Earthworm Dissection - biology with mrs. h
... a. To find the aortic arches, locate the region in between the pharynx and the crop. You should be able to find 5 pairs of aortic arches that lie on top of the esophagus. b. Find the do ...
... a. To find the aortic arches, locate the region in between the pharynx and the crop. You should be able to find 5 pairs of aortic arches that lie on top of the esophagus. b. Find the do ...
Organs, Tissues and All Living Systems Long Answer
... Overall Expectations: The focus of this unit is on A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills (related to both inquiry and research) in the learning that plants and four areas of skills (initiating and planning, performing and recording, analysing and animals are made of interpreting, and commu ...
... Overall Expectations: The focus of this unit is on A1. demonstrate scientific investigation skills (related to both inquiry and research) in the learning that plants and four areas of skills (initiating and planning, performing and recording, analysing and animals are made of interpreting, and commu ...
Most animals are invertebrates.
... knows that generally organisms in a population live long enough to reproduce because they have survival characteristics. SC.G.1.3.3: The student understands that the classification of living things is based on a given set of criteria and is a tool for understanding biodiversity and interrelationship ...
... knows that generally organisms in a population live long enough to reproduce because they have survival characteristics. SC.G.1.3.3: The student understands that the classification of living things is based on a given set of criteria and is a tool for understanding biodiversity and interrelationship ...
On Your Own” Questions - Kingdom Builders Coop
... 1.3 A biologist studies an organism and then two of its offspring. They are all identical in every possible way. Do these organisms reproduce sexually or asexually? _____________________ 1.4 When trying to convince you of something, people will often insert “Science has proven...” at the beginning o ...
... 1.3 A biologist studies an organism and then two of its offspring. They are all identical in every possible way. Do these organisms reproduce sexually or asexually? _____________________ 1.4 When trying to convince you of something, people will often insert “Science has proven...” at the beginning o ...
Chapter 1 - Everglades High School
... Characteristics of Living Organisms, continued • Cellular organization - every living thing is composed of one or more cells • Reproduction - all living things are able to reproduce • Metabolism - all obtain and use energy to run the processes of life • Homeostasis - living organisms maintain a cons ...
... Characteristics of Living Organisms, continued • Cellular organization - every living thing is composed of one or more cells • Reproduction - all living things are able to reproduce • Metabolism - all obtain and use energy to run the processes of life • Homeostasis - living organisms maintain a cons ...
1 I. The Unobservable-Observable Distinction (UOD) A. UOD`s
... “dense body” is simply something that appears under the electron microscope without staining. a. Reply: But not all IBE’s trade in unobservables. 2. “We are not concerned with explanation. We see the same constellations of dots whether we use an electron microscope or fluorescent staining, and it is ...
... “dense body” is simply something that appears under the electron microscope without staining. a. Reply: But not all IBE’s trade in unobservables. 2. “We are not concerned with explanation. We see the same constellations of dots whether we use an electron microscope or fluorescent staining, and it is ...
GCSE Biology Textbook sample
... Learning objectives: • apply knowledge to select techniques, instruments, apparatus and materials to observe cells • make and record observations and measurements • present observations and other data using appropriate ...
... Learning objectives: • apply knowledge to select techniques, instruments, apparatus and materials to observe cells • make and record observations and measurements • present observations and other data using appropriate ...
Chapter 24 Introduction to Animals
... living organisms were classified into two kingdoms–Animalia (animals) and Plantae (plants). In 1866, Ernst Haeckel, a German scientist, proposed adding a third kingdom called Protista. The organisms in this kingdom are mainly unicellular eukaryotes. Some protists have cell walls, while others do not ...
... living organisms were classified into two kingdoms–Animalia (animals) and Plantae (plants). In 1866, Ernst Haeckel, a German scientist, proposed adding a third kingdom called Protista. The organisms in this kingdom are mainly unicellular eukaryotes. Some protists have cell walls, while others do not ...
video slide
... and boiling hot springs. Domain Archaea includes multiple kingdoms. The photo shows a colony composed of many cells. ...
... and boiling hot springs. Domain Archaea includes multiple kingdoms. The photo shows a colony composed of many cells. ...
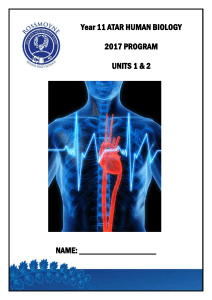
Year 11 ATAR HUMAN BIOLOGY
... mRNA in the nucleus, and translation into an amino acid sequence at the ribosome with the aid of tRNA. ...
... mRNA in the nucleus, and translation into an amino acid sequence at the ribosome with the aid of tRNA. ...
STAAR Biology Assessment Activities Sample
... All three systems are involved in protecting the organism from infection and disease. The lymph system produces lymphocytes to fight infection that may be found in the blood stream. It also collects and transports fluids around the tissues back to the veins of the circulatory system. In the circulat ...
... All three systems are involved in protecting the organism from infection and disease. The lymph system produces lymphocytes to fight infection that may be found in the blood stream. It also collects and transports fluids around the tissues back to the veins of the circulatory system. In the circulat ...
Chapter 17: Cellular Mechanisms of Development
... At the most basic level, the developmental paths of plants and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose wall ...
... At the most basic level, the developmental paths of plants and animals share many key elements. However, the mechanisms used to achieve body form are quite different. While animal cells follow an orchestrated series of movements during development, plant cells are encased within stiff cellulose wall ...
SECONDARY STAGE BIOLOGY Sindh Textbook
... measure up to 40 metres in length and weigh 150 tons and trees, redwood tree, measuring over 300 feet in height. Modern biology does not only concern with the recognition and classification of these species but also deals with their vital structural and functional aspects. This has led to the divisi ...
... measure up to 40 metres in length and weigh 150 tons and trees, redwood tree, measuring over 300 feet in height. Modern biology does not only concern with the recognition and classification of these species but also deals with their vital structural and functional aspects. This has led to the divisi ...
functions
... • The glandular epithelia that line the lumen of the digestive and respiratory tracts form a mucous membrane that secretes a slimy solution called mucus that lubricates the surface and keeps it moist. • The free epithelial surfaces of some mucous membranes have beating cilia that move the film of mu ...
... • The glandular epithelia that line the lumen of the digestive and respiratory tracts form a mucous membrane that secretes a slimy solution called mucus that lubricates the surface and keeps it moist. • The free epithelial surfaces of some mucous membranes have beating cilia that move the film of mu ...
Phylum Mollusca: Macroevolution Module
... around three unifying themes – the macroevolutionary patterns of divergence, convergence, and coevolution – and students learn to interpret diverse biological examples of these patterns. ...
... around three unifying themes – the macroevolutionary patterns of divergence, convergence, and coevolution – and students learn to interpret diverse biological examples of these patterns. ...
90927 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to
... Review the pictures and consider this statement: ‘Bacteria are living cells, viruses are not.’ Compare and contrast these two types of micro-organisms in order to prove this statement is correct. In your answer: ...
... Review the pictures and consider this statement: ‘Bacteria are living cells, viruses are not.’ Compare and contrast these two types of micro-organisms in order to prove this statement is correct. In your answer: ...
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
... HOMEOSTASIS • And Feedback Systems (Loops) – a cycle of events in which information about the status of a condition is continually monitored and fed back (reported) to a central control region. – Any stress that changes a controlled condition is called a ...
... HOMEOSTASIS • And Feedback Systems (Loops) – a cycle of events in which information about the status of a condition is continually monitored and fed back (reported) to a central control region. – Any stress that changes a controlled condition is called a ...
1 The Diversity of Cells
... • The cell is the basic unit of all living things. Later, in 1858, Rudolf Virchow (ROO dawlf FIR koh), a doctor, stated that all cells could form only from other cells. Virchow then added the third part of the cell theory. ...
... • The cell is the basic unit of all living things. Later, in 1858, Rudolf Virchow (ROO dawlf FIR koh), a doctor, stated that all cells could form only from other cells. Virchow then added the third part of the cell theory. ...
video slide
... Diverse Forms, Common Challenges • Animals very different • All animals common problems – Obtain O2 – Obtain nourishment – Excrete waste prodts – Move ...
... Diverse Forms, Common Challenges • Animals very different • All animals common problems – Obtain O2 – Obtain nourishment – Excrete waste prodts – Move ...
The cell - Libero.it
... all sorts of chemical changes going on inside them. Every cell is like a tiny ball of jelly full of chemicals and it’s far too small to be seen without a microscope. In fact you can squeeze thousands of them into the full stop at the end of this sentence. Micron is the order size of the cell. ...
... all sorts of chemical changes going on inside them. Every cell is like a tiny ball of jelly full of chemicals and it’s far too small to be seen without a microscope. In fact you can squeeze thousands of them into the full stop at the end of this sentence. Micron is the order size of the cell. ...
marking scheme_1
... Similarly as lakes become shallower sun is more able to reach the bottom than I deep lakes which in turn increases water temperatures and plant growth. Increased productivity for photosynthesis causes even more nutrients accumulate at the bottom which causes other organism to live there. Many plants ...
... Similarly as lakes become shallower sun is more able to reach the bottom than I deep lakes which in turn increases water temperatures and plant growth. Increased productivity for photosynthesis causes even more nutrients accumulate at the bottom which causes other organism to live there. Many plants ...
chapter 40
... Two cell types predominate in the fibrous mesh of loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts secrete the protein ingredients of the extracellular fibers. Macrophages are amoeboid cells that roam the maze of fibers, engulfing bacteria and the debris of dead cells by phagocytosis. Adipose tissue is a sp ...
... Two cell types predominate in the fibrous mesh of loose connective tissue. Fibroblasts secrete the protein ingredients of the extracellular fibers. Macrophages are amoeboid cells that roam the maze of fibers, engulfing bacteria and the debris of dead cells by phagocytosis. Adipose tissue is a sp ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.