Taxonomy Review Answers
... 2. Name the eight levels of taxonomy in order. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species 3. What language is used for taxonomy? Why? Latin; it doesn’t change; it’s traditional; there is no need to rename things 4. What three things do we use to classify organisms? Physical and bi ...
... 2. Name the eight levels of taxonomy in order. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species 3. What language is used for taxonomy? Why? Latin; it doesn’t change; it’s traditional; there is no need to rename things 4. What three things do we use to classify organisms? Physical and bi ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... metaphase the second stage of mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and the pairs of sister chromatids line up end to end across the center of the cell anaphase the third stage of mitosis, in which the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to sep ...
... metaphase the second stage of mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and the pairs of sister chromatids line up end to end across the center of the cell anaphase the third stage of mitosis, in which the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to sep ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... metaphase the second stage of mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and the pairs of sister chromatids line up end to end across the center of the cell anaphase the third stage of mitosis, in which the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to sep ...
... metaphase the second stage of mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and the pairs of sister chromatids line up end to end across the center of the cell anaphase the third stage of mitosis, in which the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to sep ...
ch. 23 practice exam
... The development of a true coelom between the ectoderm and the mesoderm represents a true evolutionary advance over the pseudocoelomate body plan. All bilaterally symmetric animals have the same internal body plan. The development of a body cavity did not affect the evolution of organs. The body cavi ...
... The development of a true coelom between the ectoderm and the mesoderm represents a true evolutionary advance over the pseudocoelomate body plan. All bilaterally symmetric animals have the same internal body plan. The development of a body cavity did not affect the evolution of organs. The body cavi ...
Answer the following
... Yes, because the advanced organisms also were like the primitive ones once. They have acquired their complexity relatively recently. There is a possibility that these advanced or 'younger' organisms acquire more complex structures during evolutionary time to compete and survive in the changing envir ...
... Yes, because the advanced organisms also were like the primitive ones once. They have acquired their complexity relatively recently. There is a possibility that these advanced or 'younger' organisms acquire more complex structures during evolutionary time to compete and survive in the changing envir ...
Name: Period: _____ Teacher: Science Homework Due: Friday
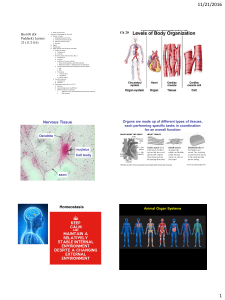
... compounds, organelles, and cells. For the next 2 months, we will investigate 4 additional levels of biological organization: tissue, organ, organ system, and organism. By now, you should be able to describe the basic structures and functions of a cell, but what happens when cells function or work to ...
... compounds, organelles, and cells. For the next 2 months, we will investigate 4 additional levels of biological organization: tissue, organ, organ system, and organism. By now, you should be able to describe the basic structures and functions of a cell, but what happens when cells function or work to ...
CHAP NUM="1" ID="CH
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
AnatomyPhysiology-English
... Cells are the building blocks of organisms. A cell is the basic structure of life. Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems ...
... Cells are the building blocks of organisms. A cell is the basic structure of life. Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems ...
English
... Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
... Cells have important structures that allow them to function. Protoplasm within a cell carries out important chemical activities. Multi-cellular organisms have many cells. These cells form specialized systems to carry out life processes. ...
Regents Packet Green
... c. A pH of 7 is neutral (water). All living things must maintain homeostasis. 1. Homeostasis is a balanced state in an organism. 2. Dynamic equilibrium means that the body stays balanced by taking action whenever the balance is disturbed (like sweating when the body is too hot). ...
... c. A pH of 7 is neutral (water). All living things must maintain homeostasis. 1. Homeostasis is a balanced state in an organism. 2. Dynamic equilibrium means that the body stays balanced by taking action whenever the balance is disturbed (like sweating when the body is too hot). ...
SC 118 Human Biology Credit for Prior Learning
... Describe how human population size has changed throughout history. Does the Earth have a set carrying capacity for humans? What was the “green revolution”? What was its effect? Do we see S-shaped (sigmoid) population growth in nature? List some species that can replenish their numbers readily after ...
... Describe how human population size has changed throughout history. Does the Earth have a set carrying capacity for humans? What was the “green revolution”? What was its effect? Do we see S-shaped (sigmoid) population growth in nature? List some species that can replenish their numbers readily after ...
Nervous Tissue Homeostasis
... Provide the basic components and overall function of each of the following organ systems: endocrine, nervous, circulatory, respiratory. ...
... Provide the basic components and overall function of each of the following organ systems: endocrine, nervous, circulatory, respiratory. ...
BI302 – Evolution - Wilfrid Laurier University
... From the Course Calendar: “A comprehensive and integrative course on evolution by natural selection as the underlying principle of modern biology. Topics include the mechanisms of selection; the concepts of adaptation, fitness and species; the evolution of sex; co-evolution; and the origin of life.” ...
... From the Course Calendar: “A comprehensive and integrative course on evolution by natural selection as the underlying principle of modern biology. Topics include the mechanisms of selection; the concepts of adaptation, fitness and species; the evolution of sex; co-evolution; and the origin of life.” ...
Worksheet Biology Word Building Skills
... As in any living language, English words are invented, as they are needed. In biology, many words are built from Greek and Latin terms that serve as root words. Every year, as biologists make new discoveries, they need to invent and introduce new words made from these roots. Word roots can be added ...
... As in any living language, English words are invented, as they are needed. In biology, many words are built from Greek and Latin terms that serve as root words. Every year, as biologists make new discoveries, they need to invent and introduce new words made from these roots. Word roots can be added ...
File
... humans’ use of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels result from the gradual transformation of layers of organic matter in sediment into natural gas, coal, and petroleum. When fossil fuels are burned, they release a gas that can be used by plants for photosynthesis. High levels of this gas in the atmosphere ...
... humans’ use of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels result from the gradual transformation of layers of organic matter in sediment into natural gas, coal, and petroleum. When fossil fuels are burned, they release a gas that can be used by plants for photosynthesis. High levels of this gas in the atmosphere ...
Biology Review
... P. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. Q. I worked with Darwin on my own studies of populations. R. I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. My name is a process to keep milk fresh. S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth cha ...
... P. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. Q. I worked with Darwin on my own studies of populations. R. I supported the idea of biogenesis by my curved flask experiment. My name is a process to keep milk fresh. S. We found that methane, ammonia, hydrogen gases from early earth cha ...
biology a2
... from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses across the capillary wall and wall of alveoli into the alveolar cavity; (12mks) Tot ...
... from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses across the capillary wall and wall of alveoli into the alveolar cavity; (12mks) Tot ...
Printable PDF
... which simple substances are synthesized into the complex materials of living tissue. ...
... which simple substances are synthesized into the complex materials of living tissue. ...
BIO 15 SM 2016 FINAL EXAM 135 Q 160804.1rac
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
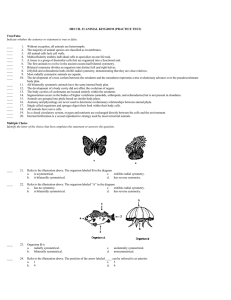
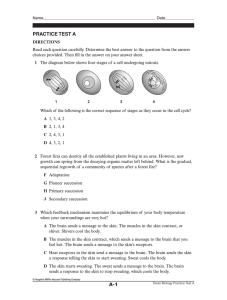
1) Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization
... 9:00 AM – 11:50 AM Lab RIDDELL ...
... 9:00 AM – 11:50 AM Lab RIDDELL ...
UNIT ONE - Cells and Heredity
... -include information on the difference between plant and animal cells. ...
... -include information on the difference between plant and animal cells. ...
Chapter 1 - Hatboro-Horsham School District
... • Beginnings of modern marine science – Challenger expedition exploring world’s oceans • 4,700 new species collected and described • significance of plankton receives attention marine studies in the United States • expeditions of Alexander Agassiz • funding of the first marine biology laboratory: An ...
... • Beginnings of modern marine science – Challenger expedition exploring world’s oceans • 4,700 new species collected and described • significance of plankton receives attention marine studies in the United States • expeditions of Alexander Agassiz • funding of the first marine biology laboratory: An ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.