long program - Pan
... Developmental constraints on the evolution of axial organization prior to the bilaterian explosion Bilaterally symmetrical animals dominate extant life on the planet comprising over 99% of all described species. However, representatives of the earliest branching forms (sponges, placozoans, ctenophor ...
... Developmental constraints on the evolution of axial organization prior to the bilaterian explosion Bilaterally symmetrical animals dominate extant life on the planet comprising over 99% of all described species. However, representatives of the earliest branching forms (sponges, placozoans, ctenophor ...
BIO102 - National Open University of Nigeria
... On the genius name begins with an initial capital letter, Hence the scientific name of Pawpaw is Carica Papaya, Lizard – Agama agama. The names are written in italics or underlined separately. ...
... On the genius name begins with an initial capital letter, Hence the scientific name of Pawpaw is Carica Papaya, Lizard – Agama agama. The names are written in italics or underlined separately. ...
the annelids and the
... possible. What are some animal cells that move within their bodies? List at least two and explain why their ability to move is important The absence of cell walls means that animals need another mechanism to give their bodies some ...
... possible. What are some animal cells that move within their bodies? List at least two and explain why their ability to move is important The absence of cell walls means that animals need another mechanism to give their bodies some ...
Moore_Timothy_LIfe Science Semester 1 Assessment
... Which of these is not one of the domains of life? Eukarya Bacteria Protozoa Archaea Starches are an example of which type of organic molecule? carbohydrate protein nucleic acid lipid Which part of the eukaryotic cell contains information to direct the cell’s functions? ribosome cytoplasm mitochondri ...
... Which of these is not one of the domains of life? Eukarya Bacteria Protozoa Archaea Starches are an example of which type of organic molecule? carbohydrate protein nucleic acid lipid Which part of the eukaryotic cell contains information to direct the cell’s functions? ribosome cytoplasm mitochondri ...
GERASIMOS DARAS Agricultural University of Athens Iera Odos 75
... XVI Congress of the Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology (FESPB 2008), Tampere, Finland, August 17-22, 2008 “Post-germinative growth in Arabidopsis is attributed to the implication of Lon1 selective proteolysis in mitochondria biogenesis” Stamatis Rigas, Gerasimos Daras, Miriam Laxa, ...
... XVI Congress of the Federation of European Societies of Plant Biology (FESPB 2008), Tampere, Finland, August 17-22, 2008 “Post-germinative growth in Arabidopsis is attributed to the implication of Lon1 selective proteolysis in mitochondria biogenesis” Stamatis Rigas, Gerasimos Daras, Miriam Laxa, ...
Biology 7 Study Guide – Exam #2
... components of blood plasma relative amounts, roles of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes) general process of blood cell formation in the bone marrow general process of blood clotting and its role in cardiovascular disease ...
... components of blood plasma relative amounts, roles of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leukocytes) general process of blood cell formation in the bone marrow general process of blood clotting and its role in cardiovascular disease ...
Jeopardy - sciencewithskinner
... Tissues that perform the same function may combine to form this. ...
... Tissues that perform the same function may combine to form this. ...
Biology of Sponges video/DVD guide.
... ... Being sedentary animals, sponges cannot swim away from a predator, and they have little in the way of structural armament (some sponges have large defensive spicules). Instead, sponges secrete poisons as their main weapon of defense. It is thought that defensive chemicals in the sponge may taste ...
... ... Being sedentary animals, sponges cannot swim away from a predator, and they have little in the way of structural armament (some sponges have large defensive spicules). Instead, sponges secrete poisons as their main weapon of defense. It is thought that defensive chemicals in the sponge may taste ...
contd.
... “foreign” cells and substances, and it can inactivate, or kill, any foreign substance or cell that enters the body. • Immune defenses are triggered by antigens, any foreign substance that can stimulate an immune response. • The immune system responds to antigens by increasing the number of cells tha ...
... “foreign” cells and substances, and it can inactivate, or kill, any foreign substance or cell that enters the body. • Immune defenses are triggered by antigens, any foreign substance that can stimulate an immune response. • The immune system responds to antigens by increasing the number of cells tha ...
body systems1
... Digestion (cont.) • The large intestine receives solid waste from the small intestine. • The large intestine absorbs excess water from the waste material. • The rectum of the large intestine stores the solid waste until the waste is expelled from the body. ...
... Digestion (cont.) • The large intestine receives solid waste from the small intestine. • The large intestine absorbs excess water from the waste material. • The rectum of the large intestine stores the solid waste until the waste is expelled from the body. ...
UMIT_July_2003 - Buffalo Ontology Site
... – replication fork part-of cell cycle, intended to mean: “a replication fork is part-of the nucleoplasm only during certain times of the cell cycle” – regulation of sleep part-of sleep, should be corrected to: “regulation of sleep is co-located with and is causally involved with the sleep process”. ...
... – replication fork part-of cell cycle, intended to mean: “a replication fork is part-of the nucleoplasm only during certain times of the cell cycle” – regulation of sleep part-of sleep, should be corrected to: “regulation of sleep is co-located with and is causally involved with the sleep process”. ...
Dissection: The Crayfish - f
... structures between different animal phyla as additional organisms are observed. - To deduce the adaptive significance of differences in the structures of animal phyla as additional organisms are studied. ...
... structures between different animal phyla as additional organisms are observed. - To deduce the adaptive significance of differences in the structures of animal phyla as additional organisms are studied. ...
earthworm_dissection_review
... Image from: http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/earthworm.html ...
... Image from: http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/earthworm.html ...
asdfs - I Love Science
... Image from: http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/earthworm.html ...
... Image from: http://biog-101-104.bio.cornell.edu/BioG101_104/tutorials/animals/earthworm.html ...
Taxonomy - Brief facts
... cell fate is predetermined and restricted; (2) inducer or "organizer" (non-cell-autonomous) mode where some isolated parts of the embryo can compensate and make a full larva in a process of self-regulation, also, some parts of the embryo, when transplanted, are capable of inducing development in the ...
... cell fate is predetermined and restricted; (2) inducer or "organizer" (non-cell-autonomous) mode where some isolated parts of the embryo can compensate and make a full larva in a process of self-regulation, also, some parts of the embryo, when transplanted, are capable of inducing development in the ...
Now! - ambition classes
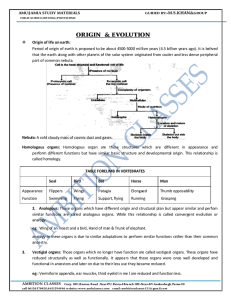
... Origin of life on earth: Period of origin of earth is proposed to be about 4500-5000 million years (4.5 billion years ago). It is belived that the earth along with other planets of the solar system originated from cooler and less dense peripheral part of common nebula. ...
... Origin of life on earth: Period of origin of earth is proposed to be about 4500-5000 million years (4.5 billion years ago). It is belived that the earth along with other planets of the solar system originated from cooler and less dense peripheral part of common nebula. ...
Biology+Term+List
... nucleus during interphase and condensed into chromosomes during meiosis and mitosis. PICTURE chromosomes Structures in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell that consist of DNA molecules that contain the genes. PICTURE chromosome theory of inheritance Holds that chromosomes are the cellular components t ...
... nucleus during interphase and condensed into chromosomes during meiosis and mitosis. PICTURE chromosomes Structures in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell that consist of DNA molecules that contain the genes. PICTURE chromosome theory of inheritance Holds that chromosomes are the cellular components t ...
printer-friendly version
... heart (except pulmonary veins). Blood passes from arteries to capillaries then to veins where it returns to the heart. Capillaries are the thinnest and most numerous of blood vessels and are responsible for exchanging gasses and nutrients to the cells in exchange for their waste products. In the clo ...
... heart (except pulmonary veins). Blood passes from arteries to capillaries then to veins where it returns to the heart. Capillaries are the thinnest and most numerous of blood vessels and are responsible for exchanging gasses and nutrients to the cells in exchange for their waste products. In the clo ...
Syllabus / Pacing Guide page 2
... - Explain Kettlewell’s observations and how they are a good example of microevolution. - The ideas of scientists whose works helped develop the theory of evolution. - Understand Darwin’s basic principles of evolution. - Explain the evidence supporting evolution. - Describe the types of natural selec ...
... - Explain Kettlewell’s observations and how they are a good example of microevolution. - The ideas of scientists whose works helped develop the theory of evolution. - Understand Darwin’s basic principles of evolution. - Explain the evidence supporting evolution. - Describe the types of natural selec ...
Paper 2 Section B
... Mr. and Mrs. V have 6 children in 12 years of marriage. Mrs. V has high blood pressure and heart problem, so they decided not to have any more kids. ...
... Mr. and Mrs. V have 6 children in 12 years of marriage. Mrs. V has high blood pressure and heart problem, so they decided not to have any more kids. ...
Life on an Ocean Planet
... kingdoms: kingdom Monera, kingdom Protista, kingdom Fungi, kingdom Plantae, and kingdom Animalia. The six-kingdom system divides kingdom Monera into two new kingdoms: kingdom Eubacteria and kingdom Archaebacteria. ...
... kingdoms: kingdom Monera, kingdom Protista, kingdom Fungi, kingdom Plantae, and kingdom Animalia. The six-kingdom system divides kingdom Monera into two new kingdoms: kingdom Eubacteria and kingdom Archaebacteria. ...
Functioning organisms
... system of a typical flowering plant, but in reality there is great variation in the size and shape of plants. For example, trees and shrubs contain woody tissues whereas herbs and grasses do not. Plants also grow in many different ways. Some plants grow vertically, some have horizontal branches that ...
... system of a typical flowering plant, but in reality there is great variation in the size and shape of plants. For example, trees and shrubs contain woody tissues whereas herbs and grasses do not. Plants also grow in many different ways. Some plants grow vertically, some have horizontal branches that ...
Biology - Snake River School District
... Biology B; The Evolution and Diversity of Life (47 days) Course Description; Biology B is the study of biological evolution on the planet Earth. Issues of unity between life forms as well as the diversity of life forms are studied with regard to solving environmental challenges. The instruction is ...
... Biology B; The Evolution and Diversity of Life (47 days) Course Description; Biology B is the study of biological evolution on the planet Earth. Issues of unity between life forms as well as the diversity of life forms are studied with regard to solving environmental challenges. The instruction is ...
BioInorganic_8Apr
... Biological Role of Magnesium and calcium Magnesium and calcium are ubiquitous and essential to all known living organisms. They are involved in more than one role, with, for example, Mg/Ca ion pumps playing a role in some cellular processes, magnesium functioning as the active ...
... Biological Role of Magnesium and calcium Magnesium and calcium are ubiquitous and essential to all known living organisms. They are involved in more than one role, with, for example, Mg/Ca ion pumps playing a role in some cellular processes, magnesium functioning as the active ...
ModBio11-5Microbiology
... plants. Many such diseases have been conquered or controlled largely as a result of studies and experimental work carried out on the causal agents by medical, veterinary and agricultural bacteriologists. Important though they are, the disease-causing bacteria represent only a very small proportion o ...
... plants. Many such diseases have been conquered or controlled largely as a result of studies and experimental work carried out on the causal agents by medical, veterinary and agricultural bacteriologists. Important though they are, the disease-causing bacteria represent only a very small proportion o ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.