Science Sample Items
... A. because many scientific discoveries are not based on facts B. because most scientific discoveries have no scientific value C. because most scientists make errors when formulating scientific discoveries D. because all scientific discoveries must be examined critically before they can be accepted C ...
... A. because many scientific discoveries are not based on facts B. because most scientific discoveries have no scientific value C. because most scientists make errors when formulating scientific discoveries D. because all scientific discoveries must be examined critically before they can be accepted C ...
Unit 1-A Cells
... 4.4.4 Describe the application of DNA profiling to determine paternity and also in forensic investigation. 4.4.5 Analyze DNA profiles to draw conclusions about paternity or forensic investigation. 4.4.6 Outline three outcomes of the sequencing of the complete human genome. 4.4.7 State that, when gen ...
... 4.4.4 Describe the application of DNA profiling to determine paternity and also in forensic investigation. 4.4.5 Analyze DNA profiles to draw conclusions about paternity or forensic investigation. 4.4.6 Outline three outcomes of the sequencing of the complete human genome. 4.4.7 State that, when gen ...
13-2 Manipulating DNA
... DNA is heated to separate its two strands, then cooled to allow the primers to bind to single-stranded DNA. DNA polymerase starts making copies of the region between the primers. ...
... DNA is heated to separate its two strands, then cooled to allow the primers to bind to single-stranded DNA. DNA polymerase starts making copies of the region between the primers. ...
13-2 - Lincoln Park High School
... DNA is heated to separate its two strands, then cooled to allow the primers to bind to single-stranded DNA. DNA polymerase starts making copies of the region between the primers. ...
... DNA is heated to separate its two strands, then cooled to allow the primers to bind to single-stranded DNA. DNA polymerase starts making copies of the region between the primers. ...
1. Characteristics of living organisms Core • List and describe the
... • nutrition as taking in of nutrients which are organic materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, • excretion as removal from organisms of toxic (chemical reactions in cells including respiration) • respiration as the chemical reactions that break energy in the environment (stimuli) and to m ...
... • nutrition as taking in of nutrients which are organic materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, • excretion as removal from organisms of toxic (chemical reactions in cells including respiration) • respiration as the chemical reactions that break energy in the environment (stimuli) and to m ...
Sample Test Items by Strand- Grade 7 Science
... A. because many scientific discoveries are not based on facts B. because most scientific discoveries have no scientific value C. because most scientists make errors when formulating scientific discoveries D. because all scientific discoveries must be examined critically before they can be accept ...
... A. because many scientific discoveries are not based on facts B. because most scientific discoveries have no scientific value C. because most scientists make errors when formulating scientific discoveries D. because all scientific discoveries must be examined critically before they can be accept ...
Bacteria
... What are the differences between archaea and bacteria and their subcategories? What are the survival methods of bacteria at both the individual and population levels? How are bacteria beneficial to humans? ...
... What are the differences between archaea and bacteria and their subcategories? What are the survival methods of bacteria at both the individual and population levels? How are bacteria beneficial to humans? ...
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz # 1
... 1. A group of cells of the same type form a(n) a. organ c. tissue b. organism d. organ system 2. A group of organs working together for a common purpose form a(n): a. organism c. organ system b. organelle d. organoid 3. A group of tissues working together for a specific function form a(n): a. organ ...
... 1. A group of cells of the same type form a(n) a. organ c. tissue b. organism d. organ system 2. A group of organs working together for a common purpose form a(n): a. organism c. organ system b. organelle d. organoid 3. A group of tissues working together for a specific function form a(n): a. organ ...
June 2015 Question Paper 11
... 20 When the temperature of the air is higher than body temperature, which of these control mechanisms can help to maintain a constant body temperature? constriction of blood vessels in skin ...
... 20 When the temperature of the air is higher than body temperature, which of these control mechanisms can help to maintain a constant body temperature? constriction of blood vessels in skin ...
Unit 4 Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Suggested Time: 18 Hours
... Teachers should ensure that students are taught the skills necessary to maintain and use the light microscope safely and effectively. The microscope is arguably the most important tool in the biological sciences. For those students who may not be taking biology courses in high school, this may be th ...
... Teachers should ensure that students are taught the skills necessary to maintain and use the light microscope safely and effectively. The microscope is arguably the most important tool in the biological sciences. For those students who may not be taking biology courses in high school, this may be th ...
90927 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to
... Reproduction of viruses and bacteria causes infections for different reasons. Viruses reproduce in a living cell, and because they can make many hundreds of viruses inside each cell before it dies, this causes many more cells to die / organs to malfunction, which leads to illness. Bacterial reproduc ...
... Reproduction of viruses and bacteria causes infections for different reasons. Viruses reproduce in a living cell, and because they can make many hundreds of viruses inside each cell before it dies, this causes many more cells to die / organs to malfunction, which leads to illness. Bacterial reproduc ...
Biology 565--Conservation Biology-
... Conservation Biology is an applied field—and a particularly intriguing one because the information we need focuses on the basic understanding of how nature works. Though a considerable amount of knowledge has accumulated, this course also seeks to push towards the unanswered questions and to test th ...
... Conservation Biology is an applied field—and a particularly intriguing one because the information we need focuses on the basic understanding of how nature works. Though a considerable amount of knowledge has accumulated, this course also seeks to push towards the unanswered questions and to test th ...
Whitman-Hanson Regional High School provides all students with a
... *Can you explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system? *Can you name the structures of the PNS and CNS? Nervous Tissue Structure and Function: *Can you state the functions of neurons and neuroglia? *Can you describe the general structure of a neuron? *Can you describe ...
... *Can you explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system? *Can you name the structures of the PNS and CNS? Nervous Tissue Structure and Function: *Can you state the functions of neurons and neuroglia? *Can you describe the general structure of a neuron? *Can you describe ...
Biology
... nature is much more inclusive and loosely defined. Have you ever asked yourself questions about your surroundings and wondered how or why they are happening? This is science. Science works best when driven by curiosity and innovation. In order for you to experience science in its fullest sense you m ...
... nature is much more inclusive and loosely defined. Have you ever asked yourself questions about your surroundings and wondered how or why they are happening? This is science. Science works best when driven by curiosity and innovation. In order for you to experience science in its fullest sense you m ...
Chapter 37 - Biology Junction
... The Animal Body: Introduction to Structure and Function Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning ...
... The Animal Body: Introduction to Structure and Function Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning ...
Free Radicals and other reactive species in Disease
... Free radicals and other reactive species are constantly generated in the human body. Some are made by ‘accidents of chemistry’; for example, leakage of electrons directly on to O2 from the intermediate electron carriers of the mitochondrial electron transport chain generates a steady stream of O2. 2 ...
... Free radicals and other reactive species are constantly generated in the human body. Some are made by ‘accidents of chemistry’; for example, leakage of electrons directly on to O2 from the intermediate electron carriers of the mitochondrial electron transport chain generates a steady stream of O2. 2 ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... 7. i. The animal secretes a new layer of cuticle underneath / on top of its existing exoskeleton. ii. The animal secretes enzymes / sugars that begin to digest and weaken the old cuticle, allowing the exoskeleton to dissolve / split open and the animal to crawl out of it. iii. The new exoskeleton is ...
... 7. i. The animal secretes a new layer of cuticle underneath / on top of its existing exoskeleton. ii. The animal secretes enzymes / sugars that begin to digest and weaken the old cuticle, allowing the exoskeleton to dissolve / split open and the animal to crawl out of it. iii. The new exoskeleton is ...
Science Investigations: Investigating Human Biology
... (You may want to explain the body has other systems: muscular, endocrine, urinary, and integumentary.) 3. Divide the class into six groups and assign each group one system above. Explain that the assignment is to learn more about this system and create a diagram highlighting its major organs. Provid ...
... (You may want to explain the body has other systems: muscular, endocrine, urinary, and integumentary.) 3. Divide the class into six groups and assign each group one system above. Explain that the assignment is to learn more about this system and create a diagram highlighting its major organs. Provid ...
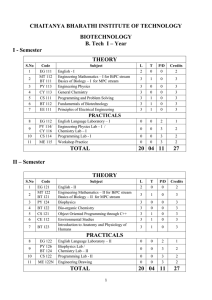
Biotechnology
... 1. Organic chemistry. Robert. T. Morrison and Robert N. Boyd, Prentice Hall India, Delhi. 6 th edition, 2002. 2. Fundamentals of Biochemstry-JL Jain. 3. Text Book of Organic Chemistry-Vol-I, L FINAR, Longman Group. 4. Text Book of Organic Chemistry. B.S.Bahl and Arun Bahl. S Chand and Co. Delhi. 19 ...
... 1. Organic chemistry. Robert. T. Morrison and Robert N. Boyd, Prentice Hall India, Delhi. 6 th edition, 2002. 2. Fundamentals of Biochemstry-JL Jain. 3. Text Book of Organic Chemistry-Vol-I, L FINAR, Longman Group. 4. Text Book of Organic Chemistry. B.S.Bahl and Arun Bahl. S Chand and Co. Delhi. 19 ...
human biology
... An experiment was carried out to determine the optimum size of alginate beads to use in this process. Three bead sizes were prepared and placed in columns. The same volume of milk was run into each column at the same rate of flow. The percentage product for each experiment was calculated. The entire ...
... An experiment was carried out to determine the optimum size of alginate beads to use in this process. Three bead sizes were prepared and placed in columns. The same volume of milk was run into each column at the same rate of flow. The percentage product for each experiment was calculated. The entire ...
Principles of Biomedical Science
... Explain how feedback systems are used by the human body to maintain homeostasis. Create a 3-D working model that demonstrates the role of insulin in transferring glucose from blood into cells. Explain the causes, symptoms, effects, and treatments of both Type I and Type II diabetes. Demonstrate an u ...
... Explain how feedback systems are used by the human body to maintain homeostasis. Create a 3-D working model that demonstrates the role of insulin in transferring glucose from blood into cells. Explain the causes, symptoms, effects, and treatments of both Type I and Type II diabetes. Demonstrate an u ...
Microsoft Word 97
... very high numbers of eggs or sperm, or both. Such a characteristic is quite common among externally fertilizing species. For instance, each spawning season, fresh and salt water fish can produce eggs or sperm which can number in the millions. Despite this, the reproductive rate can still be quite lo ...
... very high numbers of eggs or sperm, or both. Such a characteristic is quite common among externally fertilizing species. For instance, each spawning season, fresh and salt water fish can produce eggs or sperm which can number in the millions. Despite this, the reproductive rate can still be quite lo ...
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT)
... efficiently. Behavioural ecology includes study of animals form a multidisciplinary perspective, combining experimental analysis of behaviour with theoretical modeling. The environment is not just the physical world, but also the biological (predators, prey, parasites) and social (conspecifics) one. ...
... efficiently. Behavioural ecology includes study of animals form a multidisciplinary perspective, combining experimental analysis of behaviour with theoretical modeling. The environment is not just the physical world, but also the biological (predators, prey, parasites) and social (conspecifics) one. ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.