5.5: Classification - bio
... Each questions divides the group of organisms into two smaller groups based on a pair of alternative characteristics Subsequent groups may focus on more minor details In most cases the characteristic will be readily observed or ...
... Each questions divides the group of organisms into two smaller groups based on a pair of alternative characteristics Subsequent groups may focus on more minor details In most cases the characteristic will be readily observed or ...
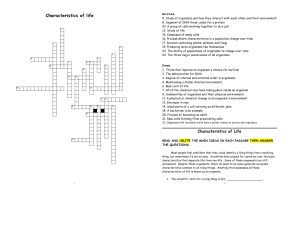
Characteristics of life
... organisms. For example, a specialized leaf of the Venus’ flytrap senses the light footsteps of a soon-to-be-digested green bottle fly. The plant responded to this environmental stimulus by rapidly folding the leaf together. An organism must respond to changes in the internal environment as well. Int ...
... organisms. For example, a specialized leaf of the Venus’ flytrap senses the light footsteps of a soon-to-be-digested green bottle fly. The plant responded to this environmental stimulus by rapidly folding the leaf together. An organism must respond to changes in the internal environment as well. Int ...
Biology 2nd Semester Exam Review 1. What is the benefit of having
... 23. The medulla, part of the brain stem, can react to stimuli from different systems of the body. If the medulla reacts to an increase in CO2 in the blood, what system of the body is the medulla receiving its information from? ...
... 23. The medulla, part of the brain stem, can react to stimuli from different systems of the body. If the medulla reacts to an increase in CO2 in the blood, what system of the body is the medulla receiving its information from? ...
Life Vocabulary
... The process by which carbondioxide and oxygen cycle among plants, animals and the environment. ...
... The process by which carbondioxide and oxygen cycle among plants, animals and the environment. ...
Oct 2310:58 AM Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
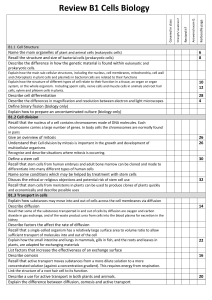
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... and nutrients for the plant Flowers: reproductive organs of some plants ...
... and nutrients for the plant Flowers: reproductive organs of some plants ...
NATURE - Biology
... Tissue – A group of cells Organs – A group of tissues Systems – A group of organs that work together Population – A group of the same kind of organisms Community – All the organisms in the ecosystem Ecosystem – All the living and nonliving things in one place At which level does life begin? Cells Wh ...
... Tissue – A group of cells Organs – A group of tissues Systems – A group of organs that work together Population – A group of the same kind of organisms Community – All the organisms in the ecosystem Ecosystem – All the living and nonliving things in one place At which level does life begin? Cells Wh ...
WHITTIER UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT
... that are carried out in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. b. Enzymes are proteins and catalyze biochemical reactions witho ...
... that are carried out in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. Cells are enclosed within semi-permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. b. Enzymes are proteins and catalyze biochemical reactions witho ...
Ecology Study/Resource Guide
... characteristic that two organisms have in common, such as flying. Bats, wasps, and robins fly. The next step would be to find some common characteristic that at least two of those flying animals share. This step is repeated until the dichotomous key leads to clearly identifying a species by separati ...
... characteristic that two organisms have in common, such as flying. Bats, wasps, and robins fly. The next step would be to find some common characteristic that at least two of those flying animals share. This step is repeated until the dichotomous key leads to clearly identifying a species by separati ...
GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
... B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
L to J PowerPoint
... time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object ...
... time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object ...
Nerve activates contraction
... structure and function. Form fits function at all the levels of life, from molecules to organisms. Knowledge of a structure provides insight into what it does and how its works. Conversely, knowing the function of a structure provides insight about its construction. ...
... structure and function. Form fits function at all the levels of life, from molecules to organisms. Knowledge of a structure provides insight into what it does and how its works. Conversely, knowing the function of a structure provides insight about its construction. ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Genetics
... The variations upon which natural selection operates are _____ and ______. According to Kettlewell, the peppered moths of England are a classic example of _______. Natural selection can operate only on an individual’s _____. A species will have the best chance for survival if it occupies an empty __ ...
... The variations upon which natural selection operates are _____ and ______. According to Kettlewell, the peppered moths of England are a classic example of _______. Natural selection can operate only on an individual’s _____. A species will have the best chance for survival if it occupies an empty __ ...
End of Course Exam 6th Grade Review Answer Key
... helpful to environment and humans, and can also cause disease if pathogenic in humans Fungi: non-green, eukaryotic, does not move, reproduce by spore, no photosynthesis, break down substances in their surroundings and absorb nutrients for food. Big Idea 15 1. How are living things classified? Into g ...
... helpful to environment and humans, and can also cause disease if pathogenic in humans Fungi: non-green, eukaryotic, does not move, reproduce by spore, no photosynthesis, break down substances in their surroundings and absorb nutrients for food. Big Idea 15 1. How are living things classified? Into g ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 - Organization - mics-bio2
... output results in decrease in input Thermostat example ...
... output results in decrease in input Thermostat example ...
The Big Picture: A Review of Biology
... o Represented by a capital letter o B is the dominant gene for brown eyes Recessive gene: “Weaker” of 2 genes and only shows up when there is no dominant gene present o Represented by a lowercase letter o b is the recessive gene for blue eyes Homozygous (purebred): When 2 genes are alike for a trait ...
... o Represented by a capital letter o B is the dominant gene for brown eyes Recessive gene: “Weaker” of 2 genes and only shows up when there is no dominant gene present o Represented by a lowercase letter o b is the recessive gene for blue eyes Homozygous (purebred): When 2 genes are alike for a trait ...
Midterm Studyguide Avery L
... offspring to ensure that some survive. The individuals with the best traits for their environment will survive and reproduce. This is natural selection in its simplest form: survival of the fittest. Finally, a population will change over time. As the habitat and environment of certain species change ...
... offspring to ensure that some survive. The individuals with the best traits for their environment will survive and reproduce. This is natural selection in its simplest form: survival of the fittest. Finally, a population will change over time. As the habitat and environment of certain species change ...
Chapter 14.
... mutation = CAG repeats glutamine amino acid repeats in protein one of 1st genes to be identified ...
... mutation = CAG repeats glutamine amino acid repeats in protein one of 1st genes to be identified ...
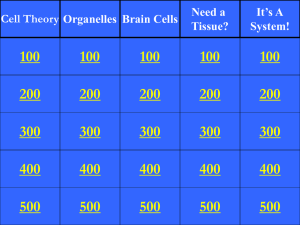
Cell Theory Organelles Brain Cells Need a Tissue?
... responsible for the development of cell theory. ...
... responsible for the development of cell theory. ...
The Cell: A Review
... other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its life. Even more important, the DNA provides a means of passing genetic information to the next generati ...
... other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its life. Even more important, the DNA provides a means of passing genetic information to the next generati ...
Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells and viruses differ
... Organelles involved in producing proteins Process of producing proteins ...
... Organelles involved in producing proteins Process of producing proteins ...
Computational (Structural) Biology
... to fresh buds, and these if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful rami ...
... to fresh buds, and these if vigorous, branch out and overtop on all sides many a feebler branch, so by generation I believe it has been with the great Tree of Life, which fills with its dead and broken branches the crust of the earth, and covers the surface with its ever branching and beautiful rami ...
Akerley Biology Final Review
... B. Common Assessment: 100 multiple choice questions that all biology classes are taking. This is more of an assessment of how well I taught the material. This covers content from the entire year. Please review all your field journals, not just the second semester. Please. C. Specific Assessment: 100 ...
... B. Common Assessment: 100 multiple choice questions that all biology classes are taking. This is more of an assessment of how well I taught the material. This covers content from the entire year. Please review all your field journals, not just the second semester. Please. C. Specific Assessment: 100 ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE PART 2
... (1) tissues, organs, and organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis in all living things (2) interference with nerve signals disrupts cellular communication and homeostasis within organisms (3) a disruption in a body system may disrupt the homeostasis of a single-celled organism (4) structu ...
... (1) tissues, organs, and organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis in all living things (2) interference with nerve signals disrupts cellular communication and homeostasis within organisms (3) a disruption in a body system may disrupt the homeostasis of a single-celled organism (4) structu ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.