natural selection) Speciation – over numerous generations, new species arise by accumulation of inherited variations of traits; considered new species when members cannot interbreed 9. What is Pangea? How does it show evidence of evolu ...
4a-Intro-to-AP-1
... MKO A person who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. Examples: instructors, assistant instructors, and classmates! ...
... MKO A person who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. Examples: instructors, assistant instructors, and classmates! ...
4a-Intro-to-AP-1
... MKO A person who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. Examples: instructors, assistant instructors, and classmates! ...
... MKO A person who has a better understanding or a higher ability level than the learner, with respect to a particular task, process, or concept. Examples: instructors, assistant instructors, and classmates! ...
Molecular Biology PowerPoint
... • Through the process of cellular respiration, cells convert energy (glucose) to a usable form of energy (ATP). • Energy stored in ATP enables cells to grow, develop, repair organisms, locomotion and transportation of molecules across the cell membrane. • Some plants (like legumes - i.e. peas) form ...
... • Through the process of cellular respiration, cells convert energy (glucose) to a usable form of energy (ATP). • Energy stored in ATP enables cells to grow, develop, repair organisms, locomotion and transportation of molecules across the cell membrane. • Some plants (like legumes - i.e. peas) form ...
Cell Structure - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Mr and Mrs Smith both have a history of cystic fibrosis in their families. Neither of them has cystic fibrosis. Mr and Mrs Smith are concerned that they may have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dom ...
... Mr and Mrs Smith both have a history of cystic fibrosis in their families. Neither of them has cystic fibrosis. Mr and Mrs Smith are concerned that they may have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dom ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.